
what are the postulates of Dalton’s atomic theory.
Answer
578.1k+ views
Hint: The atomic structure consists of Atomic particles. Atoms consist of three basic particles, protons, electrons, and neutrons. The nucleus (center) of an atom contains the protons (positively charged) and the neutrons (no charge). The outermost regions of the atom are called electron shells and they contain the electrons.
Complete step by step answer:
Dalton's atomic theory is based on the law of conservation of mass and law of constant proportion. The Law of conservation of mass states that mass can neither be created nor be destroyed. In simpler terms, it says over the course of a reaction, the total mass of the reactants before the start of the reaction, is equivalent to the total mass of products at the end of the reaction. This law was proposed by Antoine L Lavoisier.
The primary structure of an atom has protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons and neutrons together make up the nucleus of an electron and are known as nucleons, while electrons remain outside the nucleus of an atom. In a neutral atom, there is an equal number of protons and electrons present.
The atomic structure of an element refers to the constitution of its nucleus and the arrangement of the electrons around it. Primarily, the atomic structure of matter is made up of protons, electrons, and neutrons.
But, the atoms of different elements have different atomic structures because they contain different numbers of protons and electrons.
The first scientific theory of atomic structure was proposed by John Dalton 1800s. The atomic structure is as shown
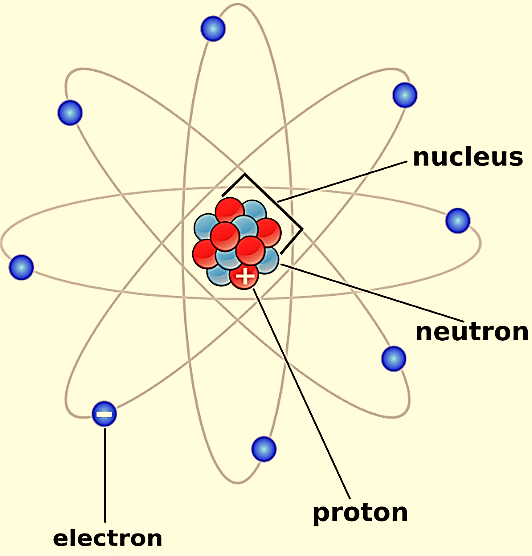
John Dalton suggested that all matter is made up of atoms, which were invisible and indestructible. He also stated that all the atoms of an element were the same, but the atoms of different elements differ in size and mass.
The postulates of this theory:
1.Every matter is made up of atoms.
2.Atoms are invisible and cannot be created or be destroyed. Atoms also cannot be divided into small parts.
3.Specific elements have only one type of atom in them. Atoms of different elements exhibit different 4.properties and vary in mass and size.
5.Each atom has its constant mass that varies from element to element.
6.Atoms undergo rearrangement, combined, or be separated during a chemical reaction.
Note: There exist some more particles in the nucleus other than these three because protons and neutrons are made up of particles called quarks. These are found in baryons, mesons, and plasmas. A proton has two up quarks and one down quark.
Complete step by step answer:
Dalton's atomic theory is based on the law of conservation of mass and law of constant proportion. The Law of conservation of mass states that mass can neither be created nor be destroyed. In simpler terms, it says over the course of a reaction, the total mass of the reactants before the start of the reaction, is equivalent to the total mass of products at the end of the reaction. This law was proposed by Antoine L Lavoisier.
The primary structure of an atom has protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons and neutrons together make up the nucleus of an electron and are known as nucleons, while electrons remain outside the nucleus of an atom. In a neutral atom, there is an equal number of protons and electrons present.
The atomic structure of an element refers to the constitution of its nucleus and the arrangement of the electrons around it. Primarily, the atomic structure of matter is made up of protons, electrons, and neutrons.
But, the atoms of different elements have different atomic structures because they contain different numbers of protons and electrons.
The first scientific theory of atomic structure was proposed by John Dalton 1800s. The atomic structure is as shown

John Dalton suggested that all matter is made up of atoms, which were invisible and indestructible. He also stated that all the atoms of an element were the same, but the atoms of different elements differ in size and mass.
The postulates of this theory:
1.Every matter is made up of atoms.
2.Atoms are invisible and cannot be created or be destroyed. Atoms also cannot be divided into small parts.
3.Specific elements have only one type of atom in them. Atoms of different elements exhibit different 4.properties and vary in mass and size.
5.Each atom has its constant mass that varies from element to element.
6.Atoms undergo rearrangement, combined, or be separated during a chemical reaction.
Note: There exist some more particles in the nucleus other than these three because protons and neutrons are made up of particles called quarks. These are found in baryons, mesons, and plasmas. A proton has two up quarks and one down quark.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




