
At high concentration of soap in water, soap behaves as:
(A)- molecular colloid
(B)- associated colloid
(C)- macromolecular colloid
(D)- lyophilic colloid
Answer
590.7k+ views
Hint: Soaps are sodium or potassium salts of long chain carboxylic acids and can be represented as $RCOONa$. Soap behaves as a normal electrolyte at low concentration whereas at high concentration forms an ionic micelle.
Complete step by step answer:
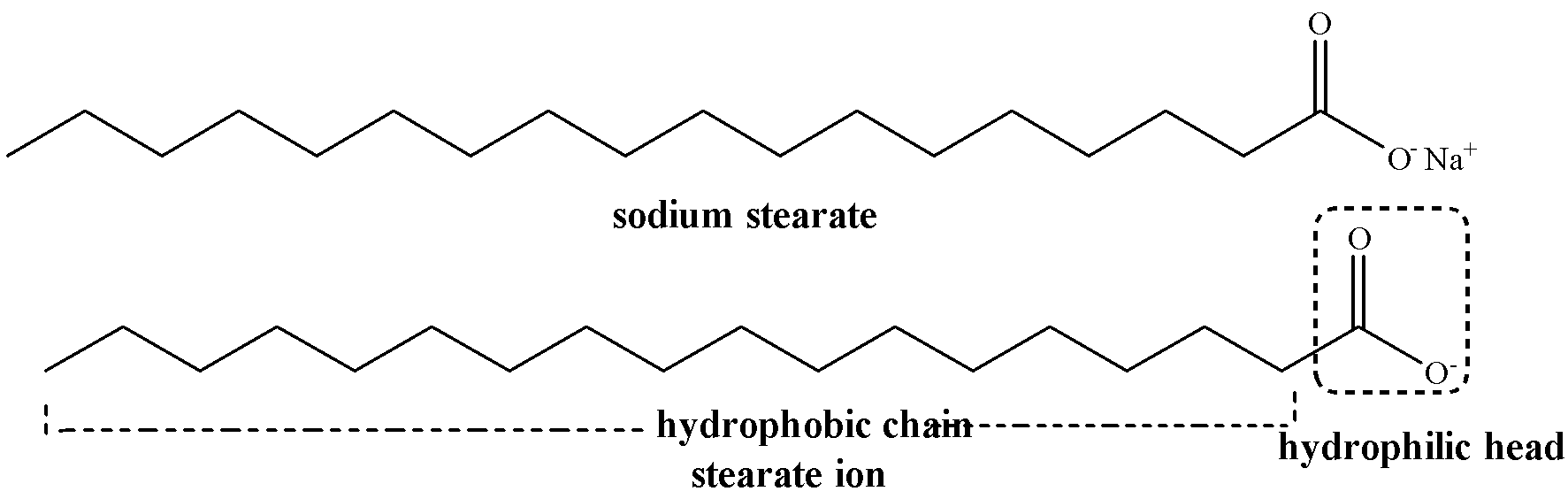
Soap (RCOONa) when dissolved in water at low concentration dissociates to give $RCO{{O}^{-}}$ and $N{{a}^{+}}$ ions.
\[RCOONa\to RCO{{O}^{-}}+N{{a}^{+}}\]
Thus, soap behaves as an electrolyte at low concentration. The carboxylate ion ($RCO{{O}^{-}}$) consists of two parts, i.e. polar hydrophilic (water loving) group $CO{{O}^{-}}$, called the head and non-polar hydrophobic (water repelling) chain R which is called the tail.
Dissociation of sodium stearate ${{C}_{17}}{{H}_{35}}CO{{O}^{-}}N{{a}^{+}}$ soap in water is shown below:
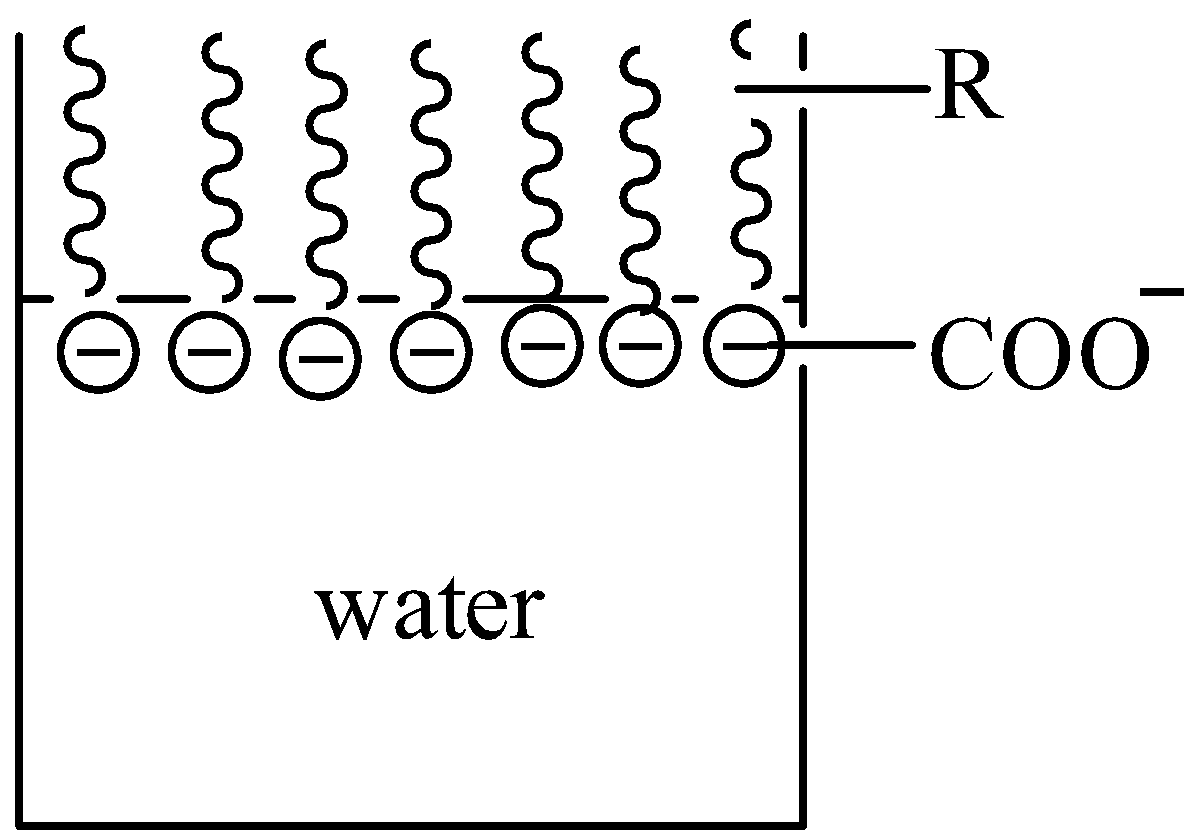
At low concentration of soap in water, the carboxylate ion remains on the surface with its polar head ($CO{{O}^{-}}$) dissolved in water and the nonpolar tail (R) away from it on the surface.
When the concentration of soap is increased, these $RCO{{O}^{-}}$ ions are pulled into the bulk of water solution. Consequently, $RCO{{O}^{-}}$ ions aggregate to form a structure with hydrophobic tails pointing towards the centre and polar head pointing outwards.
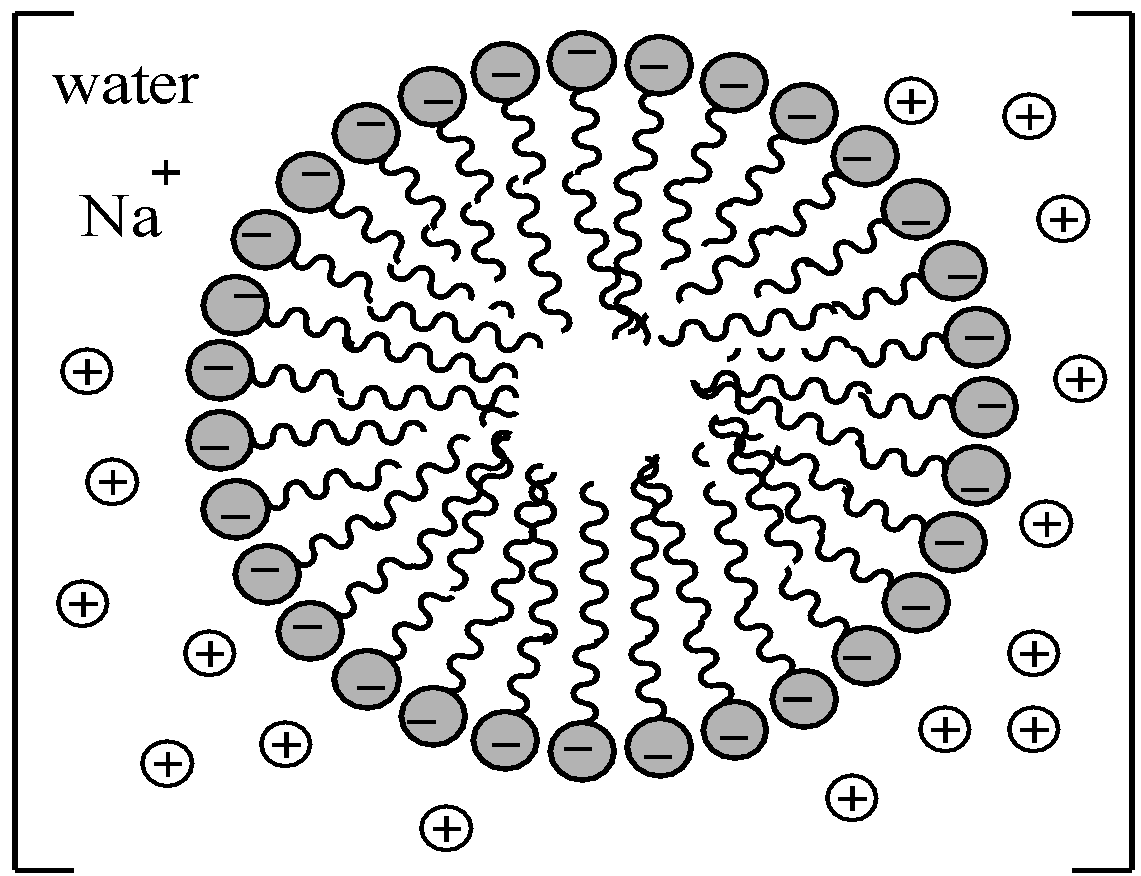
The aggregate thus formed has size in the colloidal range and is called a micelle.
Now, we know that associated colloids are the substances which when dissolved in a medium at low concentrations behave as normal electrolytes but at higher concentration aggregate to form particles which have sizes in the colloidal range.
Therefore, based on the behavior of soap we can say that soap behaves as an associated colloid at higher concentration in water.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Additional Information:
The narrow concentration range above which the soap molecules aggregate to form micelle is called critical micelle concentration (CMC). For soaps CMC is ${{10}^{-4}}-{{10}^{-3}}mol{{L}^{-1}}$. The formation of micelle takes place at a particular temperature called Kraft temperature ${{T}_{k}}$ .
Note: Do not get confused between associated and multimolecular colloids. Multimolecular colloids are formed when a large number of simple atoms or molecules aggregate together to form species in the colloidal range whereas associated colloids are formed when electrolytes are present in solution at higher concentration.
Complete step by step answer:
Soap (RCOONa) when dissolved in water at low concentration dissociates to give $RCO{{O}^{-}}$ and $N{{a}^{+}}$ ions.
\[RCOONa\to RCO{{O}^{-}}+N{{a}^{+}}\]
Thus, soap behaves as an electrolyte at low concentration. The carboxylate ion ($RCO{{O}^{-}}$) consists of two parts, i.e. polar hydrophilic (water loving) group $CO{{O}^{-}}$, called the head and non-polar hydrophobic (water repelling) chain R which is called the tail.
Dissociation of sodium stearate ${{C}_{17}}{{H}_{35}}CO{{O}^{-}}N{{a}^{+}}$ soap in water is shown below:

At low concentration of soap in water, the carboxylate ion remains on the surface with its polar head ($CO{{O}^{-}}$) dissolved in water and the nonpolar tail (R) away from it on the surface.

When the concentration of soap is increased, these $RCO{{O}^{-}}$ ions are pulled into the bulk of water solution. Consequently, $RCO{{O}^{-}}$ ions aggregate to form a structure with hydrophobic tails pointing towards the centre and polar head pointing outwards.

The aggregate thus formed has size in the colloidal range and is called a micelle.
Now, we know that associated colloids are the substances which when dissolved in a medium at low concentrations behave as normal electrolytes but at higher concentration aggregate to form particles which have sizes in the colloidal range.
Therefore, based on the behavior of soap we can say that soap behaves as an associated colloid at higher concentration in water.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Additional Information:
The narrow concentration range above which the soap molecules aggregate to form micelle is called critical micelle concentration (CMC). For soaps CMC is ${{10}^{-4}}-{{10}^{-3}}mol{{L}^{-1}}$. The formation of micelle takes place at a particular temperature called Kraft temperature ${{T}_{k}}$ .
Note: Do not get confused between associated and multimolecular colloids. Multimolecular colloids are formed when a large number of simple atoms or molecules aggregate together to form species in the colloidal range whereas associated colloids are formed when electrolytes are present in solution at higher concentration.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




