
How are the graphs for
A. Boyle’s Law
B. Pressure Law
C. Charles law
Answer
558.9k+ views
Hint:Boyle’s Law gives the relation between pressure and volume when the temperature is constant. Therefore, Boyle’s Law gives the graph for pressure versus volume. Charles Law gives the relation between volume and temperature of a gas at constant pressure. It gives a graph of temperature versus volume. Similarly, Pressure Law gives the relation between pressure and temperature at constant volume. Therefore, it gives the graph of pressure versus temperature.
Formula Used:
Boyle’s Law is given as: \[V \propto \dfrac{1}{P}\] at constant temperature
Charles Law is given as: \[V \propto T\] at constant pressure
Pressure Law is given as: \[P \propto T\] at constant volume
where, \[V\]is the volume, \[P\] is the pressure and \[T\] is the temperature.
Complete step by step answer:
Boyle’s Law, Pressure Law and Charles law are the three gas laws. The properties of a gas depends upon pressure \[P\], temperature \[T\] and volume \[V\]of the gas.
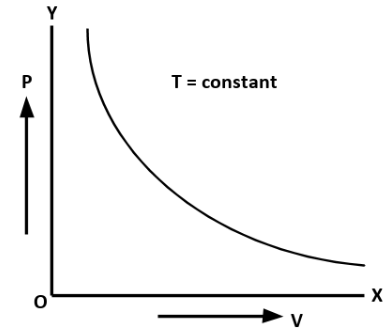
A. Boyle’s Law: At constant temperature for a given mass of ideal gas, the volume of the gas is inversely proportional to its pressure.
\[V \propto \dfrac{1}{P}\]
where, \[V\]is the volume and \[P\] is the pressure.
The graph between pressure and volume at constant temperature is known as isotherm.
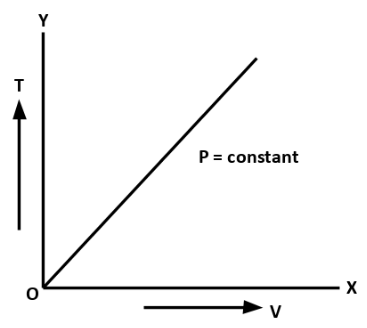
B. Charles Law: At constant pressure, volume of a given mass of gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature.
\[V \propto T\]
The curves between volume and temperature at constant pressure are called Isobars.
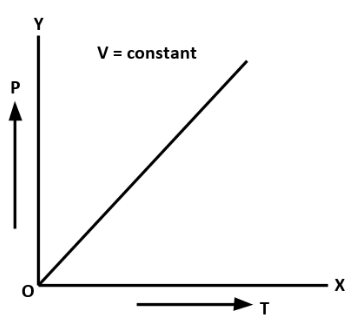
C. Pressure Law: At constant volume, the pressure of a given mass of an ideal gas is directly proportional to the absolute temperature of the gas.
\[P \propto T\]
The graph for pressure law is as follows
Note: In Boyle’s law, the volume of a given gas is inversely proportional to its pressure. Therefore, pressure times volume will be a constant term. That is \[PV = {\text{constant}}\]. The pressure law is also known as Gay Lussac’s Law. Note that the Boyle’s Law, Pressure Law and Charles law are only applicable to Ideal gases. Ideal gas is the perfect gas. But, the behaviour of real gases at high temperature and low pressure is very similar to that of the ideal gas.
Formula Used:
Boyle’s Law is given as: \[V \propto \dfrac{1}{P}\] at constant temperature
Charles Law is given as: \[V \propto T\] at constant pressure
Pressure Law is given as: \[P \propto T\] at constant volume
where, \[V\]is the volume, \[P\] is the pressure and \[T\] is the temperature.
Complete step by step answer:
Boyle’s Law, Pressure Law and Charles law are the three gas laws. The properties of a gas depends upon pressure \[P\], temperature \[T\] and volume \[V\]of the gas.
A. Boyle’s Law: At constant temperature for a given mass of ideal gas, the volume of the gas is inversely proportional to its pressure.
\[V \propto \dfrac{1}{P}\]
where, \[V\]is the volume and \[P\] is the pressure.
The graph between pressure and volume at constant temperature is known as isotherm.

B. Charles Law: At constant pressure, volume of a given mass of gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature.
\[V \propto T\]
The curves between volume and temperature at constant pressure are called Isobars.

C. Pressure Law: At constant volume, the pressure of a given mass of an ideal gas is directly proportional to the absolute temperature of the gas.
\[P \propto T\]
The graph for pressure law is as follows

Note: In Boyle’s law, the volume of a given gas is inversely proportional to its pressure. Therefore, pressure times volume will be a constant term. That is \[PV = {\text{constant}}\]. The pressure law is also known as Gay Lussac’s Law. Note that the Boyle’s Law, Pressure Law and Charles law are only applicable to Ideal gases. Ideal gas is the perfect gas. But, the behaviour of real gases at high temperature and low pressure is very similar to that of the ideal gas.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




