
How do the attractive and repulsive forces between two atoms compare when the atoms form a covalent bond?
Answer
548.1k+ views
Hint: When the electrons are shared by each atom to form a chemical bond force of attraction or repulsion is observed which as a result covalent bonding takes place. The covalent bond is observed between two nonmetal atoms.
Complete step by step answer:
In chemistry, the covalent bonds are formed between the two atoms or an ion where sharing of electrons takes place. The covalent bonds formed are also known as the molecular bond. The force of attraction or repulsion between the two atoms when they share a pair of electrons are known as covalent bonding.
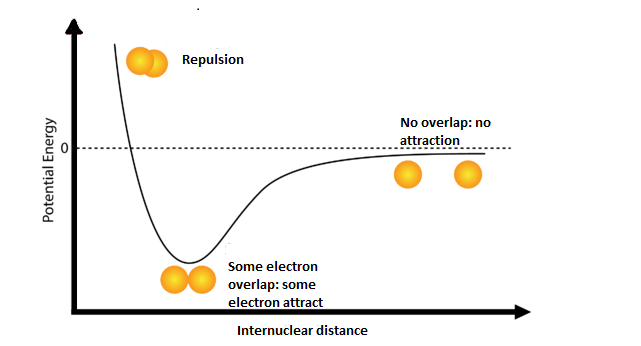
The covalent compounds are formed by two or more nonmetals atoms. You can see examples which include water ${H_2}O$, carbon dioxide $C{O_2}$ and ammonia $N{H_3}$. Most of the atoms have lower potential energy when they are bonded with each other and when they are separated. Let's take an example of two isolated hydrogen atoms which are separated by a distance which is large enough to prevent any interaction between them. At this point the potential energy is equal to zero.
As the atoms come towards one another, the electron clouds of both the hydrogen atoms gradually begin to overlap each other. As a result several interactive forces are observed. The single electron carried by each hydrogen tends to repel each other due to the repulsive force potential energy of the system increases. Now the electrons present in each atom are attracted towards the nucleus of the other atom. This attractive force makes the potential energy of the system decrease.
As the atoms first begin to interact, the attractive force between the atoms is stronger than the repulsive force and as a result the potential energy of the system decreases, as you can see in the diagram. You must know that the lower potential energy increases the stability of the system. As the two hydrogen atoms move closer and closer together, the potential energy is at its lowest point. If the hydrogen atoms move any closer together, a third interaction begins to dominate which is the repulsive force between the two positively-charged nuclei. This repulsive force is very strong which can be observed by the sharp rise in energy at the far left of the diagram.
The point at which the potential energy reaches its minimum point refers to the ideal distance between hydrogen atoms for a stable chemical bond to form. This type of chemical bond is called a covalent bond.
Note: You must know that covalent bond can be single, double or triple bond. Single covalent bond is formed when one electron is shared by each atom, in double bond two electrons are shared by each atom, in triple bond three pairs of electrons are shared.
Complete step by step answer:
In chemistry, the covalent bonds are formed between the two atoms or an ion where sharing of electrons takes place. The covalent bonds formed are also known as the molecular bond. The force of attraction or repulsion between the two atoms when they share a pair of electrons are known as covalent bonding.
The covalent compounds are formed by two or more nonmetals atoms. You can see examples which include water ${H_2}O$, carbon dioxide $C{O_2}$ and ammonia $N{H_3}$. Most of the atoms have lower potential energy when they are bonded with each other and when they are separated. Let's take an example of two isolated hydrogen atoms which are separated by a distance which is large enough to prevent any interaction between them. At this point the potential energy is equal to zero.
As the atoms come towards one another, the electron clouds of both the hydrogen atoms gradually begin to overlap each other. As a result several interactive forces are observed. The single electron carried by each hydrogen tends to repel each other due to the repulsive force potential energy of the system increases. Now the electrons present in each atom are attracted towards the nucleus of the other atom. This attractive force makes the potential energy of the system decrease.
As the atoms first begin to interact, the attractive force between the atoms is stronger than the repulsive force and as a result the potential energy of the system decreases, as you can see in the diagram. You must know that the lower potential energy increases the stability of the system. As the two hydrogen atoms move closer and closer together, the potential energy is at its lowest point. If the hydrogen atoms move any closer together, a third interaction begins to dominate which is the repulsive force between the two positively-charged nuclei. This repulsive force is very strong which can be observed by the sharp rise in energy at the far left of the diagram.
The point at which the potential energy reaches its minimum point refers to the ideal distance between hydrogen atoms for a stable chemical bond to form. This type of chemical bond is called a covalent bond.

Note: You must know that covalent bond can be single, double or triple bond. Single covalent bond is formed when one electron is shared by each atom, in double bond two electrons are shared by each atom, in triple bond three pairs of electrons are shared.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a labelled diagram of the human heart and label class 11 biology CBSE

What is 1s 2s 2p 3s 3p class 11 chemistry CBSE




