
Bond angle of \[{{H}_{2}}O\] (104.5) is higher than the bond angle of \[{{H}_{2}}S\] (92.1). The difference is due to
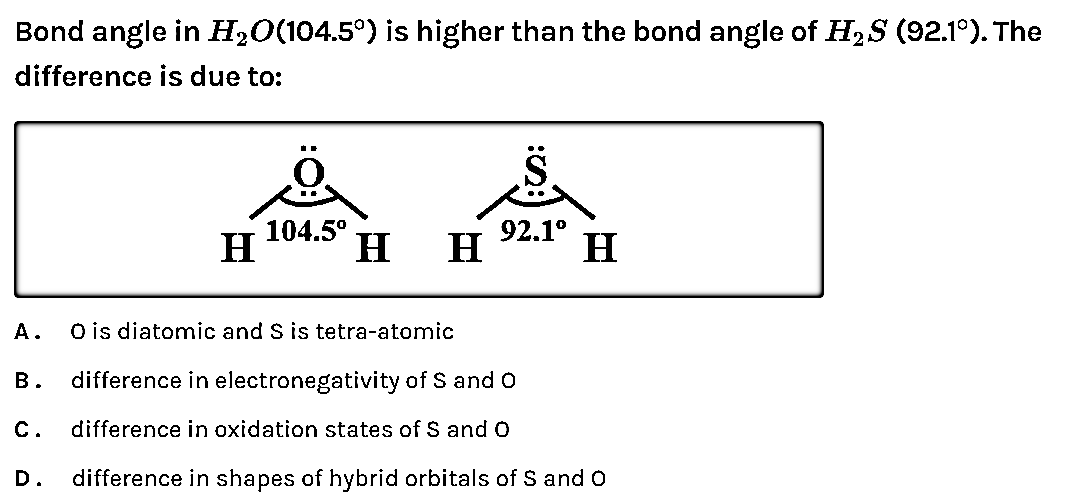
A. O is diatomic and S is tetra atomic
B. Difference in electronegativity of S and O
C. Difference in oxidation state of S and O
D. Difference in shapes of hybrid orbitals of S and O

Answer
607.5k+ views
Hint: We can use the concept of electronegativity and the atomic size and the type of hybridisation.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We should explain this by difference in electronegativity. As we know that if we move down the group from O to Te, the size of the central atom goes on increasing and its electronegativity goes on decreasing.
As a result, we can observe that the position of the two bond pairs shifts away and away from the central atom as we move from ${{H}_{2}}O$ to \[{{H}_{2}}Te\]. And the repulsion between the bond pairs decreases as we move from \[{{H}_{2}}O\] to \[{{H}_{2}}Te~\] and therefore, the bond angle decreases in the order.
Hence the correct option is B.
Additional information:
The difference in atomic size between oxygen and sulphur impacts the sizes and energy levels of the valence shell orbitals, which in turn affects how these orbitals are being used for bonding. $sp^3$ hybridized for oxygen in water, possibly un-hybridized for sulphur in hydrogen sulphide.
Note: As we know that the electronegativity of the group 16 decreases down the group, so does their tendency to acquire two electrons to form compounds in the −2 oxidation state. The lightest member, oxygen, has the greatest tendency to form multiple bonds with other elements. Because of its high electronegativity, the chemistry of oxygen is generally restricted to compounds in which it has a negative oxidation state, and its bonds to other elements tend to be highly polar. We should remember the trend of electronegativity that is followed in group 16. Lone pair repulsion also takes place, that’s why bond angle differs in oxygen.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We should explain this by difference in electronegativity. As we know that if we move down the group from O to Te, the size of the central atom goes on increasing and its electronegativity goes on decreasing.
As a result, we can observe that the position of the two bond pairs shifts away and away from the central atom as we move from ${{H}_{2}}O$ to \[{{H}_{2}}Te\]. And the repulsion between the bond pairs decreases as we move from \[{{H}_{2}}O\] to \[{{H}_{2}}Te~\] and therefore, the bond angle decreases in the order.
Hence the correct option is B.
Additional information:
The difference in atomic size between oxygen and sulphur impacts the sizes and energy levels of the valence shell orbitals, which in turn affects how these orbitals are being used for bonding. $sp^3$ hybridized for oxygen in water, possibly un-hybridized for sulphur in hydrogen sulphide.
Note: As we know that the electronegativity of the group 16 decreases down the group, so does their tendency to acquire two electrons to form compounds in the −2 oxidation state. The lightest member, oxygen, has the greatest tendency to form multiple bonds with other elements. Because of its high electronegativity, the chemistry of oxygen is generally restricted to compounds in which it has a negative oxidation state, and its bonds to other elements tend to be highly polar. We should remember the trend of electronegativity that is followed in group 16. Lone pair repulsion also takes place, that’s why bond angle differs in oxygen.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




