
Bond angle in water molecule is:
A. ${{100}^{o}}$
B. ${{90}^{o}}$
C. ${{105}^{o}}$
D. ${{110}^{o}}$
Answer
586.8k+ views
Hint: As per the question asked, we have to find out the bond angle of the water molecule which can be derived by knowing that the oxygen in the water molecule has four electron groups (i.e. two lone pairs of electrons). So, the molecule will have two lone pairs and two bond pairs giving it a tetrahedral electron geometry.
Complete step by step answer:
We should know that,
Water i.e. ${{H}_{2}}O$, is a polar molecule with one oxygen atom bonded to the two different hydrogen atoms. Due to high electronegativity of oxygen atoms, the bond formed (i.e. covalent bond) between oxygen and hydrogen is polar.
Hence, oxygen atom acquires two partial negative charges whereas, each hydrogen atom acquires one partial positive charge.
So, oxygen has two lone pairs of electrons. Thus, now water molecules have two bond pairs and two lone pairs of electrons which are arranged in tetrahedral geometry around the central atom which is oxygen.
Normally, we know that tetrahedral bond angle is ${{109.5}^{o}}$, but in water molecule, because of the presence of two lone pair-lone pair repulsion and lone pair-bond pair repulsion, the bond angle gets decreased from ${{109.5}^{o}}$ to ${{104.5}^{o}}$ which is approximately ${{105}^{o}}$.
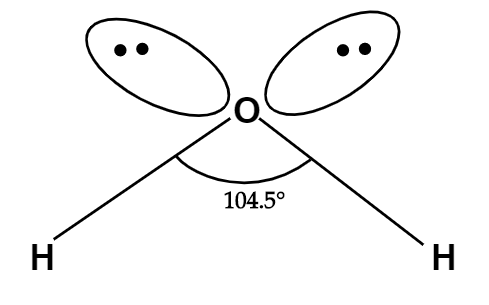
Leaving the lone pairs, the shape of the water molecule will be bent shaped.
We know that, oxygen atom acquires $s{{p}^{3}}$ hybridisation. Because of the polarity of the bonds, water molecules have high dipole moments where negative charge is directed towards the lone pair.
As we know that, polar molecules attract each other by dipole-dipole forces where the negative part of one water molecule is attracted to the positive part of another water molecule. So here, in water molecules the hydrogen atom has low density. Thus, the hydrogen atom of one molecule is attracted to the lone pair of the oxygen atom of another molecule. Thereby decreasing its bond angle.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: We should know that, the lone pair-lone pair repulsions are of the greatest magnitude and bond pair-bond pair repulsions are of the lowest magnitude and the lone pair-bond pair repulsions are greater than bond pair-bond pair and lower than the lone pair-lone pair repulsions.
Complete step by step answer:
We should know that,
Water i.e. ${{H}_{2}}O$, is a polar molecule with one oxygen atom bonded to the two different hydrogen atoms. Due to high electronegativity of oxygen atoms, the bond formed (i.e. covalent bond) between oxygen and hydrogen is polar.
Hence, oxygen atom acquires two partial negative charges whereas, each hydrogen atom acquires one partial positive charge.
So, oxygen has two lone pairs of electrons. Thus, now water molecules have two bond pairs and two lone pairs of electrons which are arranged in tetrahedral geometry around the central atom which is oxygen.
Normally, we know that tetrahedral bond angle is ${{109.5}^{o}}$, but in water molecule, because of the presence of two lone pair-lone pair repulsion and lone pair-bond pair repulsion, the bond angle gets decreased from ${{109.5}^{o}}$ to ${{104.5}^{o}}$ which is approximately ${{105}^{o}}$.

Leaving the lone pairs, the shape of the water molecule will be bent shaped.
We know that, oxygen atom acquires $s{{p}^{3}}$ hybridisation. Because of the polarity of the bonds, water molecules have high dipole moments where negative charge is directed towards the lone pair.
As we know that, polar molecules attract each other by dipole-dipole forces where the negative part of one water molecule is attracted to the positive part of another water molecule. So here, in water molecules the hydrogen atom has low density. Thus, the hydrogen atom of one molecule is attracted to the lone pair of the oxygen atom of another molecule. Thereby decreasing its bond angle.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: We should know that, the lone pair-lone pair repulsions are of the greatest magnitude and bond pair-bond pair repulsions are of the lowest magnitude and the lone pair-bond pair repulsions are greater than bond pair-bond pair and lower than the lone pair-lone pair repulsions.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




