
Are there synapses between the nodes of Ranvier?
Answer
481.5k+ views
Hint: A Neuron, also known as a nerve cell, is the basic building block of the nervous system. Even though there are many similarities between neurons and other types of cells, structurally and functionally neurons are unique. At the time of birth, our brain consists of about 100 billion neurons. Neurons don’t reproduce or regenerate, once they die they can’t be replaced.
Complete answer:
Depending on their role and location, neurons show great variation in size, shape, and structure. However, all neurons consist of three basic parts; a cell body, an axon, and dendrites.
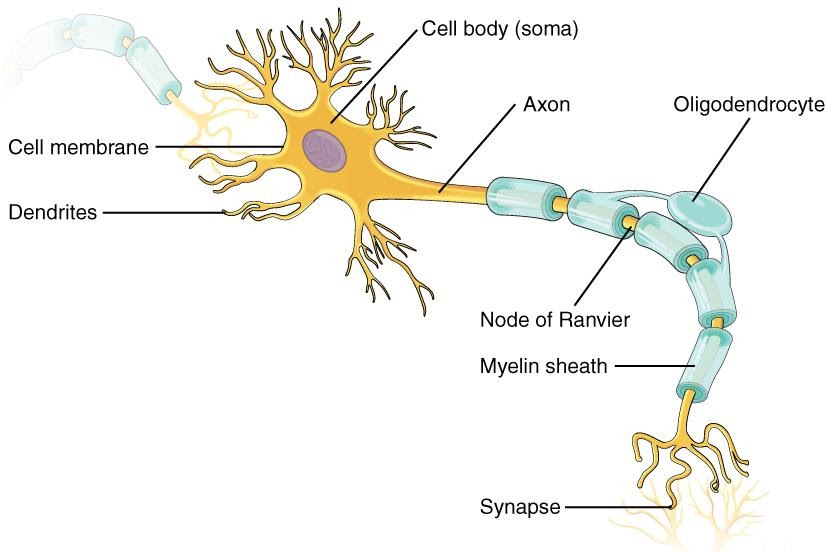
1. Cell body or soma: It is the neuron's core. It plays important roles such as carrying genetic information, maintaining a neuron's structure, and providing energy to drive activities. A neuron's soma contains a nucleus and specialized organelles. The Cell body is enclosed by a membrane that provides protection and allows it to interact with its surroundings.
2. Axon: It is a long, tail-like structure. It joins the cell body at a junction called the axon hillock. Myelin is a fatty substance that insulates many axons. Myelin helps axons in conducting an electrical signal.
3. Dendrites: They are fibrous roots branching from the cell body. Dendrites receive signals from the axons of other neurons and process the same. There can be more than one set of dendrites, known as dendritic trees. The number of dendrites depends on the role of neurons. For example, a special type of neuron called Purkinje cells is found in the cerebellum. These cells receive thousands of signals for which they have highly developed dendritic trees.
> A synapse is a small gap at the end of a neuron where two neurons communicate with each other. Here, the axon terminal of one neuron and dendrite terminal of another neuron lie nearby. Vesicles containing neurotransmitters exchange information at a synapse.
Some neurons are myelinated, which means they are insulated by a structure known as the myelin sheath. Myelin sheath is not continuous; it is interrupted by some gaps known as nodes of Ranvier. Action potential jumps from node to node making the conduction faster.
There are no synapses between the nodes of Ranvier.
Note:
In a chemical synapse, nerve impulses are transmitted through a cell-to-cell junction. Transmission is unidirectional by means of neurotransmitters. It is found in higher vertebrates. Transmission is slow. An electrical synapse is a cell junction between two nerve cells. The transmission of signals is bidirectional by means of ions. It is found in lower vertebrates and invertebrates. Transmission of the information is faster.
Complete answer:
Depending on their role and location, neurons show great variation in size, shape, and structure. However, all neurons consist of three basic parts; a cell body, an axon, and dendrites.

1. Cell body or soma: It is the neuron's core. It plays important roles such as carrying genetic information, maintaining a neuron's structure, and providing energy to drive activities. A neuron's soma contains a nucleus and specialized organelles. The Cell body is enclosed by a membrane that provides protection and allows it to interact with its surroundings.
2. Axon: It is a long, tail-like structure. It joins the cell body at a junction called the axon hillock. Myelin is a fatty substance that insulates many axons. Myelin helps axons in conducting an electrical signal.
3. Dendrites: They are fibrous roots branching from the cell body. Dendrites receive signals from the axons of other neurons and process the same. There can be more than one set of dendrites, known as dendritic trees. The number of dendrites depends on the role of neurons. For example, a special type of neuron called Purkinje cells is found in the cerebellum. These cells receive thousands of signals for which they have highly developed dendritic trees.
> A synapse is a small gap at the end of a neuron where two neurons communicate with each other. Here, the axon terminal of one neuron and dendrite terminal of another neuron lie nearby. Vesicles containing neurotransmitters exchange information at a synapse.
Some neurons are myelinated, which means they are insulated by a structure known as the myelin sheath. Myelin sheath is not continuous; it is interrupted by some gaps known as nodes of Ranvier. Action potential jumps from node to node making the conduction faster.
There are no synapses between the nodes of Ranvier.
Note:
In a chemical synapse, nerve impulses are transmitted through a cell-to-cell junction. Transmission is unidirectional by means of neurotransmitters. It is found in higher vertebrates. Transmission is slow. An electrical synapse is a cell junction between two nerve cells. The transmission of signals is bidirectional by means of ions. It is found in lower vertebrates and invertebrates. Transmission of the information is faster.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




