
At the foot of the mountain the angle of elevation of the summit is found to be ${45^\circ}$. After ascending 1 km towards the mountain up. On a slope of inclination ${30^\circ}$ , the angle of elevation is found to be ${60^\circ}$. The height of the mountain is
\[
A.{\text{ }}400\left( {\sqrt 3 + 2} \right)m \\
B.{\text{ 5}}00\left( {\sqrt 3 + 1} \right)m \\
C.{\text{ 2}}00\left( {\sqrt 2 + 1} \right)m \\
D.{\text{ 1}}00\left( {\sqrt 6 + \sqrt 2 } \right)m \\
\]
Answer
616.8k+ views
Hint: In order to solve the problem, first of all draw a pictorial representation of the problem statement. Then use the concept of heights and distance along with trigonometric identities and the values for trigonometric terms at some particular angle in order to proceed.
Complete step-by-step answer:
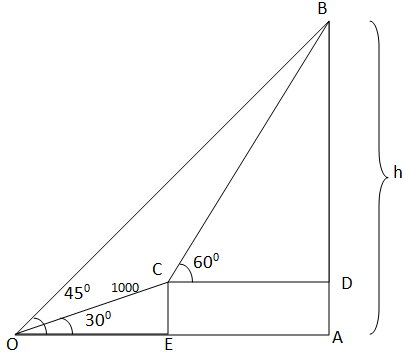
In the given figure AB represents the mountain and h is the height of the mountain, O was the initial viewing point and after ascending 1km or 1000 m up the viewing point changes to C.
Let us now solve the problem geometrically rather than practically.
$
{\text{In }}\Delta OCE \\
\sin \angle COE = \dfrac{{CE}}{{OC}} \\
\sin {30^\circ} = \dfrac{{CE}}{{1000}} \\
$
Let us now substitute the values known
\[
\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2} = \dfrac{{CE}}{{1000}}\;\;{\text{ }}\left[ {\because \sin {{30}^\circ} = \dfrac{1}{2}} \right] \\
\Rightarrow CE = \dfrac{1}{2} \times 1000m = 500m \\
\]
Also we have for the same triangle
$
{\text{In }}\Delta OCE \\
\cos \angle COE = \dfrac{{OE}}{{OC}} \\
\cos {30^\circ} = \dfrac{{OE}}{{1000}} \\
$
Let us now substitute the values known
\[
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2} = \dfrac{{OE}}{{1000}}\;\;{\text{ }}\left[ {\because \cos {{30}^\circ} = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}} \right] \\
\Rightarrow OE = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2} \times 1000m = 500\sqrt 3 m \\
\]
Now let us consider triangle AOB
$
{\text{In }}\Delta AOB \\
\tan \angle AOB = \dfrac{{AB}}{{OA}} \\
\tan {45^\circ} = \dfrac{{AB}}{{OA}} \\
$
Let us now substitute the values known
\[
\Rightarrow 1 = \dfrac{{AB}}{{OA}}\;\;{\text{ }}\left[ {\because \tan {{45}^\circ} = 1} \right] \\
\Rightarrow OA = AB \\
\]
Let us find sides of upper triangle
$
CD = EA = OA - OE \\
CD = h - 500\sqrt 3 \\
BD = BA - DA = BA - CE \\
BD = h - 500 \\
$
Now let us consider triangle BCD
$
{\text{In }}\Delta BCD \\
\tan \angle BCD = \dfrac{{BD}}{{CD}} \\
\tan {60^\circ} = \dfrac{{BD}}{{CD}} \\
$
Now, let us substitute all the values in above equation
$
\tan {60^\circ} = \dfrac{{BD}}{{CD}} \\
\Rightarrow \sqrt 3 = \dfrac{{h - 500}}{{h - 500\sqrt 3 }}{\text{ }}\left[ {\because \tan {{60}^\circ} = \sqrt 3 } \right] \\
$
Now let us solve the above equation for the value of h
\[
\Rightarrow \left( {h - 500\sqrt 3 } \right)\sqrt 3 = h - 500 \\
\Rightarrow \sqrt 3 h - 1500 = h - 500 \\
\Rightarrow \sqrt 3 h - h = 1500 - 500 \\
\Rightarrow h\left( {\sqrt 3 - 1} \right) = 1000 \\
\Rightarrow h = \dfrac{{1000}}{{\left( {\sqrt 3 - 1} \right)}} \\
\]
Now, rationalizing the RHS in order to find the value of h
\[
\Rightarrow h = \dfrac{{1000}}{{\left( {\sqrt 3 - 1} \right)}} \times \dfrac{{\left( {\sqrt 3 + 1} \right)}}{{\left( {\sqrt 3 + 1} \right)}} \\
\Rightarrow h = \dfrac{{1000\left( {\sqrt 3 + 1} \right)}}{{{{\left( {\sqrt 3 } \right)}^2} - {{\left( 1 \right)}^2}}} \\
\Rightarrow h = \dfrac{{1000\left( {\sqrt 3 + 1} \right)}}{{3 - 1}} \\
\Rightarrow h = \dfrac{{1000\left( {\sqrt 3 + 1} \right)}}{2} \\
\Rightarrow h = 500\left( {\sqrt 3 + 1} \right) \\
\]
Hence, the height of the mountain is \[500\left( {\sqrt 3 + 1} \right)\]m .
So, option B is the correct option.
Note: In order to solve such questions related to the concept of heights and distances the figure plays the most important role so the problem must be started with the figure. Also the students must remember the values of trigonometric functions of some important angles as they are used several times.
Complete step-by-step answer:

In the given figure AB represents the mountain and h is the height of the mountain, O was the initial viewing point and after ascending 1km or 1000 m up the viewing point changes to C.
Let us now solve the problem geometrically rather than practically.
$
{\text{In }}\Delta OCE \\
\sin \angle COE = \dfrac{{CE}}{{OC}} \\
\sin {30^\circ} = \dfrac{{CE}}{{1000}} \\
$
Let us now substitute the values known
\[
\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2} = \dfrac{{CE}}{{1000}}\;\;{\text{ }}\left[ {\because \sin {{30}^\circ} = \dfrac{1}{2}} \right] \\
\Rightarrow CE = \dfrac{1}{2} \times 1000m = 500m \\
\]
Also we have for the same triangle
$
{\text{In }}\Delta OCE \\
\cos \angle COE = \dfrac{{OE}}{{OC}} \\
\cos {30^\circ} = \dfrac{{OE}}{{1000}} \\
$
Let us now substitute the values known
\[
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2} = \dfrac{{OE}}{{1000}}\;\;{\text{ }}\left[ {\because \cos {{30}^\circ} = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}} \right] \\
\Rightarrow OE = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2} \times 1000m = 500\sqrt 3 m \\
\]
Now let us consider triangle AOB
$
{\text{In }}\Delta AOB \\
\tan \angle AOB = \dfrac{{AB}}{{OA}} \\
\tan {45^\circ} = \dfrac{{AB}}{{OA}} \\
$
Let us now substitute the values known
\[
\Rightarrow 1 = \dfrac{{AB}}{{OA}}\;\;{\text{ }}\left[ {\because \tan {{45}^\circ} = 1} \right] \\
\Rightarrow OA = AB \\
\]
Let us find sides of upper triangle
$
CD = EA = OA - OE \\
CD = h - 500\sqrt 3 \\
BD = BA - DA = BA - CE \\
BD = h - 500 \\
$
Now let us consider triangle BCD
$
{\text{In }}\Delta BCD \\
\tan \angle BCD = \dfrac{{BD}}{{CD}} \\
\tan {60^\circ} = \dfrac{{BD}}{{CD}} \\
$
Now, let us substitute all the values in above equation
$
\tan {60^\circ} = \dfrac{{BD}}{{CD}} \\
\Rightarrow \sqrt 3 = \dfrac{{h - 500}}{{h - 500\sqrt 3 }}{\text{ }}\left[ {\because \tan {{60}^\circ} = \sqrt 3 } \right] \\
$
Now let us solve the above equation for the value of h
\[
\Rightarrow \left( {h - 500\sqrt 3 } \right)\sqrt 3 = h - 500 \\
\Rightarrow \sqrt 3 h - 1500 = h - 500 \\
\Rightarrow \sqrt 3 h - h = 1500 - 500 \\
\Rightarrow h\left( {\sqrt 3 - 1} \right) = 1000 \\
\Rightarrow h = \dfrac{{1000}}{{\left( {\sqrt 3 - 1} \right)}} \\
\]
Now, rationalizing the RHS in order to find the value of h
\[
\Rightarrow h = \dfrac{{1000}}{{\left( {\sqrt 3 - 1} \right)}} \times \dfrac{{\left( {\sqrt 3 + 1} \right)}}{{\left( {\sqrt 3 + 1} \right)}} \\
\Rightarrow h = \dfrac{{1000\left( {\sqrt 3 + 1} \right)}}{{{{\left( {\sqrt 3 } \right)}^2} - {{\left( 1 \right)}^2}}} \\
\Rightarrow h = \dfrac{{1000\left( {\sqrt 3 + 1} \right)}}{{3 - 1}} \\
\Rightarrow h = \dfrac{{1000\left( {\sqrt 3 + 1} \right)}}{2} \\
\Rightarrow h = 500\left( {\sqrt 3 + 1} \right) \\
\]
Hence, the height of the mountain is \[500\left( {\sqrt 3 + 1} \right)\]m .
So, option B is the correct option.
Note: In order to solve such questions related to the concept of heights and distances the figure plays the most important role so the problem must be started with the figure. Also the students must remember the values of trigonometric functions of some important angles as they are used several times.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




