
What are the electronic configurations of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms?
Answer
521.4k+ views
Hint :Electronic configuration- a way in which electrons are arranged into various orbitals around the nuclei of atoms or distribution of electrons in various orbitals of an atom. Every element has a different electronic configuration.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
There are three rules which are used for the electronic configuration.
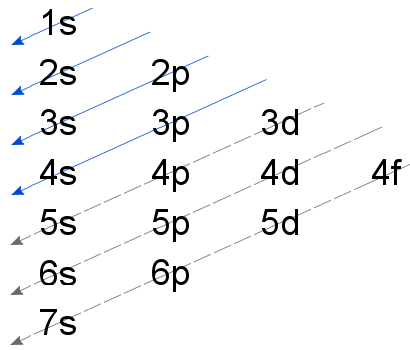
Rule 1. Aufbau principle-It says that the electrons will occupy the lowest energy level orbital that will receive it.
The order in which electrons are filled is as follows: $ :1s,{\text{ }}2s,{\text{ }}2p,{\text{ }}3s,{\text{ }}3p,{\text{ }}4s,{\text{ }}3d,{\text{ }}4p,{\text{ }}5s,{\text{ }}4d,{\text{ }}5p,{\text{ }}6s,{\text{ }}4f,{\text{ }}5d,{\text{ }}6p,{\text{ }}7s,{\text{ }}5f,{\text{ }}6d,{\text{ }}7p,{\text{ }}8s. $
Rule 2. Pauli’s exclusion principle-No two electrons with the same energy characteristics can occupy an orbital at the same time( one electron will have spin up and the other electron will have spin down)
Rule 3. Hund’s rule- While filling the multiple orbitals of the same sublevel (p, d, and f), electrons are first half-filled or singly filled, and then the pairing of electrons takes place.
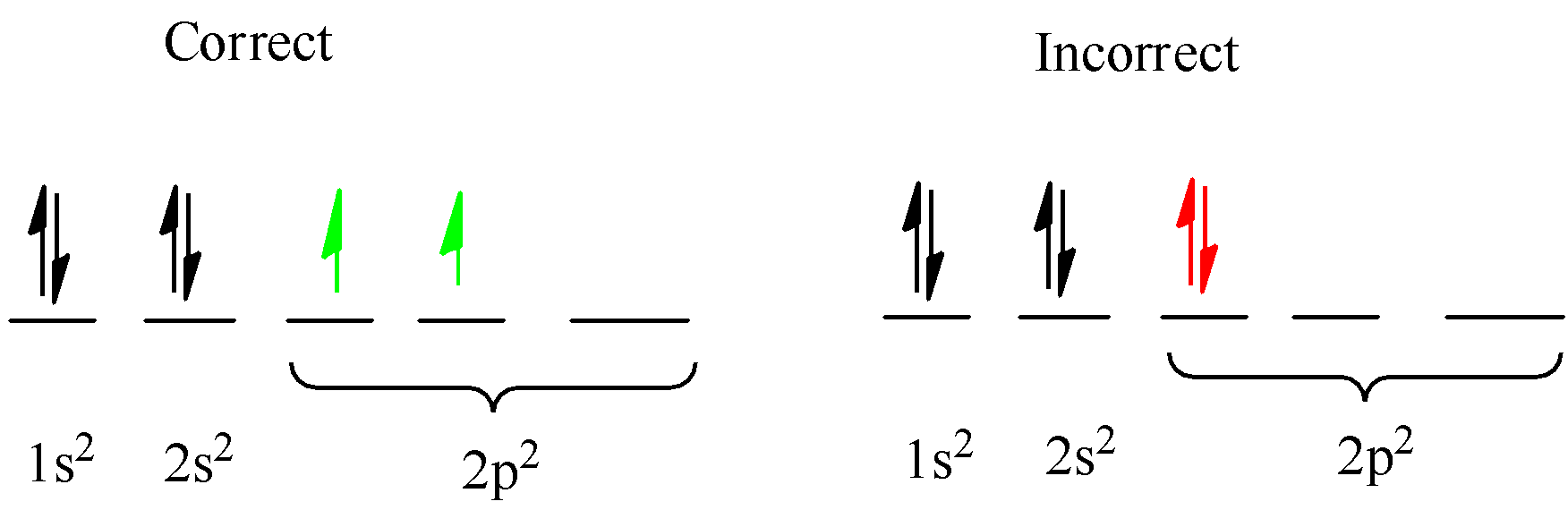
Energy of the orbital increases as follows: $ n = 1 < 2 < 3 < 4 < 5....\infty $
And the energy of orbitals increases as: $ s < p < d < f $
The number of electron that each orbital can occupy also differs: $ s = 2,p = 6,d = 10,f = 14 $ when completely filled and $ s = 1,p = 3,d = 5,f = 7 $ when half filled
Now let us try to write the electronic configuration starting with carbon.
For writing the configuration we must know the atomic number of that atom and then by following the above rules the electronic configuration of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen can be written.
Therefore the electronic configurations are:
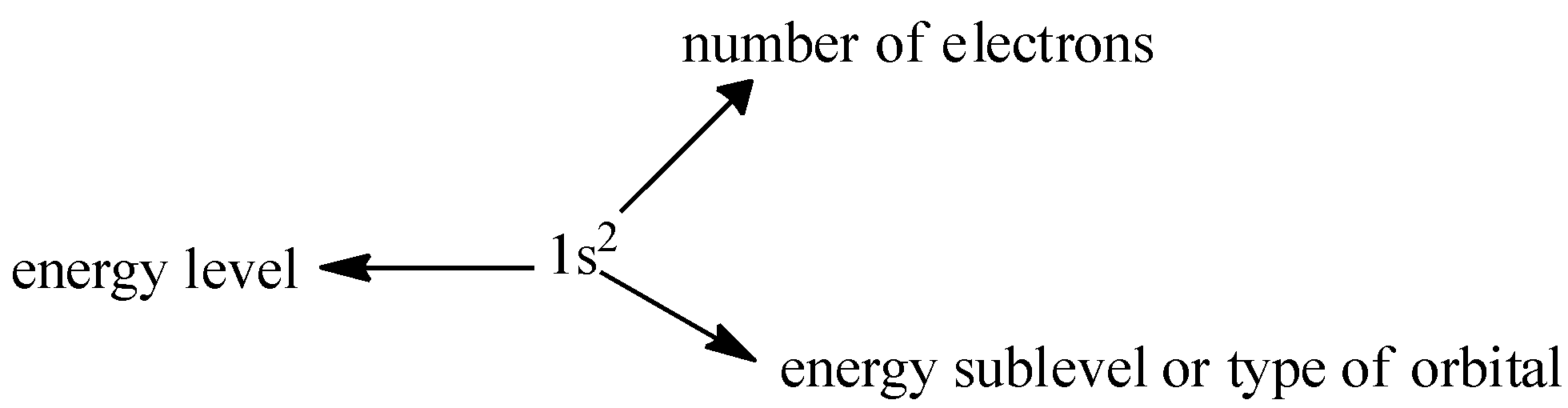
(Atomic number=6) Carbon = $ 1{s^2}2{s^2}2{p^2} $ ( $ 1s $ orbital can occupy $ 2 $ electrons so it is $ 1{s^2} $ so next electrons will go in next orbital $ 2s $ if this is completely filled the next orbital will be used and so on)
(Atomic number=1) Hydrogen= $ 1{s^1} $
(Atomic number=8) Oxygen = $ 1{s^2}2{s^2}2{p^4}. $
Note :
For writing the electronic configuration of any element, one must know the atomic number of elements, or for that periodic table can be used as a reference. Following the rules stated above (Aufbau principle, Pauli’s exclusion principle, and Hund’s rule) are very important for writing the configuration.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
There are three rules which are used for the electronic configuration.
Rule 1. Aufbau principle-It says that the electrons will occupy the lowest energy level orbital that will receive it.
The order in which electrons are filled is as follows: $ :1s,{\text{ }}2s,{\text{ }}2p,{\text{ }}3s,{\text{ }}3p,{\text{ }}4s,{\text{ }}3d,{\text{ }}4p,{\text{ }}5s,{\text{ }}4d,{\text{ }}5p,{\text{ }}6s,{\text{ }}4f,{\text{ }}5d,{\text{ }}6p,{\text{ }}7s,{\text{ }}5f,{\text{ }}6d,{\text{ }}7p,{\text{ }}8s. $

Rule 2. Pauli’s exclusion principle-No two electrons with the same energy characteristics can occupy an orbital at the same time( one electron will have spin up and the other electron will have spin down)
Rule 3. Hund’s rule- While filling the multiple orbitals of the same sublevel (p, d, and f), electrons are first half-filled or singly filled, and then the pairing of electrons takes place.
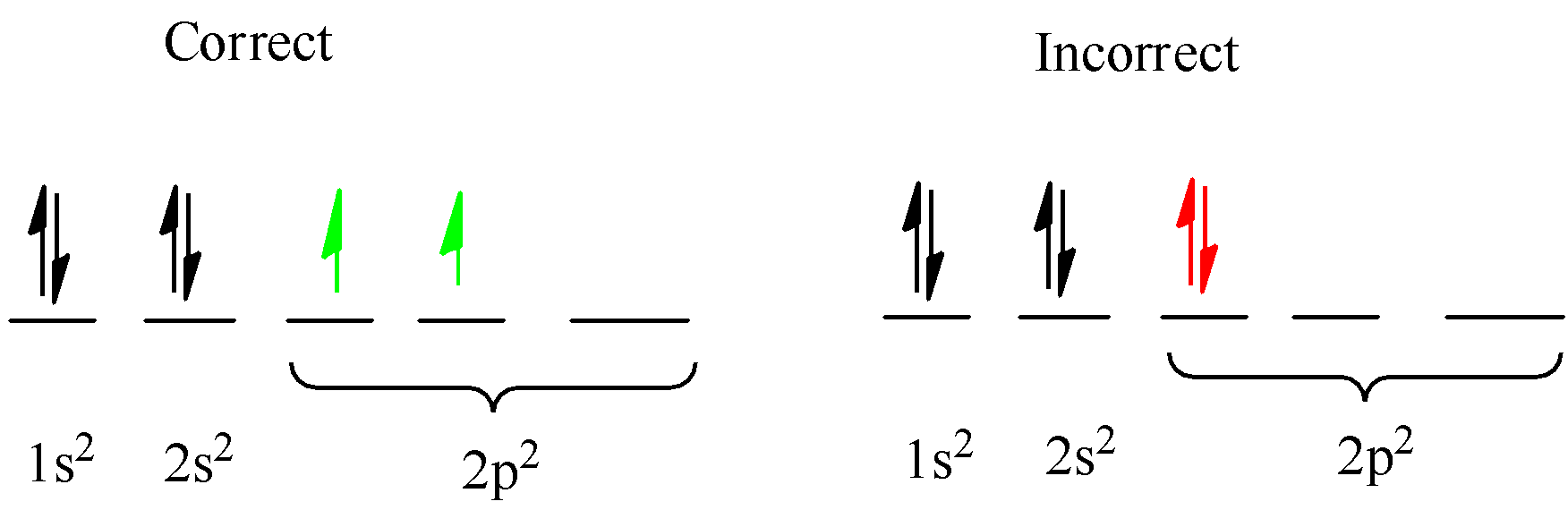
Energy of the orbital increases as follows: $ n = 1 < 2 < 3 < 4 < 5....\infty $
And the energy of orbitals increases as: $ s < p < d < f $
The number of electron that each orbital can occupy also differs: $ s = 2,p = 6,d = 10,f = 14 $ when completely filled and $ s = 1,p = 3,d = 5,f = 7 $ when half filled

Now let us try to write the electronic configuration starting with carbon.
For writing the configuration we must know the atomic number of that atom and then by following the above rules the electronic configuration of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen can be written.
Therefore the electronic configurations are:
(Atomic number=6) Carbon = $ 1{s^2}2{s^2}2{p^2} $ ( $ 1s $ orbital can occupy $ 2 $ electrons so it is $ 1{s^2} $ so next electrons will go in next orbital $ 2s $ if this is completely filled the next orbital will be used and so on)
(Atomic number=1) Hydrogen= $ 1{s^1} $
(Atomic number=8) Oxygen = $ 1{s^2}2{s^2}2{p^4}. $
Note :
For writing the electronic configuration of any element, one must know the atomic number of elements, or for that periodic table can be used as a reference. Following the rules stated above (Aufbau principle, Pauli’s exclusion principle, and Hund’s rule) are very important for writing the configuration.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




