
What are the resonance structures of benzoate anions?
Answer
528.3k+ views
Hint: Benzoate anion is the anionic form of benzoic acid where benzoic acid is represented by the chemical formula${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}COOH$where anion is the ion which contains negative charge on it and produces by losing an electron and benzoate anion is represented as $\pi $.
Complete answer:
Resonance structures are sets of Lewis structures which describe the delocalization of electrons in polyatomic ions or molecules. In many cases a single Lewis structure fails to explain the bonding in a molecule due to presence of partial charge and fractional bonds in it. In these cases resonance structure helps to describe the chemical bonding in that molecule.
In this case the formate ion i.e. $HCO{{O}^{-}}$ is composed of one atom of hydrogen and carbon and two atoms of oxygen in which the ion contains a charge of -1. It can be able to form resonance structures by considering delocalisation of electron from $\pi $ bond which shows conjugation in the benzene ring with the carbonyl group of carboxylate ion and produce 4 resonating structures which can be shown as follows:
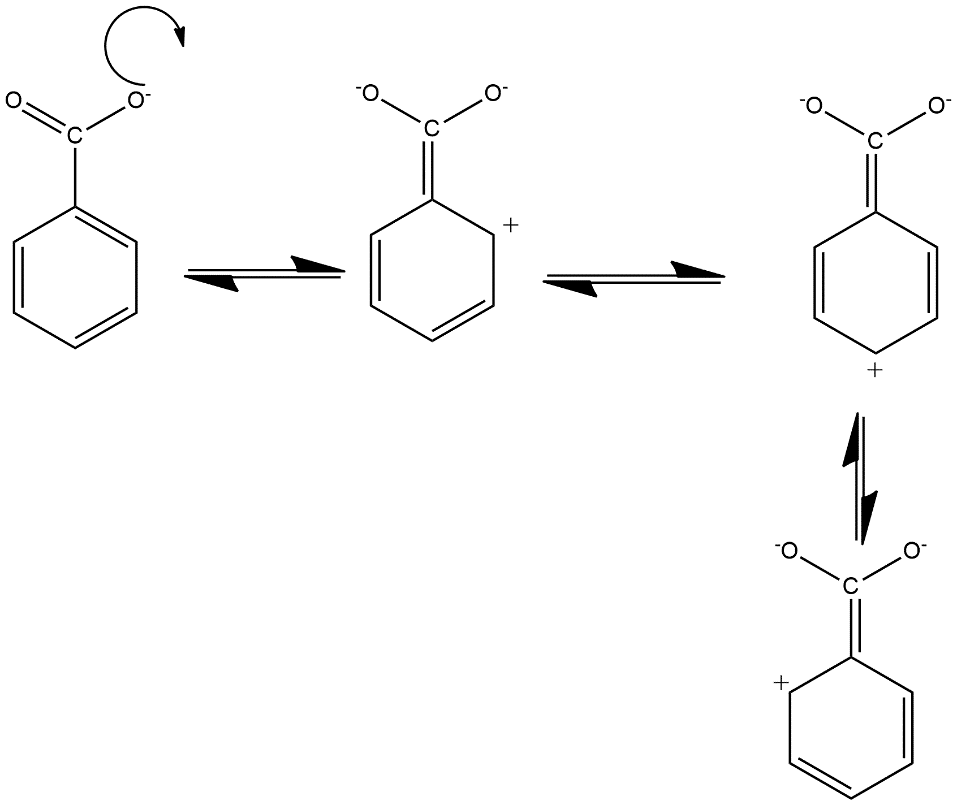
Hence in this way four resonating structures of the benzoate anion where the transference of charge is taking place with the conjugation of benzene ring.
Note:
Resonance describes the bonding in particular molecules or ions by merging a number of contributory structures or forms which are jointly known as canonical structures or resonance structures within the theory of valence bonding into a hybrid resonance also known as hybrid structure.
Complete answer:
Resonance structures are sets of Lewis structures which describe the delocalization of electrons in polyatomic ions or molecules. In many cases a single Lewis structure fails to explain the bonding in a molecule due to presence of partial charge and fractional bonds in it. In these cases resonance structure helps to describe the chemical bonding in that molecule.
In this case the formate ion i.e. $HCO{{O}^{-}}$ is composed of one atom of hydrogen and carbon and two atoms of oxygen in which the ion contains a charge of -1. It can be able to form resonance structures by considering delocalisation of electron from $\pi $ bond which shows conjugation in the benzene ring with the carbonyl group of carboxylate ion and produce 4 resonating structures which can be shown as follows:

Hence in this way four resonating structures of the benzoate anion where the transference of charge is taking place with the conjugation of benzene ring.
Note:
Resonance describes the bonding in particular molecules or ions by merging a number of contributory structures or forms which are jointly known as canonical structures or resonance structures within the theory of valence bonding into a hybrid resonance also known as hybrid structure.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




