
Arrange in the order of decreasing $p{K_b}$.
(A)
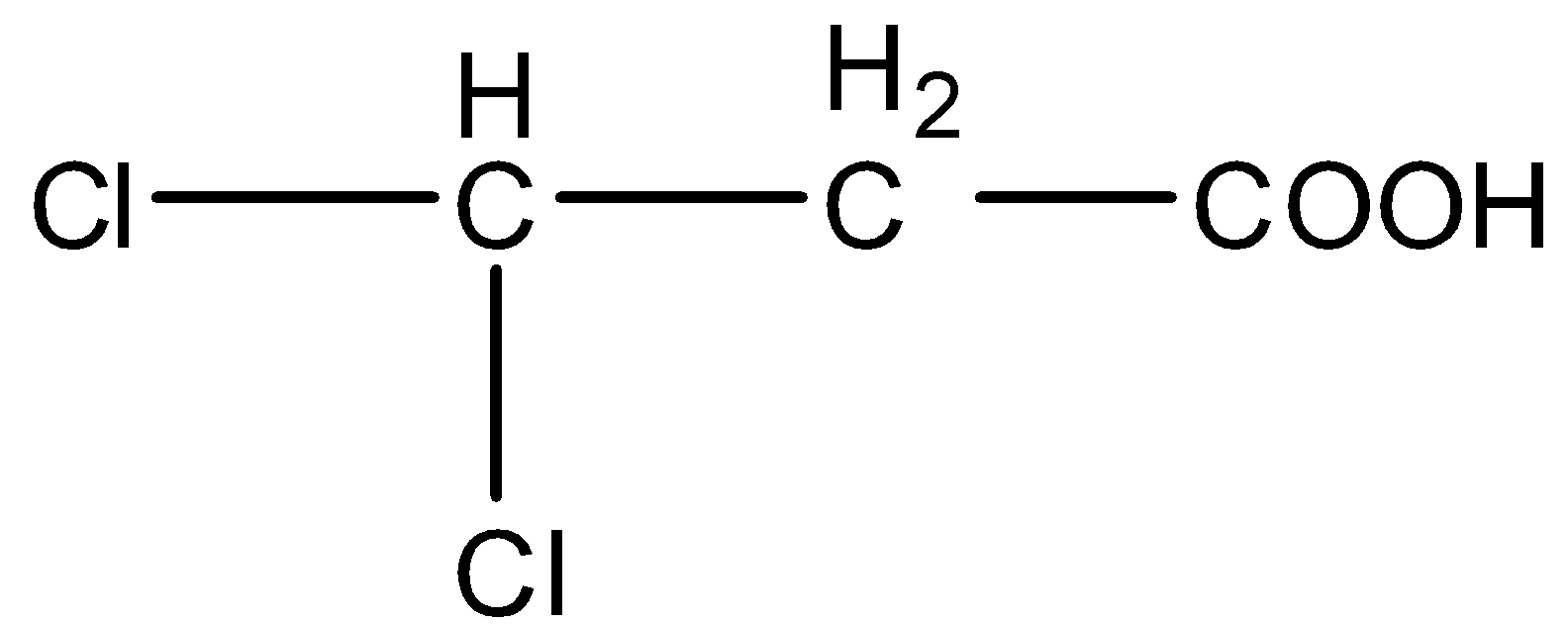
(B)
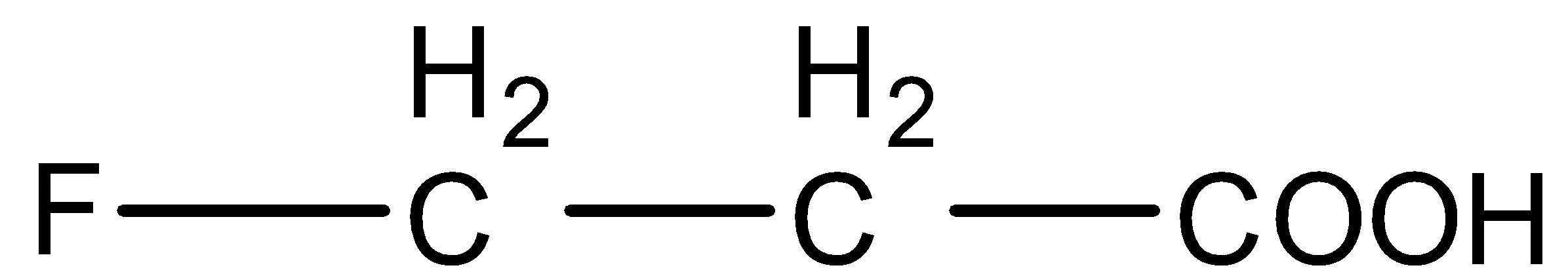
(C)
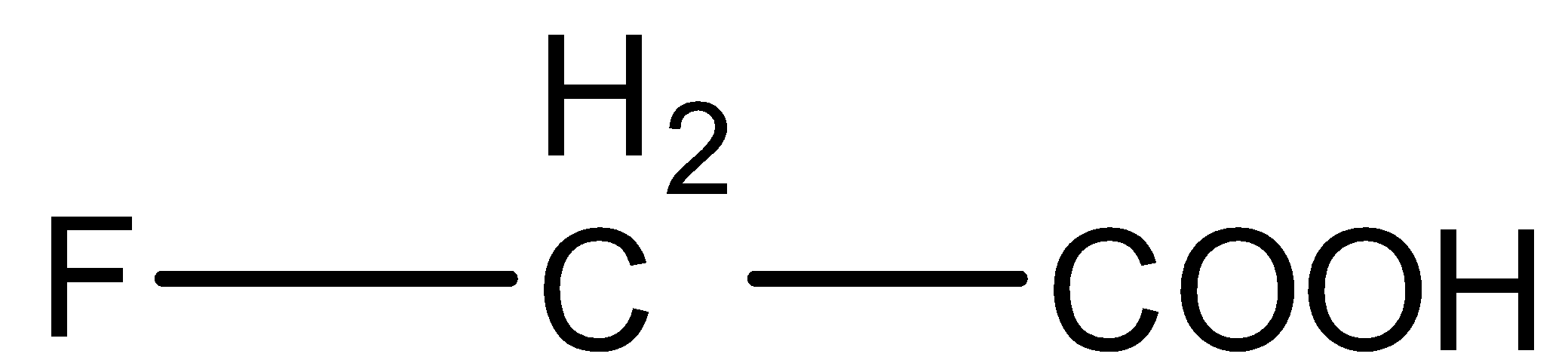
(D)
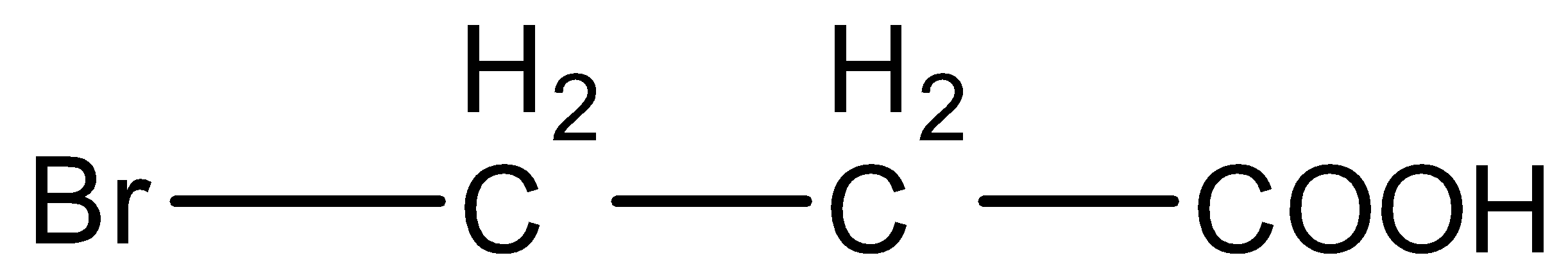

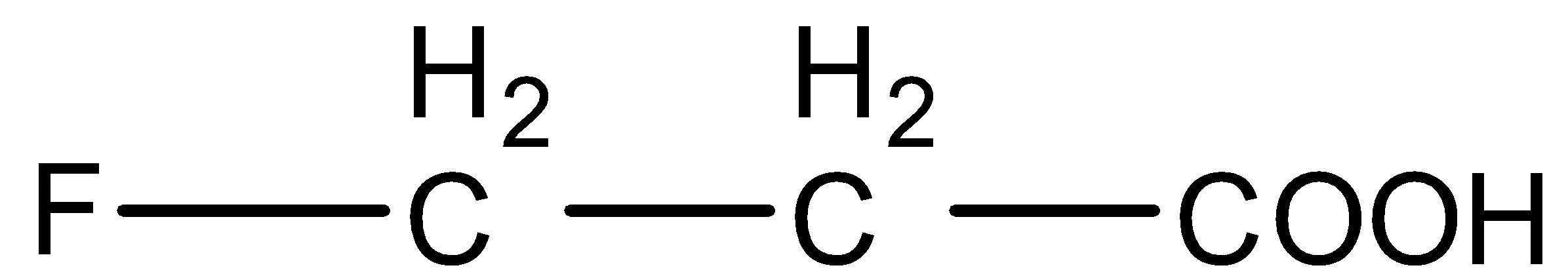
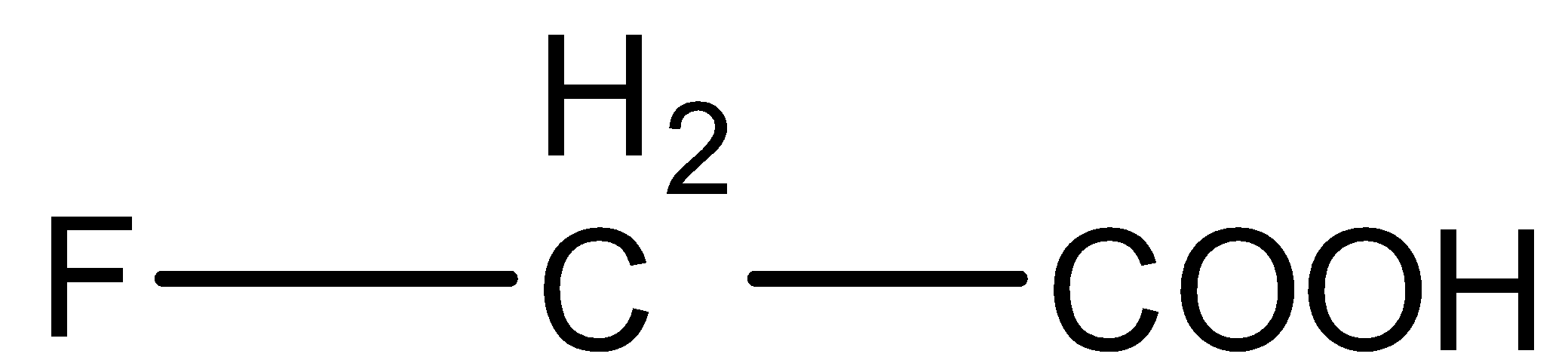

Answer
585.3k+ views
Hint: $p{K_b}$ is known as the dissociation constant of the base. $p{K_b}$ and $p{K_a}$ are related to each other by the equation $p{K_a} + p{K_b} = 14$ . The strength of the acid depends upon the stability of the conjugate base.
Complete step by step answer:
First of all, let’s know about $p{K_b}$.
- $p{K_b}$ is the negative logarithm of ${K_b}$ which is the dissociation constant for the base. Thus, we can say that $p{K_b} = - \log [{K_b}]$.
- Now, the compounds given to us are acids. So, we will first compare the strength of their acidity which will give the relation between their $p{K_a}$ and then we will find the relations between their $p{K_b}$ values which is asked in the question.
- We know that strength of an acid is determined by the stability of the conjugate base of that acid which is carboxylate ions. We can write that in form of reaction as
- Thus, we can say that the more stable the carboxylate ion, the more stable the acid will be. We are given four of such acids. Let’s compare them.
- In option (C) fluorine atom is on $\alpha $-carbon. None of the other acids given in the options have this. So, fluorine being the highest electronegative element will stabilize the negative charge on the oxygen atom and so the conjugate base will be stabilized. Thus, acid in option (C) is the most acidic.
- In option (A), there are two chlorine atoms. So, they being halogens will decrease the electron density on the negatively charged oxygen atom and stabilize the conjugate base. So, this will be the second most acidic compound from the given ones.
- In option (B) and (D), the only difference is the fluorine and bromine atoms. Fluorine is a more electronegative atom and hence it will stabilize the conjugate base more than bromine. So, Acid in option (B) will be more acidic than shown in option (D).
So, we can arrange the acids in the order of their acidic strength as (D) < (B) < (A) < (C).
- Now, we know that lower the$p{K_a}$ value, stronger the acid and higher the $p{K_a}$ value, weaker the acid. So, decreasing order of $p{K_a}$ values of these acids will be (D) > (B) > (A) > (C).
Now, we are being asked to compare their $p{K_b}$ values. We know that $p{K_a}$ and $p{K_b}$ are related by the following formula.
So, we can say that higher the $p{K_a}$ value of an acid, lower will be its $p{K_b}$ value.
So, we can arrange the acids given in the options in decreasing order of their $p{K_b}$ values as
(C) > (A) > (B) > (D).
Note: Remember that the effect of the substituent groups is most effective if the substitution is at $\alpha $-position. If the substituent group is separated by more number of bonds with the carboxylic acid, its effect on the acidity of the acid decreases gradually.
Complete step by step answer:
First of all, let’s know about $p{K_b}$.
- $p{K_b}$ is the negative logarithm of ${K_b}$ which is the dissociation constant for the base. Thus, we can say that $p{K_b} = - \log [{K_b}]$.
- Now, the compounds given to us are acids. So, we will first compare the strength of their acidity which will give the relation between their $p{K_a}$ and then we will find the relations between their $p{K_b}$ values which is asked in the question.
- We know that strength of an acid is determined by the stability of the conjugate base of that acid which is carboxylate ions. We can write that in form of reaction as
\[R - COOH\xrightarrow{{{H_2}O}}R - CO{O^ - } + {H^ + }\]
- Thus, we can say that the more stable the carboxylate ion, the more stable the acid will be. We are given four of such acids. Let’s compare them.
- In option (C) fluorine atom is on $\alpha $-carbon. None of the other acids given in the options have this. So, fluorine being the highest electronegative element will stabilize the negative charge on the oxygen atom and so the conjugate base will be stabilized. Thus, acid in option (C) is the most acidic.
- In option (A), there are two chlorine atoms. So, they being halogens will decrease the electron density on the negatively charged oxygen atom and stabilize the conjugate base. So, this will be the second most acidic compound from the given ones.
- In option (B) and (D), the only difference is the fluorine and bromine atoms. Fluorine is a more electronegative atom and hence it will stabilize the conjugate base more than bromine. So, Acid in option (B) will be more acidic than shown in option (D).
So, we can arrange the acids in the order of their acidic strength as (D) < (B) < (A) < (C).
- Now, we know that lower the$p{K_a}$ value, stronger the acid and higher the $p{K_a}$ value, weaker the acid. So, decreasing order of $p{K_a}$ values of these acids will be (D) > (B) > (A) > (C).
Now, we are being asked to compare their $p{K_b}$ values. We know that $p{K_a}$ and $p{K_b}$ are related by the following formula.
\[p{K_a} + p{K_b} = 14\]
So, we can say that higher the $p{K_a}$ value of an acid, lower will be its $p{K_b}$ value.
So, we can arrange the acids given in the options in decreasing order of their $p{K_b}$ values as
(C) > (A) > (B) > (D).
Note: Remember that the effect of the substituent groups is most effective if the substitution is at $\alpha $-position. If the substituent group is separated by more number of bonds with the carboxylic acid, its effect on the acidity of the acid decreases gradually.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




