
What are the different types of adventitious root modifications?
Answer
596.1k+ views
Hint: The roots that grow from any part of the plant other than the radicle or its branches are called adventitious roots. They generally develop from stem nodes, internodals, leaves, etc.
Complete answer:
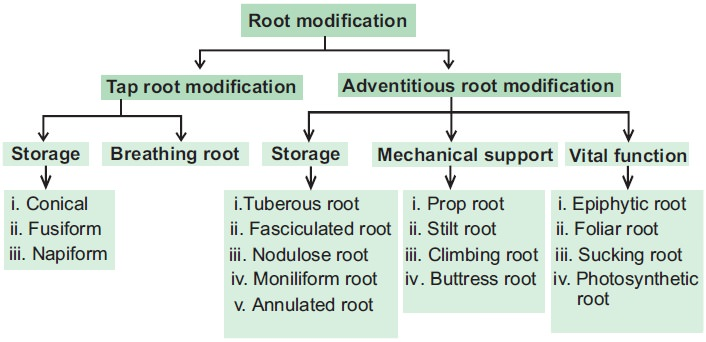
Fig: Flowchart showing modifications of tap root and adventitious root systems.
Adventitious roots are modified for a variety of functions such as storage of food, mechanical support, etc. from their typical functions. Some modifications of adventitious roots are listed as:
1. Storage of Food:

Tuberous roots: Tuberous roots are fleshy, do not have any particular shape, and often get swollen. Example- Sweet Potato (Ipomoea batatas)
Moniliform roots: These roots are also swollen at regular intervals which renders a beaded appearance to the roots. Example- Rose moss (Portulaca grandiflora)
Annulated roots: In this root, a series of outgrowths, which resemble the shape of rings, are present on the body. Example- Ipecac (Cephaelis ipecacuanha)
2. Mechanical Strength:
Prop or Pillar Adventitious Roots: These roots grow downward from the branches of the trees and are modified to support the thick and heavy branches. The aerial roots are hygroscopic. Example- Banyan Tree (Ficus benghalensis)
Climbing Roots: These roots are found in climbers. They are non-absorptive roots that help the plant to anchor to the structure. Example: Tecoma (Tecoma stans)
Buttress Roots: These roots develop at the base of the stem and help in maintaining the structural integrity of the plant. The basal part of the stem is vertically elongated and spreads in different directions in the soil. Example: Arjuna Tree (Terminalia arjuna)
3. Vital functions: In plants like Trapa, some roots are green in color and are capable of photosynthesis and are known as assimilatory roots. In some plants, the roots occur in parasites for absorbing nourishment from the host known as sucking roots.
Note: In the Banyan tree, even if the trunk dies, the tree as a whole remains alive because the prop roots of the tree are supporting and nourishing the crown. The largest tree specimen of Banyan in the Guinness Book of World Records is found in Thimmamma Marrimanu village of Anantapur district in Andhra Pradesh, India.
Complete answer:

Fig: Flowchart showing modifications of tap root and adventitious root systems.
Adventitious roots are modified for a variety of functions such as storage of food, mechanical support, etc. from their typical functions. Some modifications of adventitious roots are listed as:
1. Storage of Food:

Tuberous roots: Tuberous roots are fleshy, do not have any particular shape, and often get swollen. Example- Sweet Potato (Ipomoea batatas)
Moniliform roots: These roots are also swollen at regular intervals which renders a beaded appearance to the roots. Example- Rose moss (Portulaca grandiflora)
Annulated roots: In this root, a series of outgrowths, which resemble the shape of rings, are present on the body. Example- Ipecac (Cephaelis ipecacuanha)
2. Mechanical Strength:
Prop or Pillar Adventitious Roots: These roots grow downward from the branches of the trees and are modified to support the thick and heavy branches. The aerial roots are hygroscopic. Example- Banyan Tree (Ficus benghalensis)
Climbing Roots: These roots are found in climbers. They are non-absorptive roots that help the plant to anchor to the structure. Example: Tecoma (Tecoma stans)
Buttress Roots: These roots develop at the base of the stem and help in maintaining the structural integrity of the plant. The basal part of the stem is vertically elongated and spreads in different directions in the soil. Example: Arjuna Tree (Terminalia arjuna)
3. Vital functions: In plants like Trapa, some roots are green in color and are capable of photosynthesis and are known as assimilatory roots. In some plants, the roots occur in parasites for absorbing nourishment from the host known as sucking roots.
Note: In the Banyan tree, even if the trunk dies, the tree as a whole remains alive because the prop roots of the tree are supporting and nourishing the crown. The largest tree specimen of Banyan in the Guinness Book of World Records is found in Thimmamma Marrimanu village of Anantapur district in Andhra Pradesh, India.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




