
Axis vertebra is identified by
a. Sigmoid notch
b. Odontoblast
c. Odontoid process
d. Olecranon process
Answer
586.2k+ views
Hint: In the higher animals like mammals, where cervical vertebrae present in the neck region, that is below the skull, and the truncal vertebrae are lying caudal to the cervical vertebrae, and the axis is one of the cervical vertebrae present next to the atlas vertebrae.
Complete answer:
Axis is the second cervical vertebrae, and it is also called epistrophe. This axis forms the atlantoaxial joint with 1st cervical vertebrae, which carries the head, and also the strong odontoid process is present, which is an important characteristic feature of the axis, because of the presence of the odontoid process or dens, it brings third to the axis called vertebra dentata.
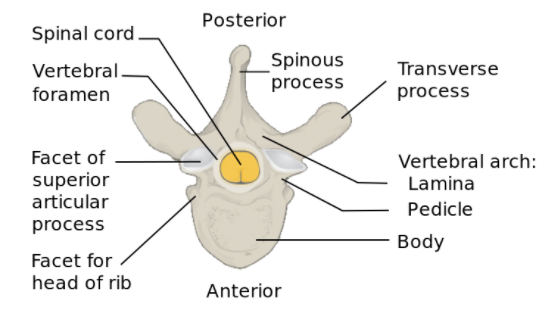
Structure of axis:
- The body of the axis deeper in the front than behind and it is prolonged downwards anteriorly so as to overlap the upper and front part of the 3rd vertebrae.
- This body has 2 lateral depressions for the attachment of the Longus collis muscle.
- The odontoid process or dens, is the most pronounced or projecting feature of the axis, and this odontoid process has constriction, which forms the neck and from where the body begins.
- On the anterior surface of the odontoid process, it has circular faceat used for articulation.
- Lateral surfaces provide the groove for the attachment of transverse atlantal ligament.
- The apex is pointed and it gives attachment to the apical odontoid ligament. Below the apex process there is a rough surface for the attachment of the alar ligament, it helps the vertebrae to connect to the occipital bone.
- The internal surface of the axis is compact than the external surface. The pedicles are broad and strong, the lamina are thick and strong and the vertebral foramen are large,
- The transverse process are very small and have the transverse foramen
- Superior articular surfaces are round and slightly convex, while inferior articular surfaces also remain the same.
- The superior vertebral notches are very shallow, and they lie behind the particular processes, and the spinous process is very large and very strong.
Hence, the correct answer is option (C).
Additional information:
Fracture of dens or odontoid process are classified into following types, which include,
Type 1: Fracture line pass through the tip, and the fracture is stable
Type 2: The fracture line passes through the neck of the odontoid process and it is unstable.
Type 3: The fracture line passes through the body of the vertebral axis, it may be stable or may not be stable and it requires surgery to correct it.
Note: Axis form a unique joint with atlas, which is called as atlantoaxial joint, and it is of two types, medial atlantoaxial joint – This is a pivot type synovial joint,and lateral atlantoaxial joint- This is a plane type synovial joint.
Complete answer:
Axis is the second cervical vertebrae, and it is also called epistrophe. This axis forms the atlantoaxial joint with 1st cervical vertebrae, which carries the head, and also the strong odontoid process is present, which is an important characteristic feature of the axis, because of the presence of the odontoid process or dens, it brings third to the axis called vertebra dentata.

Structure of axis:
- The body of the axis deeper in the front than behind and it is prolonged downwards anteriorly so as to overlap the upper and front part of the 3rd vertebrae.
- This body has 2 lateral depressions for the attachment of the Longus collis muscle.
- The odontoid process or dens, is the most pronounced or projecting feature of the axis, and this odontoid process has constriction, which forms the neck and from where the body begins.
- On the anterior surface of the odontoid process, it has circular faceat used for articulation.
- Lateral surfaces provide the groove for the attachment of transverse atlantal ligament.
- The apex is pointed and it gives attachment to the apical odontoid ligament. Below the apex process there is a rough surface for the attachment of the alar ligament, it helps the vertebrae to connect to the occipital bone.
- The internal surface of the axis is compact than the external surface. The pedicles are broad and strong, the lamina are thick and strong and the vertebral foramen are large,
- The transverse process are very small and have the transverse foramen
- Superior articular surfaces are round and slightly convex, while inferior articular surfaces also remain the same.
- The superior vertebral notches are very shallow, and they lie behind the particular processes, and the spinous process is very large and very strong.
Hence, the correct answer is option (C).
Additional information:
Fracture of dens or odontoid process are classified into following types, which include,
Type 1: Fracture line pass through the tip, and the fracture is stable
Type 2: The fracture line passes through the neck of the odontoid process and it is unstable.
Type 3: The fracture line passes through the body of the vertebral axis, it may be stable or may not be stable and it requires surgery to correct it.
Note: Axis form a unique joint with atlas, which is called as atlantoaxial joint, and it is of two types, medial atlantoaxial joint – This is a pivot type synovial joint,and lateral atlantoaxial joint- This is a plane type synovial joint.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




