
What are the five primary functions of the respiratory system?
Answer
530.7k+ views
Hint: The respiratory system is the system which comprises organs and tissues that help us to breathe. It includes airways, lungs and the blood vessels. The breathing involves taking in of oxygen and giving out of carbon dioxide and other waste gases.
Complete answer:
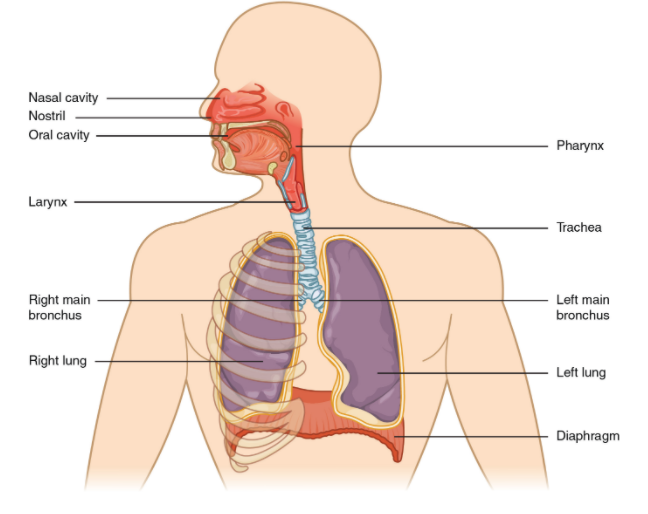
The respiratory system is the most important system in our body. Without this the organisms cannot survive. All the organisms including the plants have certain mechanisms and processes through which they respire. Human body is composed of a definite pair of lungs which helps in carrying out the process of respiration. The respiratory system in our body comprises Nose, Mouth, Throat (pharynx), Voice box (larynx), Windpipe (trachea), Large airways (bronchi) and Lungs.
1) The main function of the respiratory system is to breathe in fresh air and remove carbon dioxide and other waste gases. The exchange of gases takes place between the tissue and the blood.
2) Another function of the respiratory system is breathing which involves movement of air.
3) The larynx present in the respiratory system is important as it produces voice. Larynx is known as the voice box.
4) The nose through which the air is inhaled serves as an important organ of smell i.e it is an important olfactory organ.
5) The windpipe, nose is lined with minute hairs and mucus which serves as a protective shield against dust and microbes.
Note: The oxygen exchanges during the process of respiration helps in carrying out all the metabolic activities going on in our body. The major role of oxygen is breakdown of food and energy. The food is metabolised to liberate energy which is required to carry out physiological activities in a living body.
Complete answer:
The respiratory system is the most important system in our body. Without this the organisms cannot survive. All the organisms including the plants have certain mechanisms and processes through which they respire. Human body is composed of a definite pair of lungs which helps in carrying out the process of respiration. The respiratory system in our body comprises Nose, Mouth, Throat (pharynx), Voice box (larynx), Windpipe (trachea), Large airways (bronchi) and Lungs.
1) The main function of the respiratory system is to breathe in fresh air and remove carbon dioxide and other waste gases. The exchange of gases takes place between the tissue and the blood.
2) Another function of the respiratory system is breathing which involves movement of air.
3) The larynx present in the respiratory system is important as it produces voice. Larynx is known as the voice box.
4) The nose through which the air is inhaled serves as an important organ of smell i.e it is an important olfactory organ.
5) The windpipe, nose is lined with minute hairs and mucus which serves as a protective shield against dust and microbes.

Note: The oxygen exchanges during the process of respiration helps in carrying out all the metabolic activities going on in our body. The major role of oxygen is breakdown of food and energy. The food is metabolised to liberate energy which is required to carry out physiological activities in a living body.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




