
What are the examples of anhydrous compounds?
Answer
524.1k+ views
Hint: First of all, anhydrous means no water, therefore, anhydrous compounds are compounds with no water element in it. Anhydrous compounds exist in all three forms, that is, solid, liquid and gas. They are used for several purposes, the main purpose is to undergo certain chemical reactions in which no water is required.
Complete step by step solution: First of all, let’s study about anhydrous compounds, what are they, their synthesis, their uses.
Anhydrous compounds can be defined as the compounds with no water in it. Anhydrous is a term which is often applied to some crystalline substance after the removal of water of crystallization. They exist in solid, liquid or gas. We use some solvents in its anhydrous state for some reactions in which no water is required or we can say, to avoid the production of some unwanted products. Sometimes they can be synthesized by simply heating the compound or sometimes we need to boil them in the presence of such a material which absorbs moisture from the air, hygroscopic material.
Now, let’s have a look at their examples:
First example is acetic anhydride.
Now we know the formula of acetic acid which is \[C{H_3}COOH\]. when water molecules are removed from the two molecules of acetic acid then it will give us anhydride of acetic acid:
\[C{H_3}COOCOC{H_3}\]
Acetic anhydride is used as an acetylating agent, that is to introduce acetyl groups with the help of a chemical reaction. It is also used for the production of cellulose acetate, plastics or for fibres.
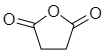
Another example: succinic anhydride-
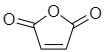
Maleic anhydride-
Some other examples of anhydrous compounds:
Common salt which we use is known as anhydrous sodium chloride, that is, $NaCl$.
Gaseous hydrochloric acid is in anhydrous form, therefore, it differs from hydrochloric acid.
When we heat copper(II)sulfate pentahydrate, that is, $CuS{O_4} \cdot 5{H_2}O$ we get copper sulphate in its anhydrous form, that is, $CuS{O_{4}}$.
Note:
We say anhydrous compounds means compounds having no water molecule but it is really very difficult to get a compound with full perfect dryness. Even after heating or keeping it in desiccator or boiling it with hygroscopic solvents, still the compounds absorb moisture from the atmosphere.
Complete step by step solution: First of all, let’s study about anhydrous compounds, what are they, their synthesis, their uses.
Anhydrous compounds can be defined as the compounds with no water in it. Anhydrous is a term which is often applied to some crystalline substance after the removal of water of crystallization. They exist in solid, liquid or gas. We use some solvents in its anhydrous state for some reactions in which no water is required or we can say, to avoid the production of some unwanted products. Sometimes they can be synthesized by simply heating the compound or sometimes we need to boil them in the presence of such a material which absorbs moisture from the air, hygroscopic material.
Now, let’s have a look at their examples:
First example is acetic anhydride.
Now we know the formula of acetic acid which is \[C{H_3}COOH\]. when water molecules are removed from the two molecules of acetic acid then it will give us anhydride of acetic acid:
\[C{H_3}COOCOC{H_3}\]
Acetic anhydride is used as an acetylating agent, that is to introduce acetyl groups with the help of a chemical reaction. It is also used for the production of cellulose acetate, plastics or for fibres.
Another example: succinic anhydride-

Maleic anhydride-

Some other examples of anhydrous compounds:
Common salt which we use is known as anhydrous sodium chloride, that is, $NaCl$.
Gaseous hydrochloric acid is in anhydrous form, therefore, it differs from hydrochloric acid.
When we heat copper(II)sulfate pentahydrate, that is, $CuS{O_4} \cdot 5{H_2}O$ we get copper sulphate in its anhydrous form, that is, $CuS{O_{4}}$.
Note:
We say anhydrous compounds means compounds having no water molecule but it is really very difficult to get a compound with full perfect dryness. Even after heating or keeping it in desiccator or boiling it with hygroscopic solvents, still the compounds absorb moisture from the atmosphere.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




