
What are the three types of capillaries?
Answer
479.1k+ views
Hint: Blood is a connective tissue that supplies nutrients and oxygen to all the parts of the body. The blood circulation happens with the help of vessels. Three types of vessels that are found in blood are arteries, veins and capillaries. Each of these vessels perform specific functions.
Complete answer:
Capillaries are very fine blood vessels which connect arteries and the veins. It helps in exchange of certain substances such as oxygen, nutrients and waste products in between the blood and tissues. Capillaries are also called microcirculation as they are the smallest blood vessels involved in the circulation process.
There are three types of capillaries on the basis of their function-
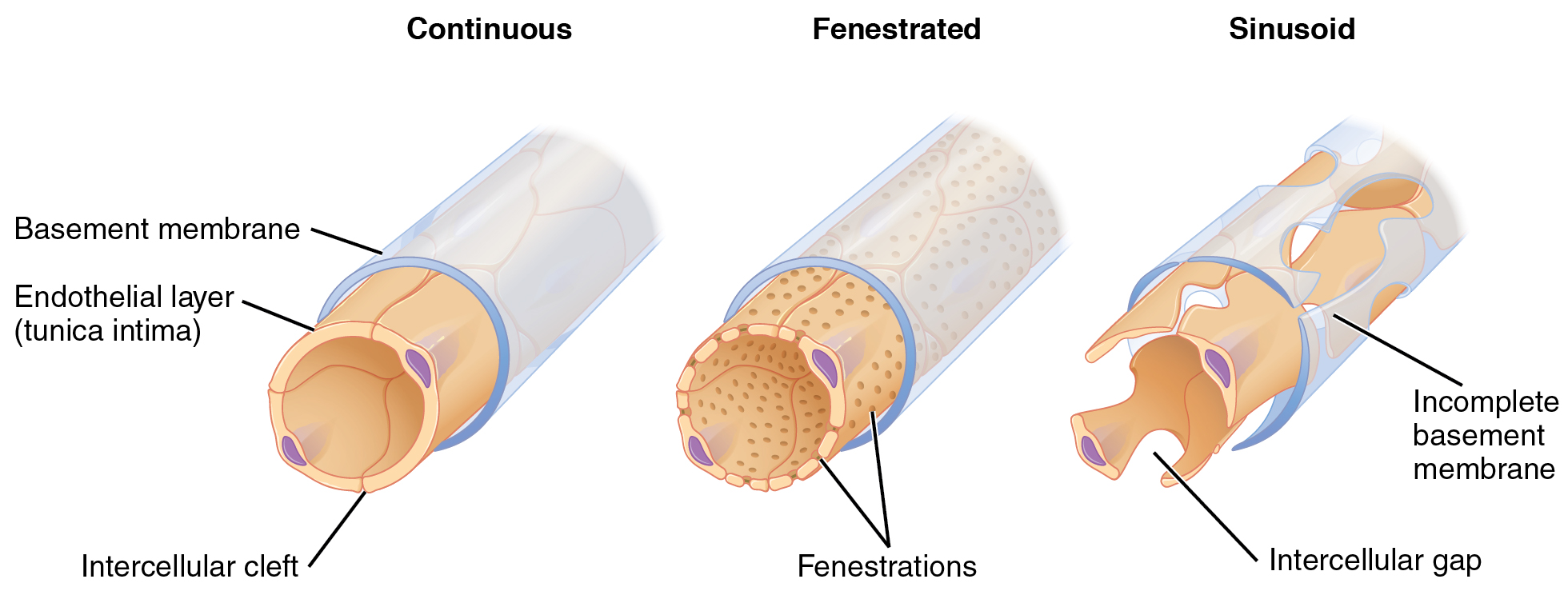
1. Continuous capillaries – This is the most common type of capillary in which small gaps are found in between the endothelial cells. These gaps help in the movement of water, sugar, gases and hormones. These capillaries are found in the brain but there is no gap in between the endothelial cells.
2. Fenestrated capillaries – In addition to small gaps these capillaries also contain small pores in between the cells. These pores are called fenestra and are present on the walls. Their main function is the exchange of large size molecules. They are present in the small intestine where absorption of nutrients takes place. It is also found in the kidneys to filter the blood.
3. Sinusoid capillaries – There are large gaps in the walls of these capillaries. Hence, they are involved in the exchange of larger molecules e.g. cells. These are rarely found capillaries. These capillaries are found in the liver and bone marrow.
Note:
Capillaries are made up of two layers of cells – endothelial and epithelial cells. The layer is called endothelial cell while the outer layer is made up of epithelial cells. The capillaries are surrounded by a basement membrane which is a protein layer.
Complete answer:
Capillaries are very fine blood vessels which connect arteries and the veins. It helps in exchange of certain substances such as oxygen, nutrients and waste products in between the blood and tissues. Capillaries are also called microcirculation as they are the smallest blood vessels involved in the circulation process.
There are three types of capillaries on the basis of their function-
1. Continuous capillaries – This is the most common type of capillary in which small gaps are found in between the endothelial cells. These gaps help in the movement of water, sugar, gases and hormones. These capillaries are found in the brain but there is no gap in between the endothelial cells.
2. Fenestrated capillaries – In addition to small gaps these capillaries also contain small pores in between the cells. These pores are called fenestra and are present on the walls. Their main function is the exchange of large size molecules. They are present in the small intestine where absorption of nutrients takes place. It is also found in the kidneys to filter the blood.
3. Sinusoid capillaries – There are large gaps in the walls of these capillaries. Hence, they are involved in the exchange of larger molecules e.g. cells. These are rarely found capillaries. These capillaries are found in the liver and bone marrow.

Note:
Capillaries are made up of two layers of cells – endothelial and epithelial cells. The layer is called endothelial cell while the outer layer is made up of epithelial cells. The capillaries are surrounded by a basement membrane which is a protein layer.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




