
What are the four possible constitutional isomers for the molecular formula \[{C_3}{H_5}Br\] ?
Answer
493.8k+ views
Hint: The given formula is of an organic compound that is connected to a bromine substituent. The ratio of carbon atoms and hydrogen atoms suggests that the bromine atom must be connected to a parent chain that has some unsaturation or a hydrocarbon ring.
Complete answer:
The constitutional isomers of an organic compound are the various structural forms with different types of bonds in which a compound can exist with the same set of atoms and the formula remains unchanged.
The number of hydrogens in the formula \[{C_3}{H_5}Br\] are less than double the carbon atoms which indicates that there must be some sort of unsaturation or a ringed structure involved. To determine the possibilities, the double bond equivalent of the compound must be calculated using the following formula:
\[{\text{double bond equivalents}} = c + 1 - \dfrac{H}{2}\]
Where \[c\] represents the number of carbon atoms in the formula and \[H\] represents all the atoms or groups that are monovalent i.e. only form single bonds with carbon atoms.
The given formula contains three carbon atoms and six monovalent species that include five hydrogen and one bromine atom. On inserting these values into the formula we get,
\[{\text{double bond equivalents}} = 3 + 1 - \dfrac{6}{2} = 1\]
\[ \Rightarrow \] One double bond equivalent could mean a double bond or a ring structure. The position of bromine atom can vary in these compounds and therefore we get the followings isomers:

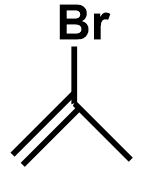

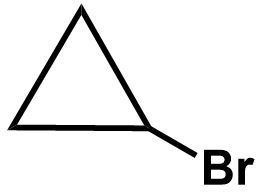
Note:
The bromine atom can be placed on any of the three carbon atoms on the cyclopropane ring as each position is equal in terms of the environment and stability of the bond. The isomers must be unique in their structure and should not include any equivalent alternative.
Complete answer:
The constitutional isomers of an organic compound are the various structural forms with different types of bonds in which a compound can exist with the same set of atoms and the formula remains unchanged.
The number of hydrogens in the formula \[{C_3}{H_5}Br\] are less than double the carbon atoms which indicates that there must be some sort of unsaturation or a ringed structure involved. To determine the possibilities, the double bond equivalent of the compound must be calculated using the following formula:
\[{\text{double bond equivalents}} = c + 1 - \dfrac{H}{2}\]
Where \[c\] represents the number of carbon atoms in the formula and \[H\] represents all the atoms or groups that are monovalent i.e. only form single bonds with carbon atoms.
The given formula contains three carbon atoms and six monovalent species that include five hydrogen and one bromine atom. On inserting these values into the formula we get,
\[{\text{double bond equivalents}} = 3 + 1 - \dfrac{6}{2} = 1\]
\[ \Rightarrow \] One double bond equivalent could mean a double bond or a ring structure. The position of bromine atom can vary in these compounds and therefore we get the followings isomers:




Note:
The bromine atom can be placed on any of the three carbon atoms on the cyclopropane ring as each position is equal in terms of the environment and stability of the bond. The isomers must be unique in their structure and should not include any equivalent alternative.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




