
What are the customary units of solubility on solubility curves?
Answer
516.9k+ views
Hint :Solubility is the measure of how much solute can dissolve in a given amount of solvent.
A solubility curve is a data based graph comparing the amount of solute that will dissolve in a given amount of solvent at various temperatures. The most typical solubility curves are graphed based solid and gaseous solutes dissolved in 100 grams of water.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
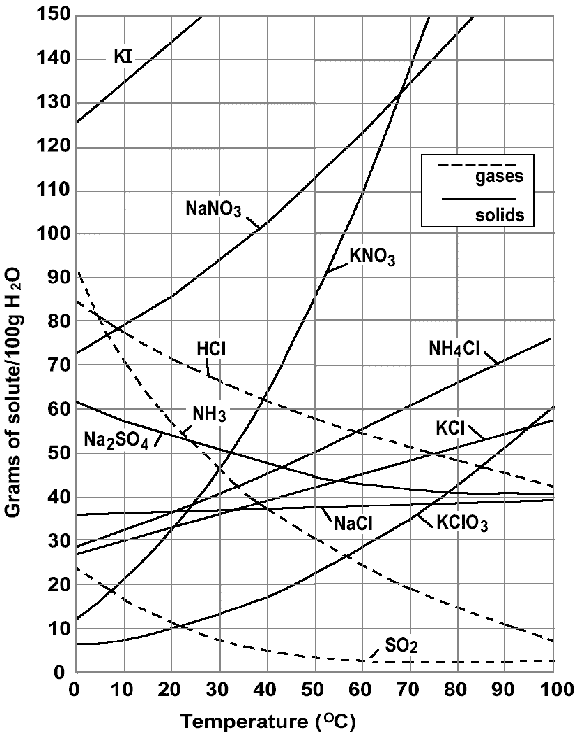
It is the solubility curve.
And from the definition of solubility, it is clear that unit of solubility is $ \dfrac{{amount{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}solute{\text{ }}dissolved}}{{{\text{ }}given{\text{ }}amount{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}solvent}} $
Hence, the customary units of solubility on solubility curves is $ \dfrac{{grams{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}solute{\text{ }}}}{{100g{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}water}} $ .
Additional Information:
Solubility can also be expressed as grams of solute per millilitres of solution or mass unit per any volume unit. It can also be expressed as moles of solute per litre of solution.
Hence, customary units of solubility on solubility curve can be taken as $ \dfrac{{gram{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}solute{\text{ }}}}{{mL{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}solution}} $ .
Note :
$\dfrac{{gram{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}solute{\text{ }}}}{{mL{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}solution}} = \dfrac{{grams{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}solute{\text{ }}}}{{100g{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}water}} $ , so not to get confused between the two.
According to the graph, the solubility of any substance changes as temperature changes, that is, solubility can increase or decrease as temperature increases.
A solubility curve is a data based graph comparing the amount of solute that will dissolve in a given amount of solvent at various temperatures. The most typical solubility curves are graphed based solid and gaseous solutes dissolved in 100 grams of water.
Complete Step By Step Answer:

It is the solubility curve.
And from the definition of solubility, it is clear that unit of solubility is $ \dfrac{{amount{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}solute{\text{ }}dissolved}}{{{\text{ }}given{\text{ }}amount{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}solvent}} $
Hence, the customary units of solubility on solubility curves is $ \dfrac{{grams{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}solute{\text{ }}}}{{100g{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}water}} $ .
Additional Information:
Solubility can also be expressed as grams of solute per millilitres of solution or mass unit per any volume unit. It can also be expressed as moles of solute per litre of solution.
Hence, customary units of solubility on solubility curve can be taken as $ \dfrac{{gram{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}solute{\text{ }}}}{{mL{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}solution}} $ .
Note :
$\dfrac{{gram{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}solute{\text{ }}}}{{mL{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}solution}} = \dfrac{{grams{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}solute{\text{ }}}}{{100g{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}water}} $ , so not to get confused between the two.
According to the graph, the solubility of any substance changes as temperature changes, that is, solubility can increase or decrease as temperature increases.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




