
What is aromatic nucleophilic substitution reaction?
Answer
508.5k+ views
Hint: In order to answer this problem let us get some idea about the Nucleophilic substitution. A nucleophilic aromatic substitution is an organic chemistry substitution reaction in which the nucleophile displaces a good leaving group on an aromatic ring, such as a halide.
Complete answer:
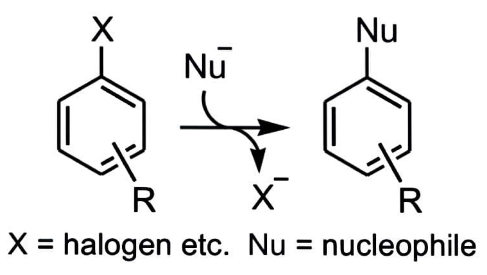
Let us understand this by an example:
A nucleophile (Nu) attacks an aromatic molecule that is electron-poor, resulting in the replacement of a leaving group.
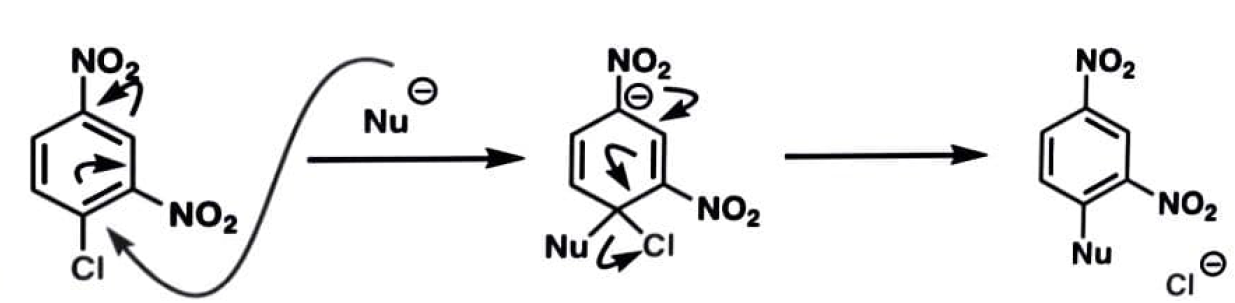
The nucleophile's attack on the aromatic ring, which disturbs aromaticity, is the rate-determining step.
The aromatic ring's electron-withdrawing groups aid in stabilising the intermediate's negative charge.
Because the rate-determining step is not the loss of the leaving group, fluorine is frequently utilised as a leaving group due to its strong electronegativity.
The following are some common arene substitution reactions.
N-phenyl hydroxylamine rearranges to \[4 - aminophenols\] in the Bamberger reaction. Water is the nucleophile.
Diazonium salts react with halides in the Sandmeyer and Gattermann reactions.
The intramolecular variant of this process is the Smiles rearrangement.
However, nucleophilic aromatic substitution is not confined to arenes; it occurs much more frequently with heteroarenes. Because the negative charge is effectively delocalized at the nitrogen position, pyridines are especially reactive when substituted in the aromatic ortho or aromatic para positions.
The Chichibabin reaction (Aleksei Chichibabin,\[1914\]) is a classic reaction in which pyridine is reacted with an alkali-metal amide, such as sodium amide, to produce \[2 - aminopyridine{\text{ }}.\]
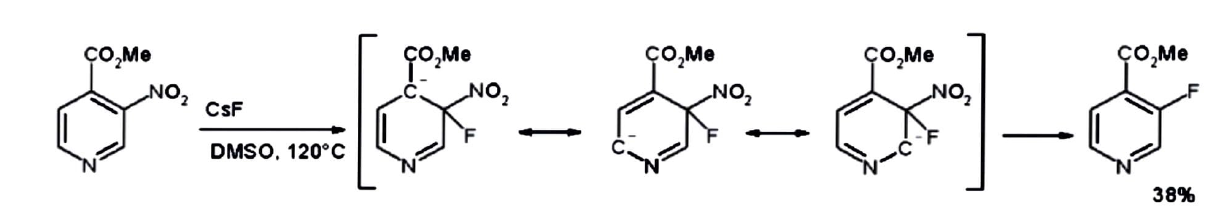
The meta nitro group is really displaced by fluorine using cesium fluoride in DMSO at \[120{\text{ }}^\circ C\] in the product methyl \[3 - nitropyridine - 4 - carboxylate.\]
Note:
All of the tendencies you learnt in electrophilic aromatic substitution (EAS) apply in nucleophilic aromatic substitution (NAS), but in reverse. The first thing to realise is that electron withdrawing groups (EWGs) greatly increase, not decrease, the pace of reaction.
Complete answer:

Let us understand this by an example:
A nucleophile (Nu) attacks an aromatic molecule that is electron-poor, resulting in the replacement of a leaving group.

The nucleophile's attack on the aromatic ring, which disturbs aromaticity, is the rate-determining step.
The aromatic ring's electron-withdrawing groups aid in stabilising the intermediate's negative charge.
Because the rate-determining step is not the loss of the leaving group, fluorine is frequently utilised as a leaving group due to its strong electronegativity.
The following are some common arene substitution reactions.
N-phenyl hydroxylamine rearranges to \[4 - aminophenols\] in the Bamberger reaction. Water is the nucleophile.
Diazonium salts react with halides in the Sandmeyer and Gattermann reactions.
The intramolecular variant of this process is the Smiles rearrangement.
However, nucleophilic aromatic substitution is not confined to arenes; it occurs much more frequently with heteroarenes. Because the negative charge is effectively delocalized at the nitrogen position, pyridines are especially reactive when substituted in the aromatic ortho or aromatic para positions.
The Chichibabin reaction (Aleksei Chichibabin,\[1914\]) is a classic reaction in which pyridine is reacted with an alkali-metal amide, such as sodium amide, to produce \[2 - aminopyridine{\text{ }}.\]
The meta nitro group is really displaced by fluorine using cesium fluoride in DMSO at \[120{\text{ }}^\circ C\] in the product methyl \[3 - nitropyridine - 4 - carboxylate.\]

Note:
All of the tendencies you learnt in electrophilic aromatic substitution (EAS) apply in nucleophilic aromatic substitution (NAS), but in reverse. The first thing to realise is that electron withdrawing groups (EWGs) greatly increase, not decrease, the pace of reaction.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




