
Why are xylem and phloem called complex tissues. How are they different from one another?
Answer
580.8k+ views
Hint: Complex tissues are made up of more than one type of cell which works together as a single unit necessary for functioning.
Complete step by step answer:
Additional Information: Xylem tissue consists of:
Tracheids: Main water transporting element. Lacks protoplasm, hence is dead. It is elongated and has tapering ends. Have thick lignified walls.
Vessels: Similar to tracheids, however, they are cylindrical tube- like structures and are a characteristic feature of angiosperms.
Xylem fibres: Have highly thickened walls with obliterated central lumens. Can be septate or aseptate.
Xylem Parenchyma: Store food material and tannins in the form of starch or fats. These are living cells with cellulose thin walls.
Phloem tissue consists of:
Sieve tubes: Long tube-like cells which work in association with companion cells. Functioning is controlled by the nucleus of companion cells.
Companion cells: Specialized parenchyma cells which help in maintaining pressure gradient in sieve tubes.
Phloem parenchyma: Elongated, dense, cylindrical cells with cellulose cell walls. Stores food material, raisins, latex and mucilage. They are absent in monocots.
Phloem fibres: Phloem fibres are made up of sclerenchymatous cells. Initially contain protoplasm but become dead on maturity. Primary phloem is referred to as protophloem and the latter one is called metaphloem.
Note:
- Gymnosperms lack xylem vessels, sieve tubes and companion cells.
- Phloem fibres are also known as bast fibres.
- Phloem fibres of jute, flax and hemp are of commercial importance
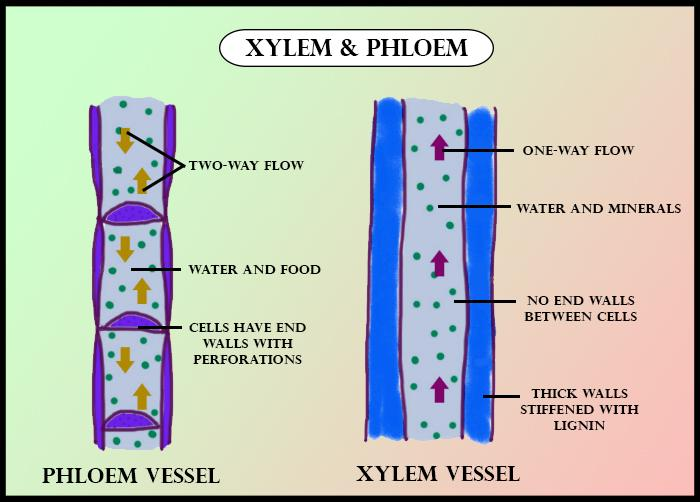
- Transfer of materials through xylem is unidirectional, from roots to above parts of the plant.
- Transfer of material through phloem is bi- directional, from leaves to other parts of the plant.
Complete step by step answer:
| S.no. | Phloem | Xylem |
| 1. | It is made up of sieve tube, companion, phloem parenchyma and phloem fibres in angiosperms. | It is made up of tracheids, vessels, xylem fibres and xylem parenchyma. |
| 2. | Help in the transfer of food from leaves to other parts of the plant. | Help in the transfer of water from roots or stem and leaves. |
| 3. | Movement is bidirectional. | Movement is unidirectional. |
| 4. | Present on the outer side of the vascular bundle. | Present in the centre of the vascular bundle. |
| 5. | Does not provide any mechanical support. | Provides mechanical support. |
Additional Information: Xylem tissue consists of:
Tracheids: Main water transporting element. Lacks protoplasm, hence is dead. It is elongated and has tapering ends. Have thick lignified walls.
Vessels: Similar to tracheids, however, they are cylindrical tube- like structures and are a characteristic feature of angiosperms.
Xylem fibres: Have highly thickened walls with obliterated central lumens. Can be septate or aseptate.

Xylem Parenchyma: Store food material and tannins in the form of starch or fats. These are living cells with cellulose thin walls.
Phloem tissue consists of:
Sieve tubes: Long tube-like cells which work in association with companion cells. Functioning is controlled by the nucleus of companion cells.
Companion cells: Specialized parenchyma cells which help in maintaining pressure gradient in sieve tubes.
Phloem parenchyma: Elongated, dense, cylindrical cells with cellulose cell walls. Stores food material, raisins, latex and mucilage. They are absent in monocots.
Phloem fibres: Phloem fibres are made up of sclerenchymatous cells. Initially contain protoplasm but become dead on maturity. Primary phloem is referred to as protophloem and the latter one is called metaphloem.
Note:
- Gymnosperms lack xylem vessels, sieve tubes and companion cells.
- Phloem fibres are also known as bast fibres.
- Phloem fibres of jute, flax and hemp are of commercial importance
- Transfer of materials through xylem is unidirectional, from roots to above parts of the plant.
- Transfer of material through phloem is bi- directional, from leaves to other parts of the plant.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




