
Assertion: Pent- 1-ene and 2- methylbut-1-ene are position isomers.
Reason: Position isomers have the same molecular formula but differ in the position of functional group
A.Both Assertion and reason are correct and reason is the correct explanation for Assertion
B.Both assertion and reason are correct but reason is not the correct explanation for Assertion
C.Assertion is correct but reason is incorrect
D.Assertion is incorrect and Reason is correct
Answer
565.5k+ views
Hint:Isomerism is the phenomenon of existence of two or more compounds possessing the same molecular formula but different chemical and physical properties. Isomerism is broadly of two types, that is, structural isomerism or constitutional isomerism, and stereoisomers.
Complete answer:
Structural isomers are those isomers in which the compounds possessing the same molecular formula differ in their properties due to the difference in the linkage of atoms inside the molecule, i.e., due to a difference in their structures or bonding.
The structures of Pent- 1-ene and 2- methyl- but- 2-ene can be drawn as:
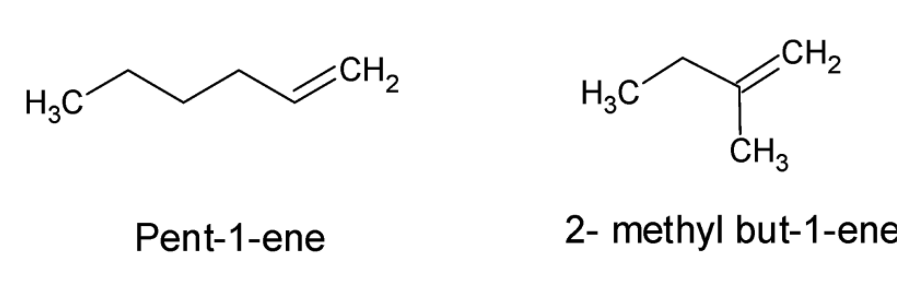
From the structures we can easily conclude that the given compounds are not positional isomers as the functional group, i.e., the double bond is present on the first carbon atom in both the compounds. The given compounds are chain isomers as they differ in the length of the parent chain. Hence the assertion is incorrect.
We know that positional isomers differ only in the position of the functional group in the compound. Thus, the reason is correct.
Hence, the correct answer is D.
Note:
Structural isomers can be of various sub types namely:
Chain isomers: They are different due to a difference in the arrangement of the parent carbon chain present in them. One of them may contain a straight chain while the others may be branched.
Positional isomers: They are different due to the difference in the position of the functional group or the multiple bonds or the branched chain attached to the parent carbon chain.
Functional isomers: They differ in the functional group present in them. For example an alcohol and an ether may have the same molecular formula.
Metamers: They differ only in the alkyl groups present and have the same functional group.
Ring chain isomers: They possess open chain and cyclic structures having the same molecular formula.
Complete answer:
Structural isomers are those isomers in which the compounds possessing the same molecular formula differ in their properties due to the difference in the linkage of atoms inside the molecule, i.e., due to a difference in their structures or bonding.
The structures of Pent- 1-ene and 2- methyl- but- 2-ene can be drawn as:

From the structures we can easily conclude that the given compounds are not positional isomers as the functional group, i.e., the double bond is present on the first carbon atom in both the compounds. The given compounds are chain isomers as they differ in the length of the parent chain. Hence the assertion is incorrect.
We know that positional isomers differ only in the position of the functional group in the compound. Thus, the reason is correct.
Hence, the correct answer is D.
Note:
Structural isomers can be of various sub types namely:
Chain isomers: They are different due to a difference in the arrangement of the parent carbon chain present in them. One of them may contain a straight chain while the others may be branched.
Positional isomers: They are different due to the difference in the position of the functional group or the multiple bonds or the branched chain attached to the parent carbon chain.
Functional isomers: They differ in the functional group present in them. For example an alcohol and an ether may have the same molecular formula.
Metamers: They differ only in the alkyl groups present and have the same functional group.
Ring chain isomers: They possess open chain and cyclic structures having the same molecular formula.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




