
Both, hydrarch and xerarch succession lead to
(a)Medium water condition
(b)Xeric condition
(c)Highly dry condition
(d) Excessive wet conditions
Answer
584.7k+ views
Hint: Ecological succession is a sequence of series from barren land to the climax. In ecological terms, the developmental stages of a community are known as seral stages and the final stage as the climax. The initial community of the area, which is replaced in time by a sequence of succeeding communities until the climax is reached, is called the pioneer stage of the pioneer community.
Complete answer:
Hydrarch succession happens in water regions and the successive arrangement progresses from hydric to the mesic conditions. As against the xerarch succession happens in dry zones and arrangement progress from xeric to mesic conditions. Consequently, both hydrarch and xerarch succession lead to medium water conditions (mesic)- neither excessively dry (xeric) nor excessively wet (hydric). Biotic succession in both arid areas and water bodies leads to long-lived plants, greater species diversity, niche specialization, increase in biomass, higher soil humus, food webs, stable biotic community, and mesic conditions.
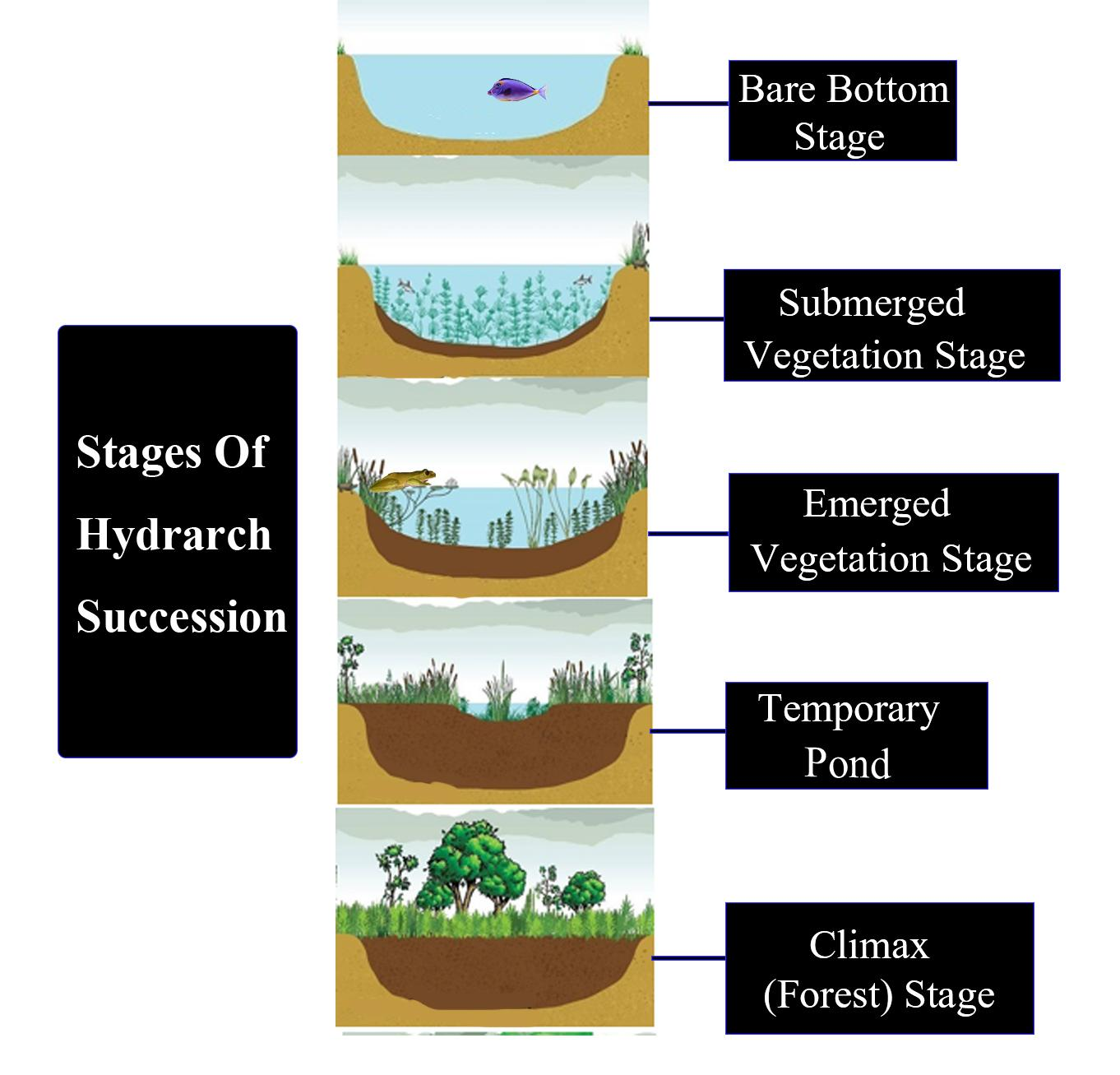
Additional Information: There are four stages of hydrarch succession:
(i) Submersed aquatic plants in the deeper water.
(ii) The Emergent cattails and bulrushes rooted in the mud of shallow water.
(iii) Willow thickets along the banks of the distant shoreline.
(iv) Conifer forest in drier, well-drained soil above the willow thickets.
In xerarch succession, the lichen colonies on these boulders are the first step. With the help of mosses, they trap dust particles and form a layer of soil on the rock surface that allows other plants, such as grasses and herbs, to become established.
So, the correct answer is ‘Medium water condition’.
Note: In xerarch succession, plant succession starts on bare ground or rock and culminates in a mature climax forest. The pioneer species, such as mosses and lichen, result in the gradual accumulation of soil. The forested slopes in the Sierra Nevada (Yosemite National Park) were once bare granite after the last major glacial period 12,000 years ago.
Complete answer:
Hydrarch succession happens in water regions and the successive arrangement progresses from hydric to the mesic conditions. As against the xerarch succession happens in dry zones and arrangement progress from xeric to mesic conditions. Consequently, both hydrarch and xerarch succession lead to medium water conditions (mesic)- neither excessively dry (xeric) nor excessively wet (hydric). Biotic succession in both arid areas and water bodies leads to long-lived plants, greater species diversity, niche specialization, increase in biomass, higher soil humus, food webs, stable biotic community, and mesic conditions.
Additional Information: There are four stages of hydrarch succession:
(i) Submersed aquatic plants in the deeper water.
(ii) The Emergent cattails and bulrushes rooted in the mud of shallow water.
(iii) Willow thickets along the banks of the distant shoreline.
(iv) Conifer forest in drier, well-drained soil above the willow thickets.
In xerarch succession, the lichen colonies on these boulders are the first step. With the help of mosses, they trap dust particles and form a layer of soil on the rock surface that allows other plants, such as grasses and herbs, to become established.
So, the correct answer is ‘Medium water condition’.

Note: In xerarch succession, plant succession starts on bare ground or rock and culminates in a mature climax forest. The pioneer species, such as mosses and lichen, result in the gradual accumulation of soil. The forested slopes in the Sierra Nevada (Yosemite National Park) were once bare granite after the last major glacial period 12,000 years ago.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




