
Because of the great tendency of the neopentyl cation to rearrange, neopentyl chloride cannot be prepared from the alcohol. How might neopentyl chloride be prepared?
Answer
572.1k+ views
Hint: To answer this question, you should recall the concept of carbocation rearrangement and free radical chlorination. To form neopentyl chloride, we shall use a reaction which doesn’t involve formation of carbocation.
Complete Step by step solution:
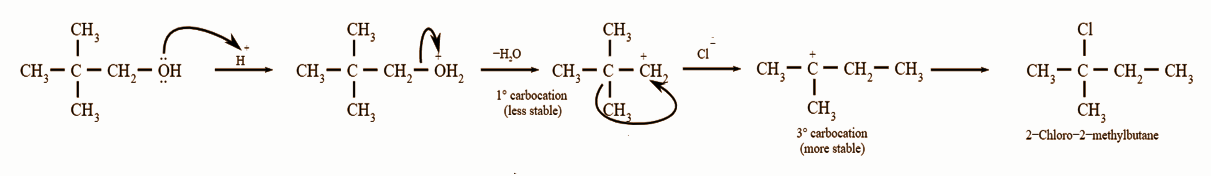
Neopentyl cation has a strong tendency to rearrange from less stable carbocation to a more stable carbocation. Hence, we get 2-chloro-2-methylbutane instead of neopentyl chloride. Carbocation rearrangements can be defined as the movement of the carbocation from an unstable state to a more stable state by making use of different structural organizational shifts within the molecule”.
Alkyl carbocation is a carbocation comprising an alkyl group. The reaction can be represented by the following mechanism:
Halogenation of an alkane produces a hydrocarbon derivative in which one or more halogen atoms have been substituted for hydrogen atoms. In halogenation of an alkane, the alkane is said to undergo fluorination, chlorination, bromination or iodination depending on the identity of the halogen reactant. Only Chlorination and bromination are the two usually used for halogenation reactions. Fluorination involves fluorine which results in explosive reactions due to high reactivity while iodination reactions go too slowly.
Halogenations usually result in the formation of a mixture of products rather than a single product. More than one product results because more than one hydrogen atom on an alkane can be replaced with halogen atoms.
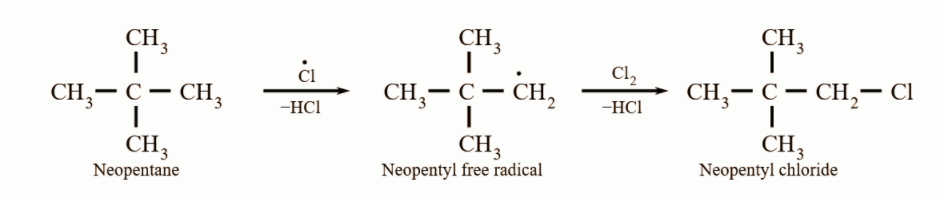
Since free radicals usually do not rearrange, the best method to prepare neopentyl chloride is by photo-chemical free-radical chlorination of neopentane. The reaction can be represented as:
Note: You should note that A severe limitation of radical halogenation however is the number of similar C-H bonds that are present in all but the simplest alkanes, so selective reactions are difficult to achieve. You should know other types of rearrangement reactions too. These include: Curtius reaction, Claisen rearrangement, Beckmann rearrangement, Hoffman rearrangement, pericyclic rearrangement and photochemical rearrangements.
Complete Step by step solution:
Neopentyl cation has a strong tendency to rearrange from less stable carbocation to a more stable carbocation. Hence, we get 2-chloro-2-methylbutane instead of neopentyl chloride. Carbocation rearrangements can be defined as the movement of the carbocation from an unstable state to a more stable state by making use of different structural organizational shifts within the molecule”.
Alkyl carbocation is a carbocation comprising an alkyl group. The reaction can be represented by the following mechanism:

Halogenation of an alkane produces a hydrocarbon derivative in which one or more halogen atoms have been substituted for hydrogen atoms. In halogenation of an alkane, the alkane is said to undergo fluorination, chlorination, bromination or iodination depending on the identity of the halogen reactant. Only Chlorination and bromination are the two usually used for halogenation reactions. Fluorination involves fluorine which results in explosive reactions due to high reactivity while iodination reactions go too slowly.
Halogenations usually result in the formation of a mixture of products rather than a single product. More than one product results because more than one hydrogen atom on an alkane can be replaced with halogen atoms.
Since free radicals usually do not rearrange, the best method to prepare neopentyl chloride is by photo-chemical free-radical chlorination of neopentane. The reaction can be represented as:

Note: You should note that A severe limitation of radical halogenation however is the number of similar C-H bonds that are present in all but the simplest alkanes, so selective reactions are difficult to achieve. You should know other types of rearrangement reactions too. These include: Curtius reaction, Claisen rearrangement, Beckmann rearrangement, Hoffman rearrangement, pericyclic rearrangement and photochemical rearrangements.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




