
Aristotle classified the animals into two groups. Which of the following is the correct one?
A. Vertebrate and invertebrate
B. Chordata and non-chordata
C. Protozoa
D. Enaima and anaima
Answer
510.3k+ views
Hint: Aristotle is also known as 'Father of Biology' for making a successful attempt to classify animals into specific categories that consequently gave a systematic approach to biology. This classification was based on physical characteristics possessed by the animals.
Complete answer:
He categorized animals into two groups, followed by five genera per group, and then into species within each genus. The two major groups of animals according to his classification were based on presence or absence of "red blood." Animals with red blood flowing in their bodies were named as Enaima (today’s vertebrates) whereas animals without any such red blood flowing in their bodies, were named as Anaima (today’s invertebrates).
Enaima included viviparous (infant yielding) and oviparous (egg yielding) organisms such as whales, fishes, and birds. On the other hand, anaima included cephalopods, crustaceans, insects, shelled animals, and plant animals.
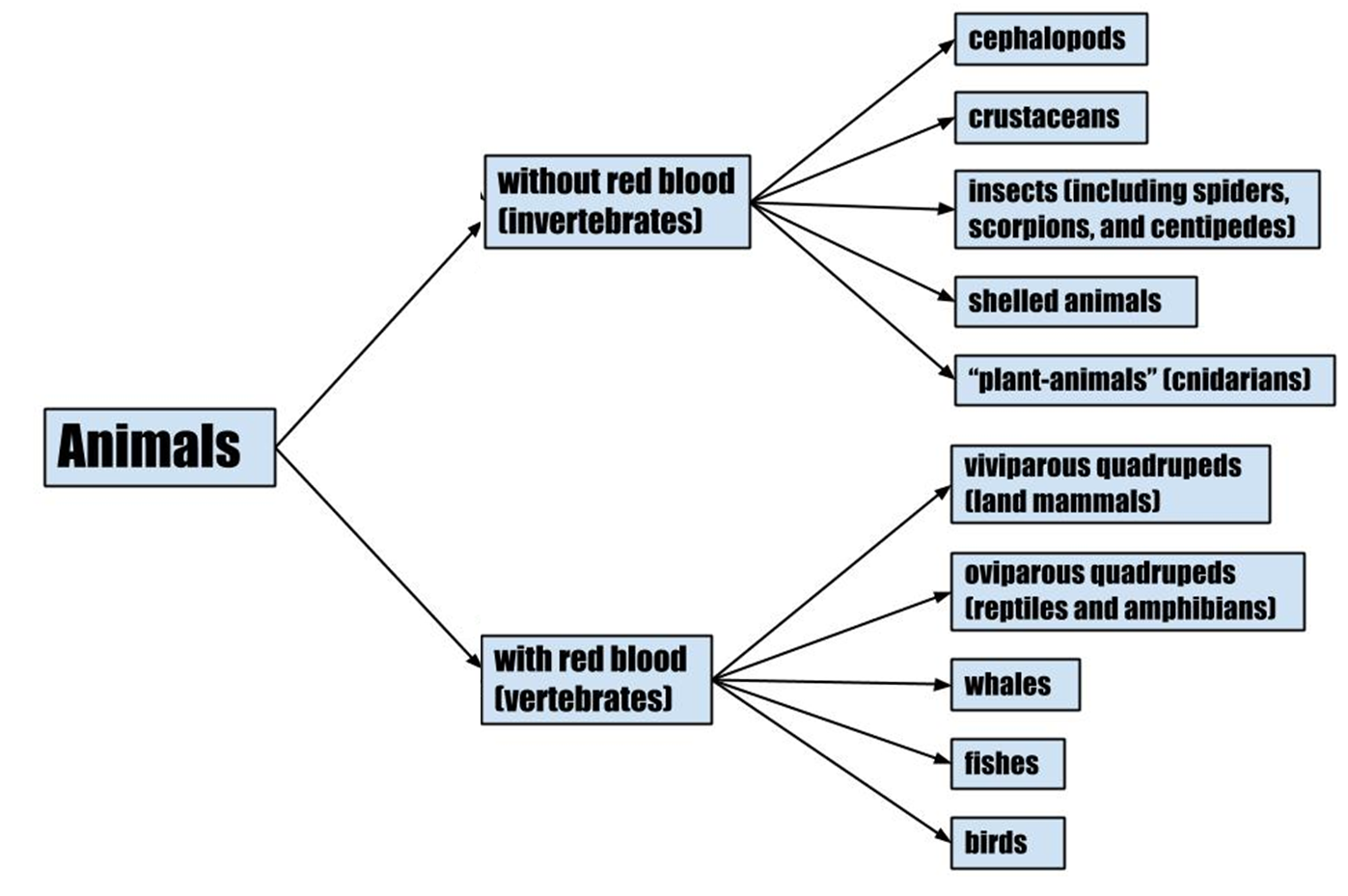
Fig: Flowchart showing Aristotle’s classification of animals.
However, the classification had some major drawbacks as well that have been enlisted below:
A variety of unrelated organisms are placed in the same group, due to their matching habitats.
A variety of related organisms are placed in varied groups due to dissimilarities in their morphological characters.
While classifying organisms, the evolutionary relationship between them has been completely neglected.
So, the correct answer is option d, ‘Enaima and anaima’.
Note: It is necessary to classify animals to understand diversity according to a uniform classification system. Classification allows us to understand physiology, behavior, and various other aspects of an organism. Classification is also important to derive phylogenetic relationships between the organisms.
Complete answer:
He categorized animals into two groups, followed by five genera per group, and then into species within each genus. The two major groups of animals according to his classification were based on presence or absence of "red blood." Animals with red blood flowing in their bodies were named as Enaima (today’s vertebrates) whereas animals without any such red blood flowing in their bodies, were named as Anaima (today’s invertebrates).
Enaima included viviparous (infant yielding) and oviparous (egg yielding) organisms such as whales, fishes, and birds. On the other hand, anaima included cephalopods, crustaceans, insects, shelled animals, and plant animals.

Fig: Flowchart showing Aristotle’s classification of animals.
However, the classification had some major drawbacks as well that have been enlisted below:
A variety of unrelated organisms are placed in the same group, due to their matching habitats.
A variety of related organisms are placed in varied groups due to dissimilarities in their morphological characters.
While classifying organisms, the evolutionary relationship between them has been completely neglected.
So, the correct answer is option d, ‘Enaima and anaima’.
Note: It is necessary to classify animals to understand diversity according to a uniform classification system. Classification allows us to understand physiology, behavior, and various other aspects of an organism. Classification is also important to derive phylogenetic relationships between the organisms.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




