
What are the different phases of growth in plants? Give characteristics of each.
Answer
588.6k+ views
Hint: They are the different stages of plant growth showing the continuous growth of the plant from seed germination to the complete plant.
Complete answer:
Growth is the most fundamental characteristic of all living organisms. It is an irreversible and permanent metabolic process. Plants have a unique ability to continue throughout their life cycle. This entire process is carried out by the specialized cells called meristems.
Phases of growth in plants
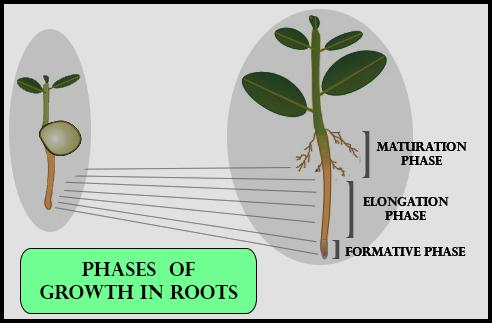
There are three phases of growth in plants.
Meristematic (Formative phase) – This phase consists of continually dividing cells called meristematic cells at the root apex and shooting apex. The cells in this region have large nuclei and rich protoplasm. The cell walls of these cells are primary, thin cellulose with abundant plasmodesmata connections.
Elongation (Cell enlargement phase) – The cells of elongation are present just after the meristematic region. The cells of this region have increased vacuolation, cell enlargement, and new cell wall deposition. Cell enlargement may be linear or in all directions.
Maturation phase – These cells are present just below the phase me of elongation, but away from the apex where the phase of maturation is found. The cells in this region reach their maximal size with cell wall thickening and new protoplasm formation. They form various simple and complex tissues of plants to perform different functions.
Note: Various plant tissues are developed due to the occurrence of three processes, they are: Differentiation (when the cells stopped dividing and are beginning to mature and perform special functions), Dedifferentiation (when the differentiated cells lost their ability to divide and then regain the capacity to divide), and Redifferentiation (dedifferentiated cells divide and once again produce cells that can no longer divide but mature to perform special functions).
Complete answer:
Growth is the most fundamental characteristic of all living organisms. It is an irreversible and permanent metabolic process. Plants have a unique ability to continue throughout their life cycle. This entire process is carried out by the specialized cells called meristems.
Phases of growth in plants
There are three phases of growth in plants.
Meristematic (Formative phase) – This phase consists of continually dividing cells called meristematic cells at the root apex and shooting apex. The cells in this region have large nuclei and rich protoplasm. The cell walls of these cells are primary, thin cellulose with abundant plasmodesmata connections.
Elongation (Cell enlargement phase) – The cells of elongation are present just after the meristematic region. The cells of this region have increased vacuolation, cell enlargement, and new cell wall deposition. Cell enlargement may be linear or in all directions.
Maturation phase – These cells are present just below the phase me of elongation, but away from the apex where the phase of maturation is found. The cells in this region reach their maximal size with cell wall thickening and new protoplasm formation. They form various simple and complex tissues of plants to perform different functions.

Note: Various plant tissues are developed due to the occurrence of three processes, they are: Differentiation (when the cells stopped dividing and are beginning to mature and perform special functions), Dedifferentiation (when the differentiated cells lost their ability to divide and then regain the capacity to divide), and Redifferentiation (dedifferentiated cells divide and once again produce cells that can no longer divide but mature to perform special functions).
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




