
What are the different types of plastids? Explain their functions within a plant body?
Answer
596.1k+ views
Hint: Plastid is a double membraned organelle that is used to perform photosynthesis, attract pollinators, restore total leaf protein and synthesize starch along with the storage of proteins, fats, and oils.
Complete answer:
The term plastid is derived from a Greek word, ‘plastos’ meaning molded. It was first discovered by Ernst Haeckel. Plastids are found in almost all plant cells, algal cells, and some other eukaryotic organisms. They are double membraned and they serve as a site for storage and manufacturing of important chemical compounds (food) by the cells. They constitute certain types of pigment which are either responsible for photosynthesis (a process by which green plants and other organisms prepare their food in the presence of sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water and produce oxygen and glucose) or which determines the color of the cell. Based on these pigments (in a plant cell), plastids are divided into four parts,
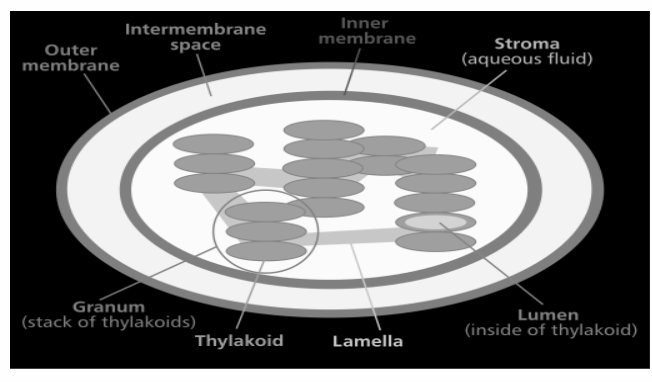
Chloroplasts are double membraned, an oval-shaped organelle that is found in the mesophyll cells (it is a type of ground tissue which is found in leaves) of the plant or the epidermal cells of the plants (they are less developed and are smaller in size as compared to that of mesophyll cells).
The outer membrane of chloroplast is semi-porous (it is permeable to small molecules and ions) in nature and the inner layer is made up of phospholipids.
The space between the outer and the inner membrane is filled by stroma (it is an aqueous matrix that contains various enzymes and proteins).
They contain the thylakoid membrane which houses a protein complex that contains chlorophyll which is responsible for photosynthesis.
Chromoplasts are a brightly colored plastic that serves as the site for pigment accumulation.
- They are found in flowers, fruits, and other pigmented parts of plants (aging leaves).
- They contain carotenoids which are responsible for the color of fruits and flowers, etc. As they impart colors, they act as visual attractors to certain organisms like bees, etc. that are involved in pollination.
- They can be formed from chloroplast in case of food ripening.
- Gerontoplasts are formed when the chloroplast goes through extensive structural modification of the thylakoid membrane which in turns result in an excessive number of plastoglobuli (it breaks down chlorophyll and the lipids).
- It helps in controlled degradation of chloroplast and in retaining 75% of total leaf protein.
- Leucoplasts are colorless plastids as they do not contain any pigment inside them. They are commonly found in roots, stems, etc. As they are deeply located (in seeds), they are not exposed to light. They serve as a site for starch formation and storage. In addition to that, they can also synthesize fats and lipids They are of three types,
- Amyloplasts which store and synthesize starch.
- Proteinoplasts which are found in seeds and help in storing proteins.
- Elaioplasts help in the storage of fats and oils which are required by the plant. They are also known as lipo lasts.
Note: Plastids are double membraned, oval-shaped organelle that serves as a site for the manufacturing and storage of chemical compounds made by the plant cells and algal cells. They can help in photosynthesis (with the help of chlorophyll), attract pollinators like bees, synthesize and store starch along with storage of protein, oil, and fats. The algal cells lack some of the plastids which are possessed by the plant cell.
Complete answer:
The term plastid is derived from a Greek word, ‘plastos’ meaning molded. It was first discovered by Ernst Haeckel. Plastids are found in almost all plant cells, algal cells, and some other eukaryotic organisms. They are double membraned and they serve as a site for storage and manufacturing of important chemical compounds (food) by the cells. They constitute certain types of pigment which are either responsible for photosynthesis (a process by which green plants and other organisms prepare their food in the presence of sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water and produce oxygen and glucose) or which determines the color of the cell. Based on these pigments (in a plant cell), plastids are divided into four parts,
Chloroplasts are double membraned, an oval-shaped organelle that is found in the mesophyll cells (it is a type of ground tissue which is found in leaves) of the plant or the epidermal cells of the plants (they are less developed and are smaller in size as compared to that of mesophyll cells).
The outer membrane of chloroplast is semi-porous (it is permeable to small molecules and ions) in nature and the inner layer is made up of phospholipids.
The space between the outer and the inner membrane is filled by stroma (it is an aqueous matrix that contains various enzymes and proteins).
They contain the thylakoid membrane which houses a protein complex that contains chlorophyll which is responsible for photosynthesis.

Chromoplasts are a brightly colored plastic that serves as the site for pigment accumulation.
- They are found in flowers, fruits, and other pigmented parts of plants (aging leaves).
- They contain carotenoids which are responsible for the color of fruits and flowers, etc. As they impart colors, they act as visual attractors to certain organisms like bees, etc. that are involved in pollination.
- They can be formed from chloroplast in case of food ripening.
- Gerontoplasts are formed when the chloroplast goes through extensive structural modification of the thylakoid membrane which in turns result in an excessive number of plastoglobuli (it breaks down chlorophyll and the lipids).
- It helps in controlled degradation of chloroplast and in retaining 75% of total leaf protein.
- Leucoplasts are colorless plastids as they do not contain any pigment inside them. They are commonly found in roots, stems, etc. As they are deeply located (in seeds), they are not exposed to light. They serve as a site for starch formation and storage. In addition to that, they can also synthesize fats and lipids They are of three types,
- Amyloplasts which store and synthesize starch.
- Proteinoplasts which are found in seeds and help in storing proteins.
- Elaioplasts help in the storage of fats and oils which are required by the plant. They are also known as lipo lasts.

Note: Plastids are double membraned, oval-shaped organelle that serves as a site for the manufacturing and storage of chemical compounds made by the plant cells and algal cells. They can help in photosynthesis (with the help of chlorophyll), attract pollinators like bees, synthesize and store starch along with storage of protein, oil, and fats. The algal cells lack some of the plastids which are possessed by the plant cell.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




