
What are the formal charges on each atom in sulphite, $ SO_3^{2 - } $ and chlorite, $ ClO_2^ - $ ions?
Answer
516.9k+ views
Hint: Formal charge is a theoretical value assigned to an atom in a molecule which reflects the equal sharing of electrons in a chemical bond, neglecting the electronegativity difference between the atoms. Sketch the Lewis diagram for the given ions to find the value of formal charge of each atom.
Complete answer:
The formal charge can be assigned to an atom with the help of following formula:
$ F = V - N - \dfrac{B}{2}\,\,\,\,\,\,\, - (i) $
Where, $ F $ is the formal charge on the atom, $ V $ is the number of electrons of atom in its ground state, $ N $ is the number of lone pair of electrons present on the atom and $ B $ is the number of bonding electrons in that atom.
The Lewis structure for sulphite ions is as follows:
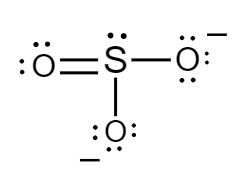
Formal charge for sulphur atom:
Number of electrons of sulphur in its ground state $ = 6 $
Count of nonbonded electrons present on sulphur atom $ = 2 $
Number of bonding electrons $ = 8 $
Substituting values in equation $ (i) $ , formal charge of sulphur atom will be as follows:
$ F = 6 - 2 - \dfrac{8}{2} $
$ \Rightarrow F = 0 $
Formal charge for doubly bonded oxygen atom:
Number of electrons of oxygen in its ground state $ = 6 $
Count of nonbonded electrons or number of lone pair of electrons present on oxygen atom $ = 4 $
Number of bonding electrons $ = 4 $
Substituting values in equation $ (i) $ , formal charge of sulphur atom will be as follows:
$ F = 6 - 4 - \dfrac{4}{2} $
$ \Rightarrow F = 0 $
Formal charge for single bonded oxygen atoms:
Number of electrons of oxygen in its ground state $ = 6 $
Count of nonbonded electrons or number of lone pair of electrons present on oxygen atom $ = 6 $
Number of bonding electrons $ = 2 $
Substituting values in equation $ (i) $ , formal charge of sulphur atom will be as follows:
$ F = 6 - 6 - \dfrac{2}{2} $
$ \Rightarrow F = - 1 $
Hence, in sulphite ions, the formal charge of sulphur atom, doubly bonded oxygen atom and singly bonded oxygen atoms is $ 0,\,0 $ and $ - 1 $ respectively.
The Lewis structure for chlorite ions is as follows:
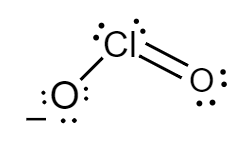
Formal charge for chlorine atom:
Number of electrons of chlorine in its ground state $ = 7 $
Count of nonbonded electrons present on chlorine atom $ = 4 $
Number of bonding electrons $ = 6 $
Substituting values in equation $ (i) $ , formal charge of sulphur atom will be as follows:
$ F = 7 - 4 - \dfrac{6}{2} $
$ \Rightarrow F = 0 $
Formal charge for doubly bonded oxygen atom:
Number of electrons of oxygen in its ground state $ = 6 $
Count of nonbonded electrons or number of lone pair of electrons present on oxygen atom $ = 4 $
Number of bonding electrons $ = 4 $
Substituting values in equation $ (i) $ , formal charge of sulphur atom will be as follows:
$ F = 6 - 4 - \dfrac{4}{2} $
$ \Rightarrow F = 0 $
Formal charge for single bonded oxygen atom:
Number of electrons of oxygen in its ground state $ = 6 $
Count of nonbonded electrons or number of lone pair of electrons present on oxygen atom $ = 6 $
Number of bonding electrons $ = 2 $
Substituting values in equation $ (i) $ , formal charge of sulphur atom will be as follows:
$ F = 6 - 6 - \dfrac{2}{2} $
$ \Rightarrow F = - 1 $
Hence, in chlorite ions, the formal charge of chlorine atom, doubly bonded oxygen atom and singly bonded oxygen atom is $ 0,\,0 $ and $ - 1 $ respectively.
Note:
Lewis structures in which the formal charges are zero for most atoms in the compound, are more preferably considered than the one with non-zero formal charges. Moreover, the negative formal charge should be present on the most electronegative element in the compound.
Complete answer:
The formal charge can be assigned to an atom with the help of following formula:
$ F = V - N - \dfrac{B}{2}\,\,\,\,\,\,\, - (i) $
Where, $ F $ is the formal charge on the atom, $ V $ is the number of electrons of atom in its ground state, $ N $ is the number of lone pair of electrons present on the atom and $ B $ is the number of bonding electrons in that atom.
The Lewis structure for sulphite ions is as follows:
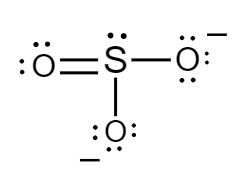
Formal charge for sulphur atom:
Number of electrons of sulphur in its ground state $ = 6 $
Count of nonbonded electrons present on sulphur atom $ = 2 $
Number of bonding electrons $ = 8 $
Substituting values in equation $ (i) $ , formal charge of sulphur atom will be as follows:
$ F = 6 - 2 - \dfrac{8}{2} $
$ \Rightarrow F = 0 $
Formal charge for doubly bonded oxygen atom:
Number of electrons of oxygen in its ground state $ = 6 $
Count of nonbonded electrons or number of lone pair of electrons present on oxygen atom $ = 4 $
Number of bonding electrons $ = 4 $
Substituting values in equation $ (i) $ , formal charge of sulphur atom will be as follows:
$ F = 6 - 4 - \dfrac{4}{2} $
$ \Rightarrow F = 0 $
Formal charge for single bonded oxygen atoms:
Number of electrons of oxygen in its ground state $ = 6 $
Count of nonbonded electrons or number of lone pair of electrons present on oxygen atom $ = 6 $
Number of bonding electrons $ = 2 $
Substituting values in equation $ (i) $ , formal charge of sulphur atom will be as follows:
$ F = 6 - 6 - \dfrac{2}{2} $
$ \Rightarrow F = - 1 $
Hence, in sulphite ions, the formal charge of sulphur atom, doubly bonded oxygen atom and singly bonded oxygen atoms is $ 0,\,0 $ and $ - 1 $ respectively.
The Lewis structure for chlorite ions is as follows:

Formal charge for chlorine atom:
Number of electrons of chlorine in its ground state $ = 7 $
Count of nonbonded electrons present on chlorine atom $ = 4 $
Number of bonding electrons $ = 6 $
Substituting values in equation $ (i) $ , formal charge of sulphur atom will be as follows:
$ F = 7 - 4 - \dfrac{6}{2} $
$ \Rightarrow F = 0 $
Formal charge for doubly bonded oxygen atom:
Number of electrons of oxygen in its ground state $ = 6 $
Count of nonbonded electrons or number of lone pair of electrons present on oxygen atom $ = 4 $
Number of bonding electrons $ = 4 $
Substituting values in equation $ (i) $ , formal charge of sulphur atom will be as follows:
$ F = 6 - 4 - \dfrac{4}{2} $
$ \Rightarrow F = 0 $
Formal charge for single bonded oxygen atom:
Number of electrons of oxygen in its ground state $ = 6 $
Count of nonbonded electrons or number of lone pair of electrons present on oxygen atom $ = 6 $
Number of bonding electrons $ = 2 $
Substituting values in equation $ (i) $ , formal charge of sulphur atom will be as follows:
$ F = 6 - 6 - \dfrac{2}{2} $
$ \Rightarrow F = - 1 $
Hence, in chlorite ions, the formal charge of chlorine atom, doubly bonded oxygen atom and singly bonded oxygen atom is $ 0,\,0 $ and $ - 1 $ respectively.
Note:
Lewis structures in which the formal charges are zero for most atoms in the compound, are more preferably considered than the one with non-zero formal charges. Moreover, the negative formal charge should be present on the most electronegative element in the compound.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




