
What are the functions of the spinal cord?
Answer
580.5k+ views
Hint: Spinal cord is a very important structure for the control and coordination of our bodies. Any damage to the spinal cord causes loss of strength, function, and sensation below the point of damage.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
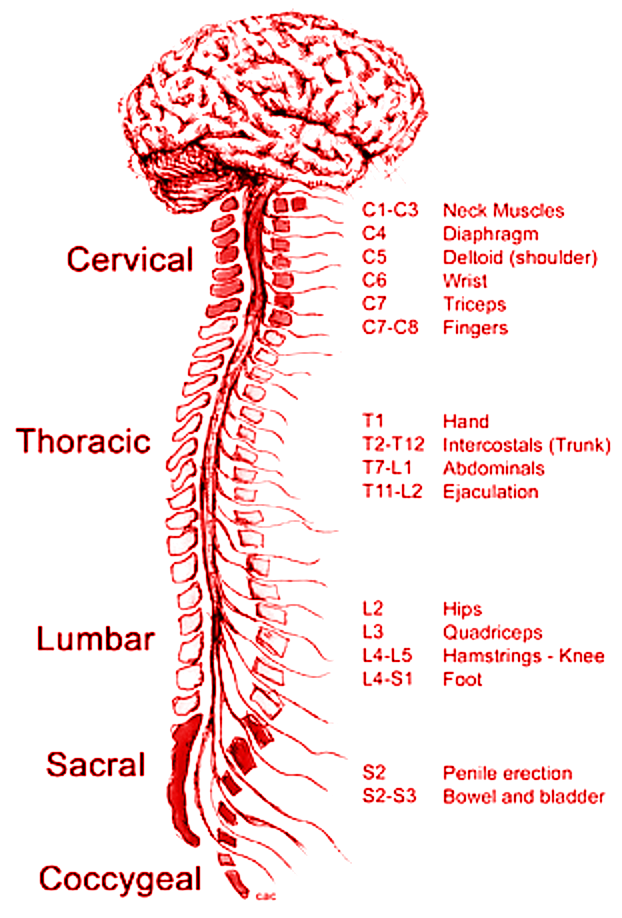
The spinal cord is an extension of the medulla oblongata that comes out from the foramen of the magnum (aperture) and continues inside the neural canal of the vertebral column. It is a long tube of 45 cm and weighs 35 gms. The brain along with the spinal cord is known as the central nervous system (CNS). CNS is the main processing center of information and control. The outer portion of the spinal cord is made up of white matter and the inner portion is made of grey matter (butterfly shape).
The functions of the spinal cord are:
- It acts as a connecting link between the body (peripheral nervous system PNS) and the brain.
- It provides a relay path for the impulses coming from the brain.
- It is responsible for the conduction of the reflex action.
Additional information: The structure of the spinal cord has 31 spinal cord nerve pairs coming out from it.
- Cervical spinal nerves: 8 pairs
- Thoracic spinal nerves: 12 pairs
- Lumbar spinal nerves: 5 pairs
- Sacral spinal nerves: 5 pairs
- Coccygeal spinal nerves: 1 pair
Caudal nerves are not present in humans as humans are tailless animals.
Note:
- The group of spinal nerves comes together at the terminal end of the spinal cord to form a horse tail- like structure called cauda equina.
- The spinal cord just like the brain is also covered by dura mater, arachnoid, and pia mater i.e. meninges. There is a narrow space between the vertebrae and dura mater and it is known as Epidural space.
- Conditioned reflex action was first studied by Evan Parlov on a dog.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
The spinal cord is an extension of the medulla oblongata that comes out from the foramen of the magnum (aperture) and continues inside the neural canal of the vertebral column. It is a long tube of 45 cm and weighs 35 gms. The brain along with the spinal cord is known as the central nervous system (CNS). CNS is the main processing center of information and control. The outer portion of the spinal cord is made up of white matter and the inner portion is made of grey matter (butterfly shape).

The functions of the spinal cord are:
- It acts as a connecting link between the body (peripheral nervous system PNS) and the brain.
- It provides a relay path for the impulses coming from the brain.
- It is responsible for the conduction of the reflex action.
Additional information: The structure of the spinal cord has 31 spinal cord nerve pairs coming out from it.
- Cervical spinal nerves: 8 pairs
- Thoracic spinal nerves: 12 pairs
- Lumbar spinal nerves: 5 pairs
- Sacral spinal nerves: 5 pairs
- Coccygeal spinal nerves: 1 pair
Caudal nerves are not present in humans as humans are tailless animals.
Note:
- The group of spinal nerves comes together at the terminal end of the spinal cord to form a horse tail- like structure called cauda equina.
- The spinal cord just like the brain is also covered by dura mater, arachnoid, and pia mater i.e. meninges. There is a narrow space between the vertebrae and dura mater and it is known as Epidural space.
- Conditioned reflex action was first studied by Evan Parlov on a dog.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




