
Bacteria cell wall is composed of peptidoglycan, a complex of oligosaccharides and proteins. The oligosaccharide component consists of _____________.
(a) Linear chain of alternating NAG and NAM linked by $\alpha$ (1-4) linkage
(b) Linear chain of alternating NAG and NAM linked by $\beta$ (1-4) linkage
(c) Linear chain of glucose linked by $\beta$ (1-4) linkage
(d) Linear chain of glucose linked by $\alpha$ (1-4) linkage
Answer
573.3k+ views
Hint: A polymer composed of sugars and amino acids that forms a mesh-like layer outside the plasma membrane of most bacteria, forming the cell wall, is peptidoglycan or murein.
Complete answer:
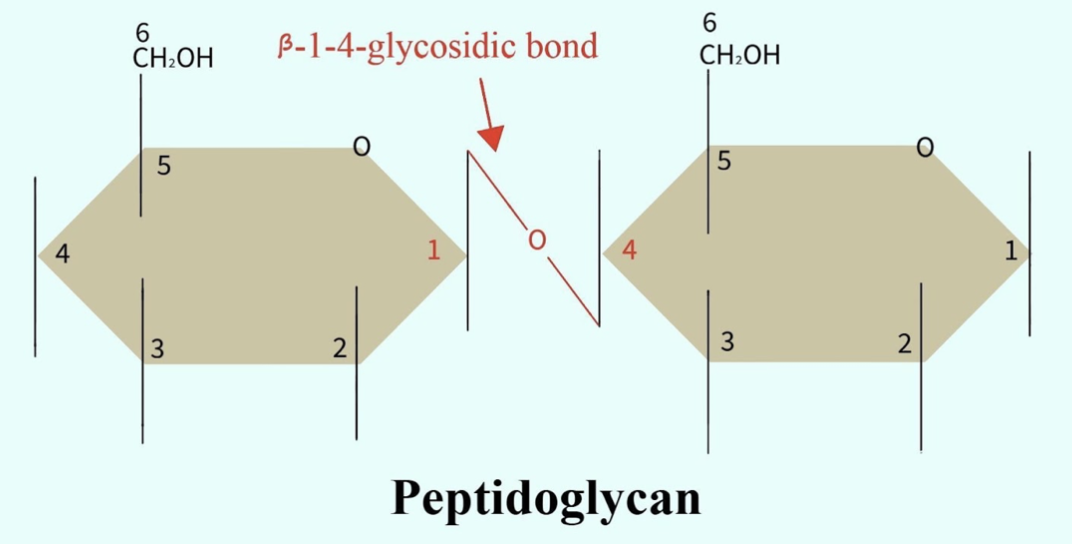
The oligosaccharide part of the bacterial cell wall consists of alternating NAG and NAM linear chains bound by $\beta$ (1-4) binding. A crystal lattice structure formed from linear chains of two alternating amino sugars, namely N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc or NAGA) and N-acetylmuramic acid (MurNAc or NAMA), forms the peptidoglycan layer in the bacterial cell wall. A $\beta$-(1-4) -glycosidic bond connects the alternating sugars.
Additional information: In Gram-positive bacteria (20 to 80 nanometers) , the peptidoglycan layer is considerably thicker than in Gram-negative bacteria (7 to 8 nanometers). The peptidoglycan forms about 40 to 90 percent of the cell wall's dry weight of Gram-positive bacteria, depending on pH growth conditions, but only about 10 percent of Gram-negative strains.
The presence of high levels of peptidoglycan is thus the primary determinant of Gram-positive bacterial characterization. It is important for attachment roles and serotyping purposes in Gram-positive strains. Particles of approximately 2 nm will pass through the peptidoglycan in both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria.
So, the correct answer is ‘Linear chain of alternating NAG and NAM linked by $\beta$ (1-4) linkage’.
Note: In the bacterial cell wall, peptidoglycan plays a structural role, giving structural strength as well as counteracting the cytoplasm's osmotic pressure. In binary fission during bacterial cell replication, peptidoglycan is also involved. A peptide chain of three to five amino acids is bound to the N-acetylmuramic acid. You may cross-link the peptide chain to the peptide chain of another strand that forms a 3D mesh-like sheet.
Complete answer:
The oligosaccharide part of the bacterial cell wall consists of alternating NAG and NAM linear chains bound by $\beta$ (1-4) binding. A crystal lattice structure formed from linear chains of two alternating amino sugars, namely N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc or NAGA) and N-acetylmuramic acid (MurNAc or NAMA), forms the peptidoglycan layer in the bacterial cell wall. A $\beta$-(1-4) -glycosidic bond connects the alternating sugars.
Additional information: In Gram-positive bacteria (20 to 80 nanometers) , the peptidoglycan layer is considerably thicker than in Gram-negative bacteria (7 to 8 nanometers). The peptidoglycan forms about 40 to 90 percent of the cell wall's dry weight of Gram-positive bacteria, depending on pH growth conditions, but only about 10 percent of Gram-negative strains.

The presence of high levels of peptidoglycan is thus the primary determinant of Gram-positive bacterial characterization. It is important for attachment roles and serotyping purposes in Gram-positive strains. Particles of approximately 2 nm will pass through the peptidoglycan in both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria.
So, the correct answer is ‘Linear chain of alternating NAG and NAM linked by $\beta$ (1-4) linkage’.
Note: In the bacterial cell wall, peptidoglycan plays a structural role, giving structural strength as well as counteracting the cytoplasm's osmotic pressure. In binary fission during bacterial cell replication, peptidoglycan is also involved. A peptide chain of three to five amino acids is bound to the N-acetylmuramic acid. You may cross-link the peptide chain to the peptide chain of another strand that forms a 3D mesh-like sheet.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




