
Assertion: When inductive and electromeric effects operate in opposite directions then the inductive effect predominates.
Reason: Inductive effect is complete transfer of a shared pair of ${{\pi }}{{{e}}^{{ - }}}$ to one of the atoms.
(A) Both assertion and reason are correct and reason is the correct explanation for the assertion.
(B) Both assertion and reason are correct but reason is not the correct explanation for the assertion.
(C) Assertion is correct but reason is incorrect.
(D) Both assertion and reason are incorrect.
Answer
558.9k+ views
Hint: We should know what is inductive and electromeric effect and at what conditions does the molecule show these effects separately. Then we will compare both the effects when they are operating in the same molecule.
Complete step by step answer:
Inductive effect is like a dipole created between two attached groups in a molecule which have differences in their electronegativities. The dipoles created in the inductive bond have a slight shift of ${{\sigma }}{{{e}}^{{ - }}}$ towards the more electronegative group. So it happens only through ${{\sigma }}$ bond. It is a polarization of the bond due to the nature of the group attached.
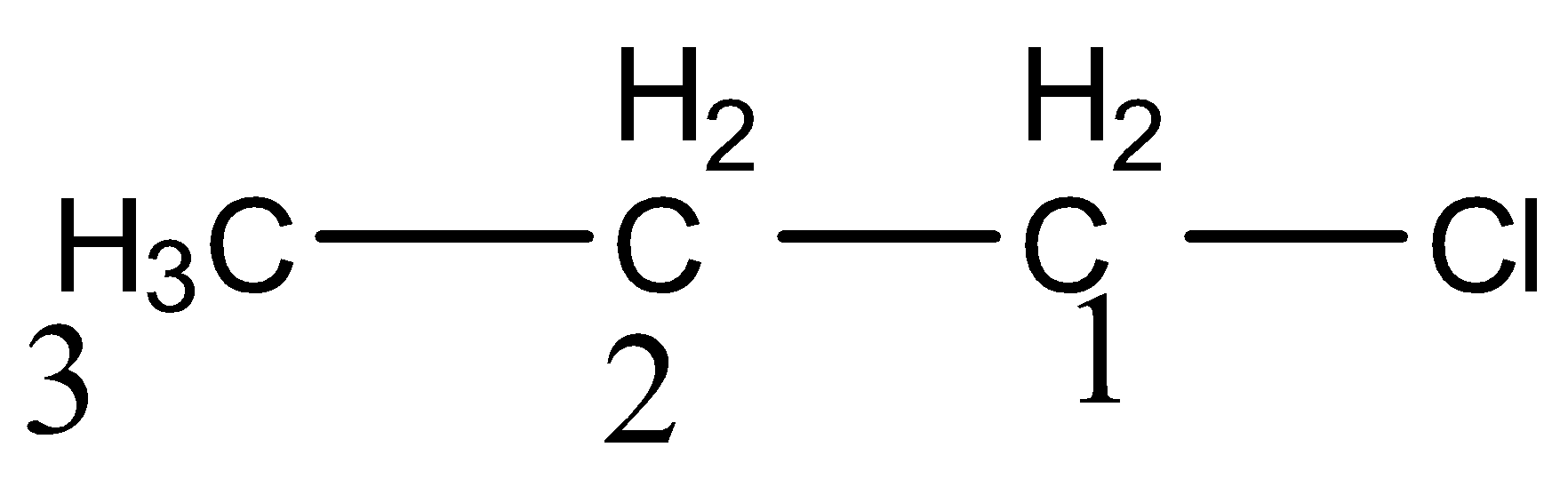
Here carbon ${{1}}$ and chloride bond is most polarized due to direct attachment of electronegative groups. Carbon ${{2 \;and \;3}}$ are lesser and least polarized respectively. So inductive effect is inversely proportional to distance.
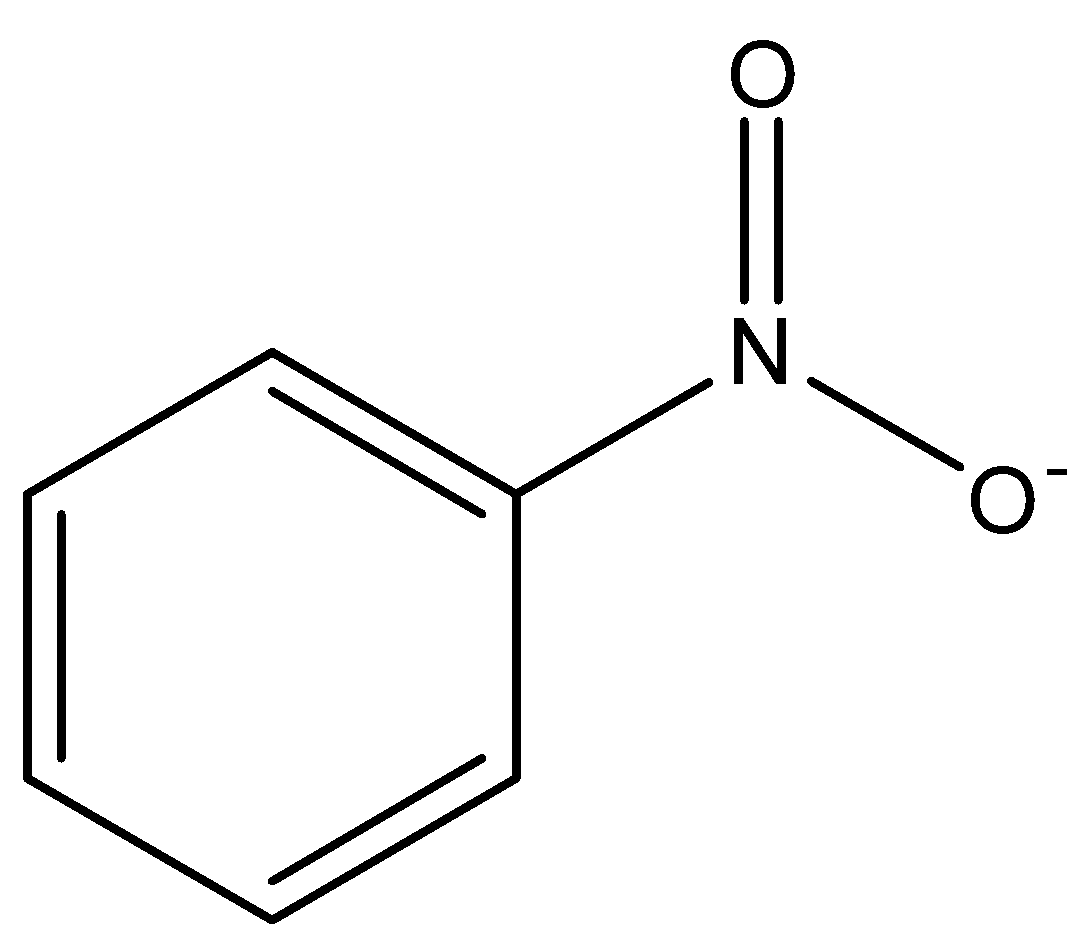
Electromeric effect is also a polarizing effect but, in this electron, actually displace themselves intramolecularly through ${{\pi }}$ bond. It is also called conjugation. It shows its effect only when a nucleophile or electrophile is about to attack. Example: conjugation in Nitro-benzene
So, the correct answer is Option D.
Note: The inductive as well as electromeric both have + I , - I and + E , - E depending on the group attached to them. +E happens when electrophiles attack and –E when nucleophiles attack. –I is shown when carbon is attached to electronegative groups, +I is shown when it is attached to less electronegative groups.
Inductive effect is distance dependent. The closer the group attached, the more inductive effect is shown on it and when the group becomes far and far away the inductive effect weakens. Electromeric effect is not distance dependent as it has electron displacement.
Complete step by step answer:
Inductive effect is like a dipole created between two attached groups in a molecule which have differences in their electronegativities. The dipoles created in the inductive bond have a slight shift of ${{\sigma }}{{{e}}^{{ - }}}$ towards the more electronegative group. So it happens only through ${{\sigma }}$ bond. It is a polarization of the bond due to the nature of the group attached.
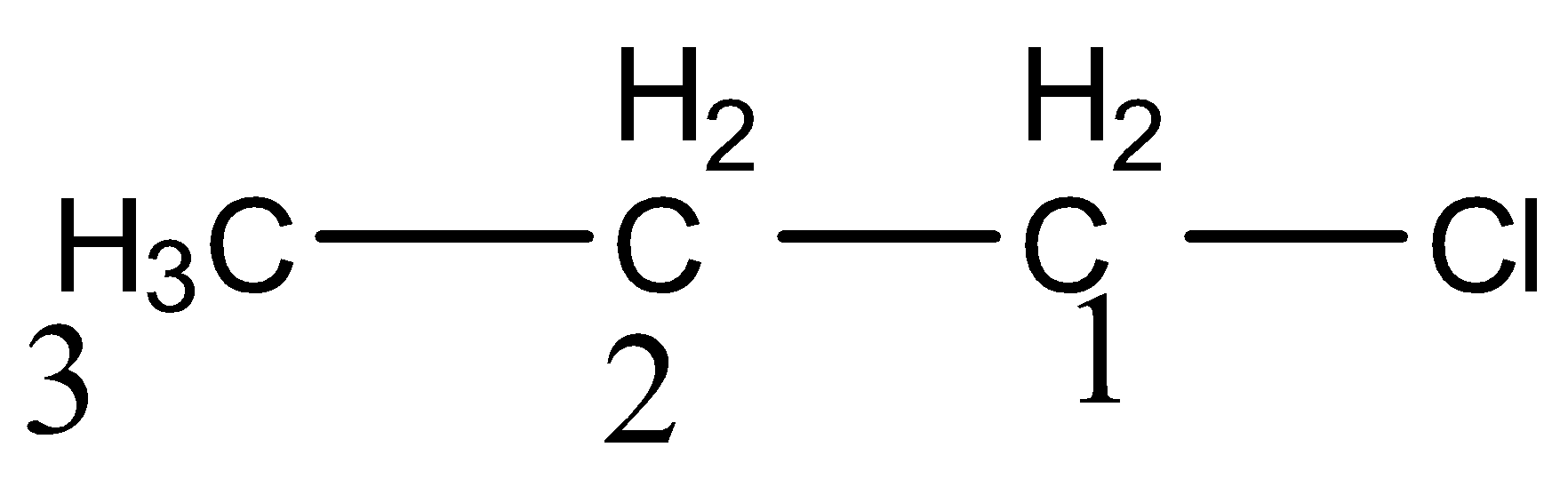
Here carbon ${{1}}$ and chloride bond is most polarized due to direct attachment of electronegative groups. Carbon ${{2 \;and \;3}}$ are lesser and least polarized respectively. So inductive effect is inversely proportional to distance.
Electromeric effect is also a polarizing effect but, in this electron, actually displace themselves intramolecularly through ${{\pi }}$ bond. It is also called conjugation. It shows its effect only when a nucleophile or electrophile is about to attack. Example: conjugation in Nitro-benzene

So, the correct answer is Option D.
Note: The inductive as well as electromeric both have + I , - I and + E , - E depending on the group attached to them. +E happens when electrophiles attack and –E when nucleophiles attack. –I is shown when carbon is attached to electronegative groups, +I is shown when it is attached to less electronegative groups.
Inductive effect is distance dependent. The closer the group attached, the more inductive effect is shown on it and when the group becomes far and far away the inductive effect weakens. Electromeric effect is not distance dependent as it has electron displacement.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




