
What are the four regions of the stomach?
Answer
492.9k+ views
Hint: The stomach is a j-shaped organ having two openings (esophageal and duodenal) and four parts (cardia, fundus, body, and pylorus). The stomach is a muscular digestive organ that retains partially digested food before releasing it into the small intestine. The stomach is easily identifiable by its J-shaped structure and the presence of rugae, which are ridges in the inner wall of the stomach (which are evident when the stomach is empty).
Complete answer:
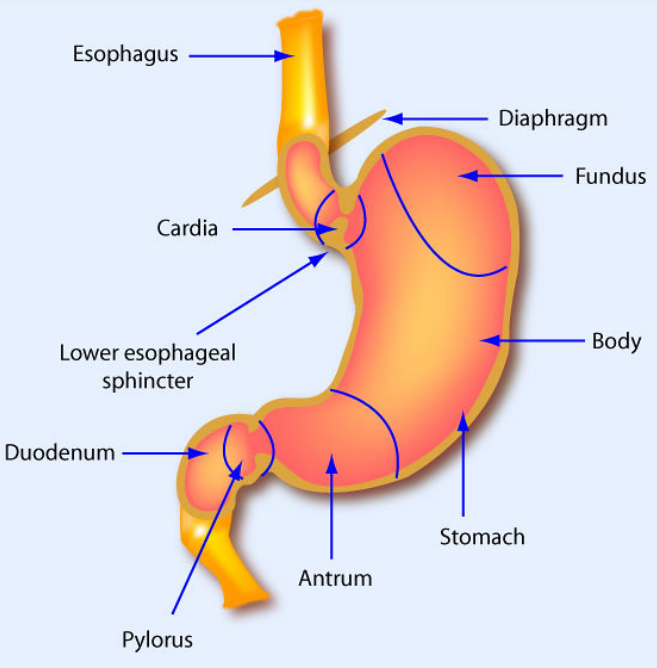
The stomach is a J-shaped organ with a maximum length of 10 inches (25 centimetres) and a maximum width of 6 inches. It is located directly beneath the dome of the diaphragm and is protected by the rib cage (15 centimeters). It's split into four sections: The cardia, fundus, body, and pylorus are the four parts of the stomach. Anatomically, each region differs slightly. Near the gastroesophageal junction is where the cardia is found.
Above the gastroesophageal sphincter is the fundus, a tiny, spherical portion of the stomach. The stomach's major section is called the body. It's the space between the fundus and the stomach's "J" shape. The majority of food storage and mixing takes place within the body. The pylorus is the bottom curve of the “J” shape. It is located at the junction between the stomach and the small intestine.
The cardia, fundus, body, and pyloric antrum are the four regions of the stomach. The cardia is the part of the stomach closest to the oesophagus that receives the bolus of food. Following the cardia is the fundus, a dome-shaped region that stores gas produced during digestion and releases it via the mouth via the belch reflex (also called burping). The body is the largest section of the stomach, where food is combined with gastric fluids and churned into chyme. The pyloric antrum is the distal portion of the stomach where chyme is kept until it is discharged into the duodenum via the pyloric sphincter.
Note:-
Each region serves a specific purpose: the fundus gathers digestive gases, the body secretes pepsinogen and hydrochloric acid, and the pylorus secretes mucus, gastrin, and pepsinogen. There are five major functions of the stomach: Food storage that is only temporary. The rate at which food enters the duodenum can be controlled. Antibacterial activity and acid secretion Stomach contents fluidization Preliminary digestion with pepsin, lipases, and other enzymes.
Complete answer:
The stomach is a J-shaped organ with a maximum length of 10 inches (25 centimetres) and a maximum width of 6 inches. It is located directly beneath the dome of the diaphragm and is protected by the rib cage (15 centimeters). It's split into four sections: The cardia, fundus, body, and pylorus are the four parts of the stomach. Anatomically, each region differs slightly. Near the gastroesophageal junction is where the cardia is found.
Above the gastroesophageal sphincter is the fundus, a tiny, spherical portion of the stomach. The stomach's major section is called the body. It's the space between the fundus and the stomach's "J" shape. The majority of food storage and mixing takes place within the body. The pylorus is the bottom curve of the “J” shape. It is located at the junction between the stomach and the small intestine.
The cardia, fundus, body, and pyloric antrum are the four regions of the stomach. The cardia is the part of the stomach closest to the oesophagus that receives the bolus of food. Following the cardia is the fundus, a dome-shaped region that stores gas produced during digestion and releases it via the mouth via the belch reflex (also called burping). The body is the largest section of the stomach, where food is combined with gastric fluids and churned into chyme. The pyloric antrum is the distal portion of the stomach where chyme is kept until it is discharged into the duodenum via the pyloric sphincter.

Note:-
Each region serves a specific purpose: the fundus gathers digestive gases, the body secretes pepsinogen and hydrochloric acid, and the pylorus secretes mucus, gastrin, and pepsinogen. There are five major functions of the stomach: Food storage that is only temporary. The rate at which food enters the duodenum can be controlled. Antibacterial activity and acid secretion Stomach contents fluidization Preliminary digestion with pepsin, lipases, and other enzymes.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




