
What are the different types of underground stem modification?
Answer
597k+ views
Hint: Underground stem of plants show a variety of modifications, some of them are used as vegetables and spices. They may be fleshy, rounded or oval, scaly, or disc-like. Nodes and internodes are visible clearly in most of these underground stems.
Complete answer:
Underground stem modification of plants acts as an organ of perennation. The plants store the food synthesized in them in these underground stems. When required these stems serve as a source or food.
The different types of underground stem modification are:
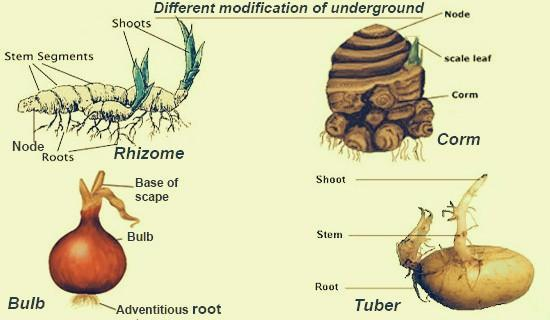
-Rhizome: It is an underground stem consisting of nodes and internodes. It is of two types. Rootstock types are a vertical rhizome, examples are banana, fern. Straggling type is a horizontal rhizome and is branched. Examples are lotus, ginger.
-Tuber: It is a terminal part of the underground stem which gets swollen due to the accumulation or storage of food. Examples are potato, artichoke.
-Bulb: It is a disc-shaped reduced form of stem. On its upper side, the bud is surrounded by concentric leaves, which are fleshy and edible. These bulbs can be of two types, tunicated and scaly.
-Corm: Short, unbranched, and thick underground stem. It shows vertical growth and is covered by a thin sheathing leaf base of dead leaves known as scales. Examples are amorphophallus, colocasia.
-Sucker: It is developed from the axillary bud of the underground stem, the branches creep below the soil and grow upwards obliquely to form new shoots. Examples are Chrysanthemum, Pineapple.
Note:
In plants, the transport of food occurs between a source, where food is synthesized and a sink, where food is stored temporarily. It should be remembered that the underground stems can act as both the source and the sink. Excess food synthesized is stored in the underground stems and during environmental stresses the food stored is used for growth and development of different parts and therefore it acts as a source.
Complete answer:
Underground stem modification of plants acts as an organ of perennation. The plants store the food synthesized in them in these underground stems. When required these stems serve as a source or food.
The different types of underground stem modification are:
-Rhizome: It is an underground stem consisting of nodes and internodes. It is of two types. Rootstock types are a vertical rhizome, examples are banana, fern. Straggling type is a horizontal rhizome and is branched. Examples are lotus, ginger.
-Tuber: It is a terminal part of the underground stem which gets swollen due to the accumulation or storage of food. Examples are potato, artichoke.
-Bulb: It is a disc-shaped reduced form of stem. On its upper side, the bud is surrounded by concentric leaves, which are fleshy and edible. These bulbs can be of two types, tunicated and scaly.
-Corm: Short, unbranched, and thick underground stem. It shows vertical growth and is covered by a thin sheathing leaf base of dead leaves known as scales. Examples are amorphophallus, colocasia.
-Sucker: It is developed from the axillary bud of the underground stem, the branches creep below the soil and grow upwards obliquely to form new shoots. Examples are Chrysanthemum, Pineapple.
Note:
In plants, the transport of food occurs between a source, where food is synthesized and a sink, where food is stored temporarily. It should be remembered that the underground stems can act as both the source and the sink. Excess food synthesized is stored in the underground stems and during environmental stresses the food stored is used for growth and development of different parts and therefore it acts as a source.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




