
What are the nodal planes of $d{z^2}$ orbital? How can we find nodal planes?
Answer
503.1k+ views
Hint: We have to know that nodal planes are areas around nuclear cores where the probability of discovering electrons is zero. The directions of these planes are found by tackling the Schrodinger wave condition for particles or atoms to discover the state of nuclear and sub-atomic orbitals.
Complete answer:
We have to see that the thickness of the electron cloud that gives the state of a nuclear orbital demonstrates the probability of discovering electrons in districts around the particle or atom. The denser the cloud is, the higher the probability of discovering an electron. Nodal planes are totally without electron cloud thickness, showing that the probability of discovering electrons in these planes is zero.
A vital idea in quantum mechanics is that electrons have both molecule and wave properties. The nodal planes around a nuclear core are a sign of the wave idea of electrons, as hubs are points of zero playfulness along a standing wave. No adequacy of vibration implies there are no electrons present.
The number and position of nodal planes bring about a considerable lot of the properties of particles and atoms. Particles with few nodal planes are profoundly steady, while those with various nodal planes are unsteady and responsive. The quantity of nodal planes is straightforwardly corresponding with the free energy of a gathering of fortified particles.
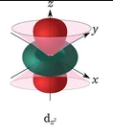
A d-orbital has four flaps and two nodal planes. Then $d{z^2}$ has three-dimensional construction, which has two projections along the z-axis and rings of high thickness in the xy-plane.
Therefore, the nodal plane is two in $d{z^2}$ .
To finding nodal planes by using the following expression,
$\dfrac{{Radial{\text{ nodes}}}}{{Spherical{\text{ nodes}}}} = n - l - 1$
Where,
$l$ is the azimuthal quantum number.
$\dfrac{{Angular{\text{ nodes}}}}{{Nodal{\text{ planes}}}} = 1$ .
Note:
We have to know that, a plane going through the core on which the likelihood of discovering electrons is zero, is known as a nodal plane. The quantity of nodal planes in an orbital is equivalent to azimuthal quantum number.
Complete answer:
We have to see that the thickness of the electron cloud that gives the state of a nuclear orbital demonstrates the probability of discovering electrons in districts around the particle or atom. The denser the cloud is, the higher the probability of discovering an electron. Nodal planes are totally without electron cloud thickness, showing that the probability of discovering electrons in these planes is zero.
A vital idea in quantum mechanics is that electrons have both molecule and wave properties. The nodal planes around a nuclear core are a sign of the wave idea of electrons, as hubs are points of zero playfulness along a standing wave. No adequacy of vibration implies there are no electrons present.
The number and position of nodal planes bring about a considerable lot of the properties of particles and atoms. Particles with few nodal planes are profoundly steady, while those with various nodal planes are unsteady and responsive. The quantity of nodal planes is straightforwardly corresponding with the free energy of a gathering of fortified particles.

A d-orbital has four flaps and two nodal planes. Then $d{z^2}$ has three-dimensional construction, which has two projections along the z-axis and rings of high thickness in the xy-plane.
Therefore, the nodal plane is two in $d{z^2}$ .
To finding nodal planes by using the following expression,
$\dfrac{{Radial{\text{ nodes}}}}{{Spherical{\text{ nodes}}}} = n - l - 1$
Where,
$l$ is the azimuthal quantum number.
$\dfrac{{Angular{\text{ nodes}}}}{{Nodal{\text{ planes}}}} = 1$ .
Note:
We have to know that, a plane going through the core on which the likelihood of discovering electrons is zero, is known as a nodal plane. The quantity of nodal planes in an orbital is equivalent to azimuthal quantum number.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




