
Arrange the carbanions, \[{{(C{{H}_{3}})}_{3}}C,CC{{l}_{3}},{{(C{{H}_{3}})}_{2}}CH,{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}C{{H}_{2}}\],in order of their decreasing stability.
A. ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}C{{H}_{2}}>CC{{l}_{3}}>{{(C{{H}_{3}})}_{3}}C>{{(C{{H}_{3}})}_{2}}CH$
B. ${{(C{{H}_{3}})}_{2}}CH>CC{{l}_{3}}>{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}C{{H}_{2}}>{{(C{{H}_{3}})}_{3}}C$
C. $CC{{l}_{3}}>{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}C{{H}_{2}}>{{(C{{H}_{3}})}_{3}}CH>{{(C{{H}_{3}})}_{2}}C$
D. ${{(C{{H}_{3}})}_{3}}C>{{(C{{H}_{3}})}_{2}}CH>{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}C{{H}_{2}}>CC{{l}_{3}}$
Answer
581.4k+ views
Hint: Stability of carbanion is directly proportional to –I effect and inversely proportional to +I effect,
Stability of carbanion $\propto \dfrac{-I\,effect}{+I\,effect}$.
As +I effect increases stability decreases and increase in –I effect increases the stability of carbanion. Stability of carbanion follows the following trend 1⁰>2⁰>3⁰ carbon.
Complete answer:
From your chemistry lessons you have learned about the carbanion, inductive effect and their stability.
Carbanions are those organic ions which contain negative charge on its carbon atom. In a covalent bond where carbon is attached with less electronegative atom breaks up through heterolysis then the atom will leave without taking the bonding pair of electrons, so the carbon atom gains extra electron and thus has a negative charge on it.
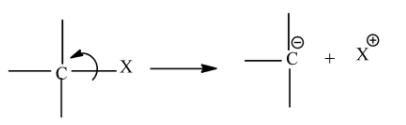
The stability of carbanion depends upon resonance, s-character of orbitals and the inductive effect.
Inductive effect is the partial displacement of sigma electrons towards the more electronegative atom or group. There are two types of inductive effect one is –I effect and other is +I effect.
-I effect is shown by electron withdrawing groups and they stabilize the carbanion through the dispersal of negative charge whereas +I effect is shown by electron donating group or electron releasing group and they stabilize the carbanion through increasing the electron density so they can donate them.
Thus stability of carbanion is directly proportional to –I effect and inversely proportional to +I effect thus the increase in +I effect will decrease the stability of carbanion and increase in –I effect will increase the stability of carbanion. And it is represented as ,
Stability of carbanion \[\propto \,\dfrac{-I\,effect}{+I\,effect}\]
So, among the given carbanion $CC{{l}_{3}}$ is more stable because it shows –I effect because chlorine is the electron withdrawing group and it decreases the electron density on the negatively charged carbon atom. After that ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}C{{H}_{2}}$ will be more stable because benzyl group show –I effect as well as decolonization of electron takes place due to resonance effect. The least stable among them will be ${{(C{{H}_{3}})}_{3}}C$(3⁰) because here three methyl groups are attached with negatively charged carbon atom and increases the electron density on them through +I effect.
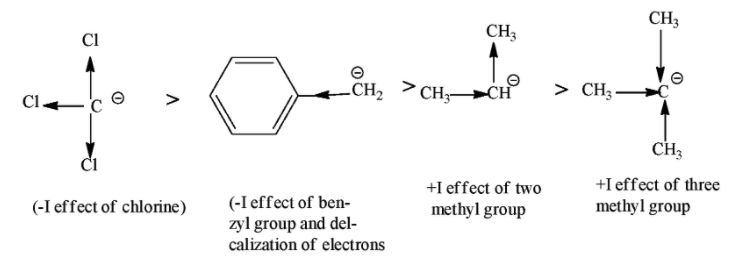
So the correct order of decreasing stability of carbanion is $CC{{l}_{3}}>{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}C{{H}_{2}}>{{(C{{H}_{3}})}_{3}}CH>{{(C{{H}_{3}})}_{2}}C$
Thus the correct option is (C).
Note:
Stability of carbanion by resonance effect is due to the presence of lone pairs of electrons and their involvement with delocalization of electrons( pi electrons). Inductive effect is inversely proportional to the distance distance increases inductive effect decreases. Carbanions are highly reactive because of the presence of negative charge and these negative charges make the carbon atom rich in electrons and thus can donate these non- bonding electrons to some other group.
Stability of carbanion $\propto \dfrac{-I\,effect}{+I\,effect}$.
As +I effect increases stability decreases and increase in –I effect increases the stability of carbanion. Stability of carbanion follows the following trend 1⁰>2⁰>3⁰ carbon.
Complete answer:
From your chemistry lessons you have learned about the carbanion, inductive effect and their stability.
Carbanions are those organic ions which contain negative charge on its carbon atom. In a covalent bond where carbon is attached with less electronegative atom breaks up through heterolysis then the atom will leave without taking the bonding pair of electrons, so the carbon atom gains extra electron and thus has a negative charge on it.

The stability of carbanion depends upon resonance, s-character of orbitals and the inductive effect.
Inductive effect is the partial displacement of sigma electrons towards the more electronegative atom or group. There are two types of inductive effect one is –I effect and other is +I effect.
-I effect is shown by electron withdrawing groups and they stabilize the carbanion through the dispersal of negative charge whereas +I effect is shown by electron donating group or electron releasing group and they stabilize the carbanion through increasing the electron density so they can donate them.
Thus stability of carbanion is directly proportional to –I effect and inversely proportional to +I effect thus the increase in +I effect will decrease the stability of carbanion and increase in –I effect will increase the stability of carbanion. And it is represented as ,
Stability of carbanion \[\propto \,\dfrac{-I\,effect}{+I\,effect}\]
So, among the given carbanion $CC{{l}_{3}}$ is more stable because it shows –I effect because chlorine is the electron withdrawing group and it decreases the electron density on the negatively charged carbon atom. After that ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}C{{H}_{2}}$ will be more stable because benzyl group show –I effect as well as decolonization of electron takes place due to resonance effect. The least stable among them will be ${{(C{{H}_{3}})}_{3}}C$(3⁰) because here three methyl groups are attached with negatively charged carbon atom and increases the electron density on them through +I effect.

So the correct order of decreasing stability of carbanion is $CC{{l}_{3}}>{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}C{{H}_{2}}>{{(C{{H}_{3}})}_{3}}CH>{{(C{{H}_{3}})}_{2}}C$
Thus the correct option is (C).
Note:
Stability of carbanion by resonance effect is due to the presence of lone pairs of electrons and their involvement with delocalization of electrons( pi electrons). Inductive effect is inversely proportional to the distance distance increases inductive effect decreases. Carbanions are highly reactive because of the presence of negative charge and these negative charges make the carbon atom rich in electrons and thus can donate these non- bonding electrons to some other group.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




