
Auxin develops at the tip of the stem. Its movement is largely
(a) Acropetal
(b) Centripetal
(c) Basipetal
(d) Acropetal and basipetal
Answer
579.3k+ views
Hint: Auxin is a phytohormone synthesized at the tip of the stem (above the region of elongation) that endorses cell elongation and it travels from an area of the plant which does not receive light to another side which is exposed to light.
Complete step by step answer:
Auxin develops at the tip of the stem. Its movement is largely basipetal. Auxin travels towards the shadier side of the plant making the cells in that region grow longer than the other cells on the brighter side of the plant known as the Basipetal movement. When auxin comes into contact with plant cells, it creates drastic changes in the expression of genes and the elongation occurs in the direction of basipetal movement. Active research is still going on to know the precise mechanisms by which this occurs, and two auxin signalling pathways are almost completely investigated.
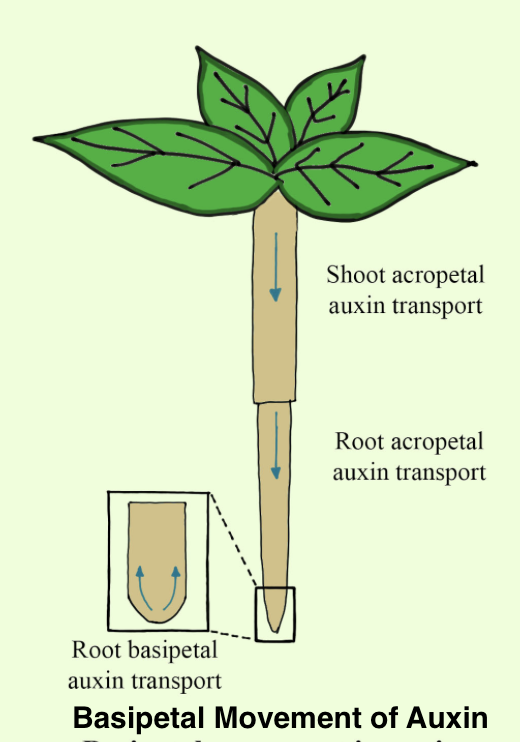
So, the correct option is ‘Basipetal’.
Additional Information:
- In 1920 the auxin was first reported by a Dutch botanist Frits Warmolt Went and explained its part in plant development. The auxin was first isolated and its chemical structure was first analyzed as indole acetic acid (IAA) by Kenneth V. Thimann who collaborated with Frits Warmolt Went to publish a book on plant hormones in 1937.
- The key part of plant development is the pattern of auxin distributed inside the plant and its behaviour to the environment, and mainly for the growth of parts of plants like leaves and flowers. It is done through a very complex and well- coordinated process called polar auxin transporting.
- Due to polar auxin transporting, a plant can react to environmental conditions and adapt to them without having a nervous system. Auxins usually act in counter to other plant hormones, such as the certain ratio of auxin and cytokinin in several plants determines the starting of root and shoot formation.
Note:
- The first important plant hormone discovered was the auxin. The name auxin was taken from the Greek word ‘auxin’ which means ‘to grow/develop’. Auxin is present in all parts of a plant but the concentration in each part varies.
- Five major types of auxins that are endogenous are indole acetic acid, phenylacetic acid, indole butyric acid, indole propionic acid, and 4- chloroindole- 3- acetic acid.
- Auxins are synthesized artificially and applied to plants. This is usually done with the combination of other hormones which plays a major role in plant tissue culture.
Complete step by step answer:
Auxin develops at the tip of the stem. Its movement is largely basipetal. Auxin travels towards the shadier side of the plant making the cells in that region grow longer than the other cells on the brighter side of the plant known as the Basipetal movement. When auxin comes into contact with plant cells, it creates drastic changes in the expression of genes and the elongation occurs in the direction of basipetal movement. Active research is still going on to know the precise mechanisms by which this occurs, and two auxin signalling pathways are almost completely investigated.

So, the correct option is ‘Basipetal’.
Additional Information:
- In 1920 the auxin was first reported by a Dutch botanist Frits Warmolt Went and explained its part in plant development. The auxin was first isolated and its chemical structure was first analyzed as indole acetic acid (IAA) by Kenneth V. Thimann who collaborated with Frits Warmolt Went to publish a book on plant hormones in 1937.
- The key part of plant development is the pattern of auxin distributed inside the plant and its behaviour to the environment, and mainly for the growth of parts of plants like leaves and flowers. It is done through a very complex and well- coordinated process called polar auxin transporting.
- Due to polar auxin transporting, a plant can react to environmental conditions and adapt to them without having a nervous system. Auxins usually act in counter to other plant hormones, such as the certain ratio of auxin and cytokinin in several plants determines the starting of root and shoot formation.
Note:
- The first important plant hormone discovered was the auxin. The name auxin was taken from the Greek word ‘auxin’ which means ‘to grow/develop’. Auxin is present in all parts of a plant but the concentration in each part varies.
- Five major types of auxins that are endogenous are indole acetic acid, phenylacetic acid, indole butyric acid, indole propionic acid, and 4- chloroindole- 3- acetic acid.
- Auxins are synthesized artificially and applied to plants. This is usually done with the combination of other hormones which plays a major role in plant tissue culture.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




