
What is Avogadro’s law? Explain Boyle’s law and Charle’s law with graphs.
Answer
497.7k+ views
Hint: We know that the Ideal gas law is based on behavior of ideal gas. It is an approximation of the behavior of many real gases under many conditions. It is a combination of Boyle’s law, Charles’ Law and Avogadro’s law.
Complete answer:
As we know , Avogadro’s law is a gas law that states that the total number of atoms or molecules present in a gas are directly proportional to the volume that the gas occupies at the constant temperature and pressure. The statement of Avogadro’s law can be given as; $V\alpha n$ where v is the volume of the gas and n is the volume of the gas and by having constant the equation can be re-written as $V=Kn$ where K is Avogadro’s number. Now if we consider two gases of volume ${{V}_{1}}$ and ${{V}_{2}}$ their number of moles as ${{n}_{1}}$ and ${{n}_{2}}$ respectively. $\Rightarrow \dfrac{{{V}_{1}}}{{{V}_{2}}}=\dfrac{{{n}_{1}}}{{{n}_{2}}}.$
Now in order to get the equation for Avogadro’s constant, we need to compare it with the same value representation in the ideal gas equation. $\dfrac{V}{n}=\dfrac{RT}{P}\Rightarrow K=\dfrac{RT}{P}.$
Therefore, from the above equation, the proportionality between the volume of a gas and the number of moles of gas is verified. The graph which is drawn between the volume of gas and the number of moles of gas is a straight line which shows these two values are directly proportional to each other.
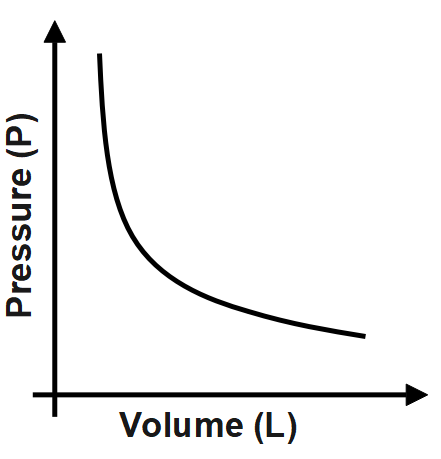
The Charle’s law is derived and stated from the ideal gas equation. The ideal gas law states for a given mass of an ideal gas and a constant volume of an ideal gas, the pressure exerted by the molecules of an ideal gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature. From the expression for the ideal gas law, we can see that the volume of the gas is directly proportional to the temperature of the gas. The same is stated by Charle’s law.
Mathematically, Charle’s law can be written as: suppose, volume of gas is \[{{V}_{0}}\] at the temperature \[0{}^\circ C.\] If temperature is increased as \[t{}^\circ C\] then volume becomes \[{{V}_{t}},\] then according to Charle’s law:
${{V}_{t}}={{V}_{0}}+\dfrac{{{V}_{0}}}{273}\times t\Rightarrow {{V}_{t}}={{V}_{0}}\left( 1+\dfrac{t}{273} \right)$
The Charle’s law states that the volume of any gas is directly proportional to the temperature of the gas on the Kelvin scale under the same amount of pressure. When we plot volume versus temperature the graph is a straight line passing through origin.
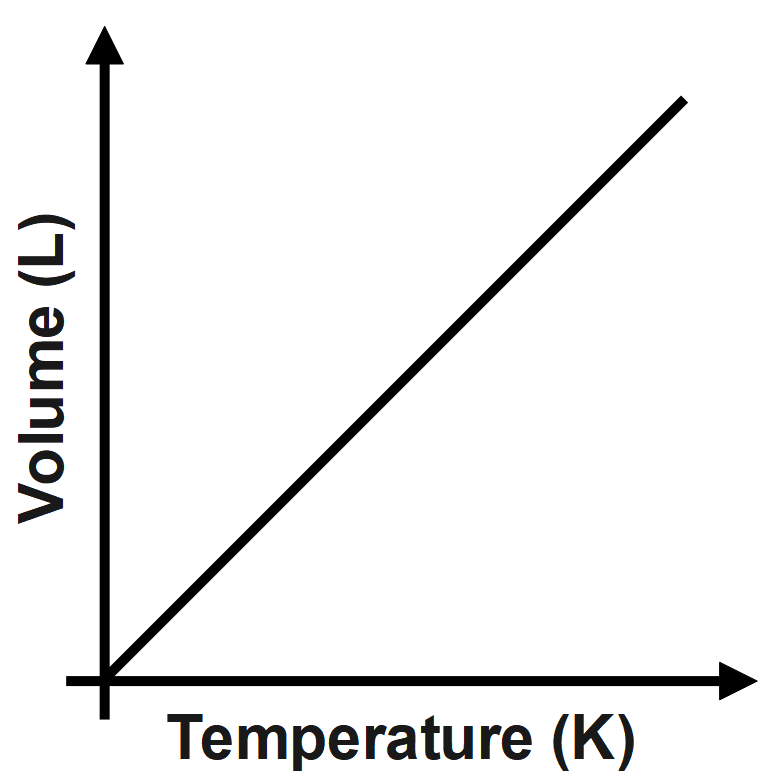
Note:
Remember that the Avogadro’s law is applicable to the ideal gases and it shows approximate values for the real gases. This law is very much applicable for light element gases such as hydrogen and helium than higher element gases. The Charle’s law states that the volume of any gas is directly proportional to the temperature of the gas on the Kelvin scale under the same amount of pressure.
Complete answer:
As we know , Avogadro’s law is a gas law that states that the total number of atoms or molecules present in a gas are directly proportional to the volume that the gas occupies at the constant temperature and pressure. The statement of Avogadro’s law can be given as; $V\alpha n$ where v is the volume of the gas and n is the volume of the gas and by having constant the equation can be re-written as $V=Kn$ where K is Avogadro’s number. Now if we consider two gases of volume ${{V}_{1}}$ and ${{V}_{2}}$ their number of moles as ${{n}_{1}}$ and ${{n}_{2}}$ respectively. $\Rightarrow \dfrac{{{V}_{1}}}{{{V}_{2}}}=\dfrac{{{n}_{1}}}{{{n}_{2}}}.$
Now in order to get the equation for Avogadro’s constant, we need to compare it with the same value representation in the ideal gas equation. $\dfrac{V}{n}=\dfrac{RT}{P}\Rightarrow K=\dfrac{RT}{P}.$
Therefore, from the above equation, the proportionality between the volume of a gas and the number of moles of gas is verified. The graph which is drawn between the volume of gas and the number of moles of gas is a straight line which shows these two values are directly proportional to each other.

The Charle’s law is derived and stated from the ideal gas equation. The ideal gas law states for a given mass of an ideal gas and a constant volume of an ideal gas, the pressure exerted by the molecules of an ideal gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature. From the expression for the ideal gas law, we can see that the volume of the gas is directly proportional to the temperature of the gas. The same is stated by Charle’s law.
Mathematically, Charle’s law can be written as: suppose, volume of gas is \[{{V}_{0}}\] at the temperature \[0{}^\circ C.\] If temperature is increased as \[t{}^\circ C\] then volume becomes \[{{V}_{t}},\] then according to Charle’s law:
${{V}_{t}}={{V}_{0}}+\dfrac{{{V}_{0}}}{273}\times t\Rightarrow {{V}_{t}}={{V}_{0}}\left( 1+\dfrac{t}{273} \right)$
The Charle’s law states that the volume of any gas is directly proportional to the temperature of the gas on the Kelvin scale under the same amount of pressure. When we plot volume versus temperature the graph is a straight line passing through origin.

Note:
Remember that the Avogadro’s law is applicable to the ideal gases and it shows approximate values for the real gases. This law is very much applicable for light element gases such as hydrogen and helium than higher element gases. The Charle’s law states that the volume of any gas is directly proportional to the temperature of the gas on the Kelvin scale under the same amount of pressure.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




