
A.Write the IUPAC name and common name of $C{H_3}Cl$.
B.Draw the structure of chlorobutane.
C. Draw the structure for bromopentane. Are structural isomers possible for bromopentane?
Answer
565.5k+ views
Hint: Alkyl halides are also referred to as haloalkanes. Alkyl halides are compounds where one or more hydrogen atoms in an alkane have been substituted by halogen atoms (namely fluorine, chlorine, bromine, or iodine). Alkyl halides fall into different categories reliant upon how the halogen atom is positioned on the chain of carbon atoms. There are some chemical differences between the various categories. There are primary, secondary, and tertiary alkyl halides.
Complete step by step answer:
A)Methyl chloride (\[C{H_3}Cl\]), also called chloromethane, is a colourless, flammable, and toxic gas. Methyl chloride is primarily produced by the reaction of methanol with hydrogen chloride, although it also can be prepared by chlorination of methane.
IUPAC name: Chloromethane
Common name: Methyl Chloride
b)Chlorobutane is an alkyl halide with the chemical formula \[C{H_3}{(C{H_2})_3}Cl\]. It is a colorless and flammable liquid. It can be produced from \[1 - \] butanol by treatment with hydrogen chloride
Structure of Chlorobutane
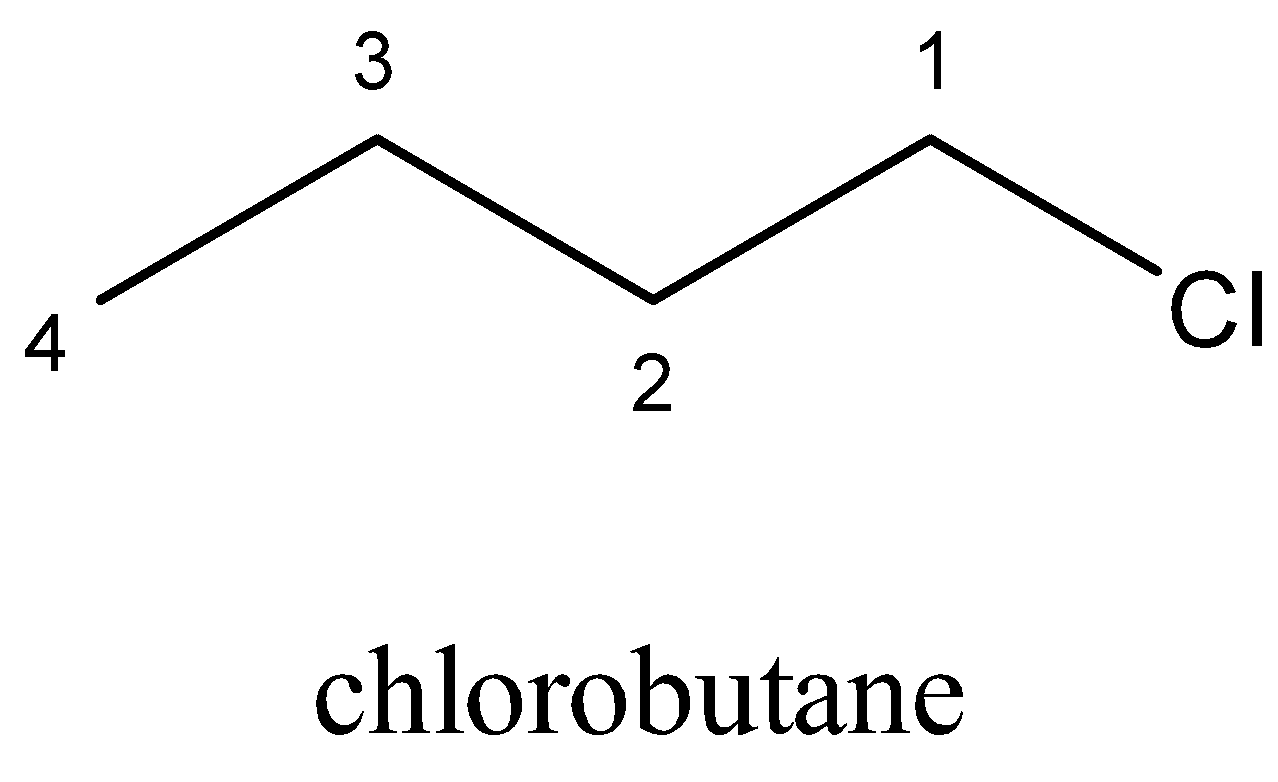
C) Bromobutane is the haloalkane with the formula \[C{H_3}{(C{H_2})_3}Br\]. It is a colourless liquid, although sometimes appears yellowish. It is insoluble in water, although soluble in organic solvents. It is usually used as a source of the butyl group in organic synthesis and is one of the multiple isomers of butyl bromide.
Most bromoalkanes are prepared by free-radical addition of hydrogen bromide to the alkenes.
Structure of bromopentane

Yes, there exist structural isomers of bromopentane.
Note: When comparing alkanes and haloalkanes, we will notice that haloalkanes have higher boiling points than alkanes containing the same number of carbons. London dispersion force is the first of two types of forces contributing to this physical property. In comparing haloalkanes with alkanes, haloalkanes exhibit a higher surface area due to the substitution of a halogen for hydrogen. The increase in the surface area leads to an increase in London dispersion forces, which further results in a higher boiling point.
Complete step by step answer:
A)Methyl chloride (\[C{H_3}Cl\]), also called chloromethane, is a colourless, flammable, and toxic gas. Methyl chloride is primarily produced by the reaction of methanol with hydrogen chloride, although it also can be prepared by chlorination of methane.
IUPAC name: Chloromethane
Common name: Methyl Chloride
b)Chlorobutane is an alkyl halide with the chemical formula \[C{H_3}{(C{H_2})_3}Cl\]. It is a colorless and flammable liquid. It can be produced from \[1 - \] butanol by treatment with hydrogen chloride
Structure of Chlorobutane

C) Bromobutane is the haloalkane with the formula \[C{H_3}{(C{H_2})_3}Br\]. It is a colourless liquid, although sometimes appears yellowish. It is insoluble in water, although soluble in organic solvents. It is usually used as a source of the butyl group in organic synthesis and is one of the multiple isomers of butyl bromide.
Most bromoalkanes are prepared by free-radical addition of hydrogen bromide to the alkenes.
Structure of bromopentane

Yes, there exist structural isomers of bromopentane.
Note: When comparing alkanes and haloalkanes, we will notice that haloalkanes have higher boiling points than alkanes containing the same number of carbons. London dispersion force is the first of two types of forces contributing to this physical property. In comparing haloalkanes with alkanes, haloalkanes exhibit a higher surface area due to the substitution of a halogen for hydrogen. The increase in the surface area leads to an increase in London dispersion forces, which further results in a higher boiling point.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




