
What are the various types of thalamus in relation to position in various types of floral organs?
Answer
579.9k+ views
Hint:Flower is a reproductive part of a plant. Flower has floral whorls calyx, corolla, androecium and gynoecium arranged around the thalamus. Calyx and corolla are accessory parts. Androecium, gynoecium are reproductive essential parts of a flower.
Complete answer:
Thalamus is basically the receptacle found in angiosperms, and it is the thickened part of the stem from which the various flowers grow. There are three types of flowers on the basis of relation to position in various types of floral organs
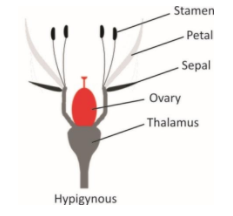
a) Hypogynous
The upper part of the thalamus is slightly swollen and forms a cushion like a disc. The gynoecium is situated at the top of the thalamus. All parts calyx, corolla, androecium arise below the level of ovary and as these are separated from ovary, so that ovary can be seen from outside. This type of ovary is called the superior ovary.
Examples – Brassica, citrus, mustard, China rose, brinjal.
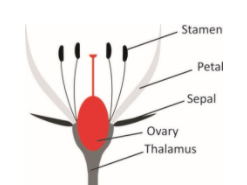
b) Perigynous
In perigynous conditions the thalamus may be – disc shaped cup-shaped and flask-shaped.
In disc shaped thalamus, the ovary of gynoecium lies in the centre and all other floral whorls lie on the peripheral side. Example: Pea
In cup-shaped thalamus, the ovary arises from the bottom of the cup and floral whorls arise at the rim of the cup. E.g. Prunus.
In flask-shaped thalamus, the ovary is placed at the bottom of flask and floral whorls are attached at the mouth of flask. E.g. Rose, plum and peach.
Ovary may or may not be seen from outside as calyx, corolla, androecium develop from common base.Ovary is half-inferior.
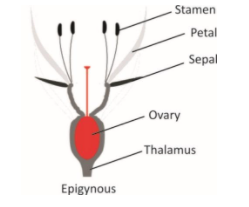
c) Epigynous
As thalamus is cup-shaped, flask or tubular shaped and the ovary is completely inserted. The wall of ovary is fused with thalamus, floral whorls borne on the upper part of thalamus. Thus the ovary is not visible from outside. Such ovaries are called inferior e.g. Guava, Cucumber and Ray florets of sunflowers.
Note:The various functions of flowers are,
>Post fertilization of the egg, the flower develops into a fruit which has seeds.
>Flowers are a source of nectar for birds and insects and both of these help in the process of cross pollination.
>They help in the process of reproduction.
>The gametophytes develop into flowers.
Complete answer:
Thalamus is basically the receptacle found in angiosperms, and it is the thickened part of the stem from which the various flowers grow. There are three types of flowers on the basis of relation to position in various types of floral organs
a) Hypogynous
The upper part of the thalamus is slightly swollen and forms a cushion like a disc. The gynoecium is situated at the top of the thalamus. All parts calyx, corolla, androecium arise below the level of ovary and as these are separated from ovary, so that ovary can be seen from outside. This type of ovary is called the superior ovary.
Examples – Brassica, citrus, mustard, China rose, brinjal.

b) Perigynous
In perigynous conditions the thalamus may be – disc shaped cup-shaped and flask-shaped.
In disc shaped thalamus, the ovary of gynoecium lies in the centre and all other floral whorls lie on the peripheral side. Example: Pea
In cup-shaped thalamus, the ovary arises from the bottom of the cup and floral whorls arise at the rim of the cup. E.g. Prunus.
In flask-shaped thalamus, the ovary is placed at the bottom of flask and floral whorls are attached at the mouth of flask. E.g. Rose, plum and peach.
Ovary may or may not be seen from outside as calyx, corolla, androecium develop from common base.Ovary is half-inferior.

c) Epigynous
As thalamus is cup-shaped, flask or tubular shaped and the ovary is completely inserted. The wall of ovary is fused with thalamus, floral whorls borne on the upper part of thalamus. Thus the ovary is not visible from outside. Such ovaries are called inferior e.g. Guava, Cucumber and Ray florets of sunflowers.

Note:The various functions of flowers are,
>Post fertilization of the egg, the flower develops into a fruit which has seeds.
>Flowers are a source of nectar for birds and insects and both of these help in the process of cross pollination.
>They help in the process of reproduction.
>The gametophytes develop into flowers.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

How do I convert ms to kmh Give an example class 11 physics CBSE




