
What is the bond order of the nitrogen molecule?
Answer
489.9k+ views
Hint: Nitrogen is the lightest element in Periodic Group 15, often known as the pnictogens. It is a common element in the cosmos, with a total abundance estimated to be around eighth in the Milky Way and Solar System. Two atoms of the element bond together at ordinary temperature and pressure to create dinitrogen, a colourless and odourless diatomic gas with the formula $ {{N}_{2}} $ .
Complete answer:
A molecular orbital diagram, also known as a MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool used to describe chemical bonding in molecules using molecular orbital theory and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) technique. Although the electrons involved may be redistributed among the orbitals, a specific number of atomic orbitals combine to produce the same number of molecular orbitals when atoms link to form molecules, according to one of these ideas.
We can observe the two molecular orbitals mixing and the energy repulsion with nitrogen. This is why the diagram was rearranged from a more known one. Observe how the 2p acts more non-bonding-like owing to mixing, and how the $ 2s\text{ }\sigma $ behaves similarly. This results in a significant increase in energy in the $ 2p\text{ }\sigma *~ $ orbital. Diatomic nitrogen has a bond order of three and is a diamagnetic molecule.
Because two electrons are now added in the 3 MO, the bond order for dinitrogen is $ 1{{\sigma }_{g}}^{2}1{{\sigma }_{u}}^{2}2{{\sigma }_{g}}^{2}2{{\sigma }_{u}}^{2}1{{\pi }_{u}}^{4}3{{\sigma }_{g}}^{2} $ . The MO diagram for nitrogen corresponds to the observed photoelectron spectrum. The $ 1\sigma $ electrons can be matched to a broad peak at 410 eV, the 2g electrons to a broad peak at 37 eV, the 2u electrons to a broad peak at 19 eV (doublet), the 1u4 electrons to a broad peak at 17 eV (multiplets), and lastly the 3g2 to a broad peak at 15.5 eV. (sharp).
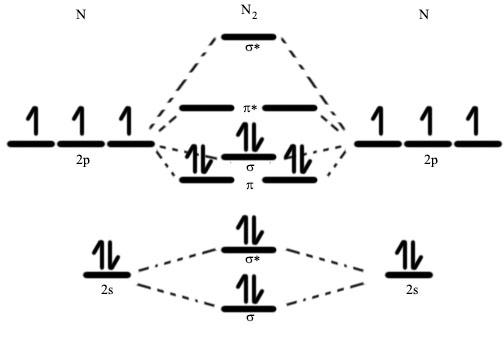
Now we can determine the number of bonds present using the formula $ B.O.=\dfrac{1}{2}({{N}_{B}}-{{N}_{A}}) $ , where
$ {{N}_{B}} $ = number of electrons in bonding molecular orbital
$ {{N}_{A}} $ = number of electrons in anti bonding molecular orbital
B.O. = Bond order of a particular molecule
According to molecular orbital theory, the bond order for dinitrogen is three:
$ B.O.=\dfrac{1}{2}(10-4)=\dfrac{6}{2}=3 $
This means that two nitrogen atoms have three bonds between them.
Note:
Nitrogen is found in a wide range of organic compounds, including Kevlar, which is used in high-strength fabrics, and cyanoacrylate, which is used in superglue. Every major pharmacological medication class, including antibiotics, contains nitrogen. Many medicines are analogues or prodrugs of natural nitrogen-containing signal molecules, such as the organic nitrates nitroglycerin and nitroprusside, which regulate blood pressure by converting to nitric oxide. Many well-known nitrogen-containing medicines, such as natural caffeine and morphine, as well as manufactured amphetamines, operate on neurotransmitter receptors in animals.
Complete answer:
A molecular orbital diagram, also known as a MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool used to describe chemical bonding in molecules using molecular orbital theory and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) technique. Although the electrons involved may be redistributed among the orbitals, a specific number of atomic orbitals combine to produce the same number of molecular orbitals when atoms link to form molecules, according to one of these ideas.
We can observe the two molecular orbitals mixing and the energy repulsion with nitrogen. This is why the diagram was rearranged from a more known one. Observe how the 2p acts more non-bonding-like owing to mixing, and how the $ 2s\text{ }\sigma $ behaves similarly. This results in a significant increase in energy in the $ 2p\text{ }\sigma *~ $ orbital. Diatomic nitrogen has a bond order of three and is a diamagnetic molecule.
Because two electrons are now added in the 3 MO, the bond order for dinitrogen is $ 1{{\sigma }_{g}}^{2}1{{\sigma }_{u}}^{2}2{{\sigma }_{g}}^{2}2{{\sigma }_{u}}^{2}1{{\pi }_{u}}^{4}3{{\sigma }_{g}}^{2} $ . The MO diagram for nitrogen corresponds to the observed photoelectron spectrum. The $ 1\sigma $ electrons can be matched to a broad peak at 410 eV, the 2g electrons to a broad peak at 37 eV, the 2u electrons to a broad peak at 19 eV (doublet), the 1u4 electrons to a broad peak at 17 eV (multiplets), and lastly the 3g2 to a broad peak at 15.5 eV. (sharp).

Now we can determine the number of bonds present using the formula $ B.O.=\dfrac{1}{2}({{N}_{B}}-{{N}_{A}}) $ , where
$ {{N}_{B}} $ = number of electrons in bonding molecular orbital
$ {{N}_{A}} $ = number of electrons in anti bonding molecular orbital
B.O. = Bond order of a particular molecule
According to molecular orbital theory, the bond order for dinitrogen is three:
$ B.O.=\dfrac{1}{2}(10-4)=\dfrac{6}{2}=3 $
This means that two nitrogen atoms have three bonds between them.
Note:
Nitrogen is found in a wide range of organic compounds, including Kevlar, which is used in high-strength fabrics, and cyanoacrylate, which is used in superglue. Every major pharmacological medication class, including antibiotics, contains nitrogen. Many medicines are analogues or prodrugs of natural nitrogen-containing signal molecules, such as the organic nitrates nitroglycerin and nitroprusside, which regulate blood pressure by converting to nitric oxide. Many well-known nitrogen-containing medicines, such as natural caffeine and morphine, as well as manufactured amphetamines, operate on neurotransmitter receptors in animals.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




