
Atoms are less stable than their___
Answer
580.8k+ views
Hint: Atoms are basically defined as the building blocks of matter. It is the smallest constituent unit of matter that possesses the properties of the chemical element. They cannot be seen easily i.e. they are too small.
Complete step by step answer:
In general terms, atoms don’t exist independently, instead they form ions and molecules which further combine in large numbers to form matter. Now, molecules consist of one or more atoms bound together by covalent bonds. So, the smallest particle of an element which may or may not have an independent existence but always takes place in a chemical reaction is known as an atom.
Now, atoms combine with another atom to form a molecule and complete its valence shell and they are less stable than their molecules. For example, chlorine is unstable as a Cl atom but it is more stable as $C{l_2}$ molecule. Only ${O_2},{N_2},{H_2},C{l_2},{F_2},B{r_2},{I_2}$ exist as diatomic molecules.
Further, an atom is composed of three particles i.e. neutrons, protons and electrons with hydrogen as an exception with neutrons. Every atom has a nucleus that bounds one or more electrons and further, the nucleus has typically similar number of protons and neutrons which are together known as nucleons. The protons are positively charged, electrons are negatively charged and the neutrons are neutral. The structure of atom is as shown:
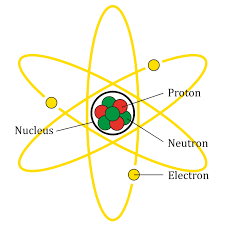
Hence, the correct answer is, Atoms are less stable than their molecule.
Note: Water is the basic molecule that consists of few atoms. Further, the weak forces bind the molecules together so that they have high melting and boiling points. Another example of a molecule is ozone. It is a molecule made up of three atoms of oxygen.
Complete step by step answer:
In general terms, atoms don’t exist independently, instead they form ions and molecules which further combine in large numbers to form matter. Now, molecules consist of one or more atoms bound together by covalent bonds. So, the smallest particle of an element which may or may not have an independent existence but always takes place in a chemical reaction is known as an atom.
Now, atoms combine with another atom to form a molecule and complete its valence shell and they are less stable than their molecules. For example, chlorine is unstable as a Cl atom but it is more stable as $C{l_2}$ molecule. Only ${O_2},{N_2},{H_2},C{l_2},{F_2},B{r_2},{I_2}$ exist as diatomic molecules.
Further, an atom is composed of three particles i.e. neutrons, protons and electrons with hydrogen as an exception with neutrons. Every atom has a nucleus that bounds one or more electrons and further, the nucleus has typically similar number of protons and neutrons which are together known as nucleons. The protons are positively charged, electrons are negatively charged and the neutrons are neutral. The structure of atom is as shown:

Hence, the correct answer is, Atoms are less stable than their molecule.
Note: Water is the basic molecule that consists of few atoms. Further, the weak forces bind the molecules together so that they have high melting and boiling points. Another example of a molecule is ozone. It is a molecule made up of three atoms of oxygen.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




