
Briefly describe the structure of the ear.
Answer
570k+ views
Hint: Ears are the sensory organs that detect and receive the sound waves and convert them into the nerve impulses, hence help in hearing. However, hearing is not the sole function of the ears. The ears also maintain the body balance or body equilibrium. So, the ears perform two sensory functions: Hearing, and maintenance of body balance
Complete answer:
Structure of human ear: Anatomically, the ear can be divided into three major sections called
1.The outer ear: The outer ear consists of the pinna and external auditory meatus that leads to a canal. Pinna is a flap of elastic cartilage, visible from outside. Pinna is simply a sound-gathering trumpet. The sound waves or the sound vibrations need a medium to travel and this medium is provided by the air. The pinna collects these sound waves travelling in the air. Next comes the external auditory meatus and canal. (Auditory term comes in the relation of the sound). The canal carries the sound waves, that is why it is called the external auditory canal. The sound waves, present in the air, are collected by the pinna and carried inwards by the external auditory canal. There are very fine' (small) hairs and wax-secretory sebaceous (oil) glands in the skin of the pinna and the meatus. The wax-secreting sebaceous glands produce an oily secretion called the ear wax.
2.The middle ear: The middle ear contains three delicate bones, called the ear ossicles. The three ear ossicles are the malleus, incus and stapes. These are their Latin names, which have simple descriptive English equivalents. The malleus bone is hammer-shaped. Out of the three ear ossicles, malleus is the outer one. The handle of malleus is attached to the inner side of the tympanic membrane. Incus bone lies in the middle of three ear ossicles and is attached to malleus on the outer side and to stapes on the inner side. The incus bone is anvil-shaped (anvil is an instrument, commonly used by cobblers). The third in line of this chain of bones is the stapes which is stirrup-shaped.
3.The inner ear: The inner ear is termed as the labyrinth. The fluid that occurs inside the inner ear is called lymph which is of two types, the perilymph and the endolymph. The labyrinth itself consists of two parts, the bony labyrinth and the membranous labyrinth. The bony labyrinth, as the name depicts, is a series of channels made up of bony parts. Inside the bony labyrinth lies the membranous labyrinth.
Hence, there is compartmentalization inside the inner ear.
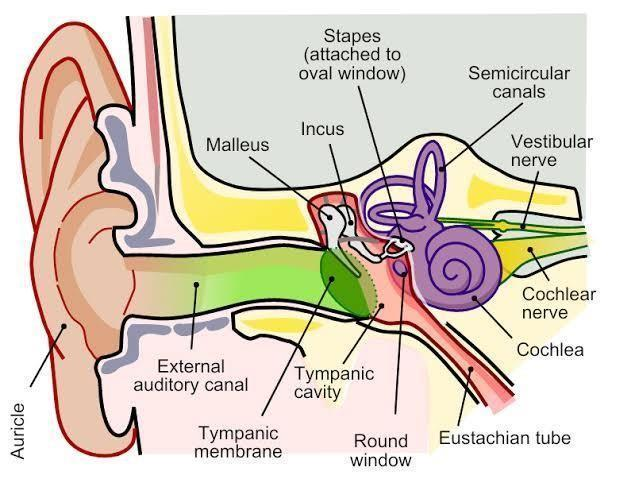
Diagram showing ear.
Note: Ear is Act as the sensory organ of the Body, along with eye ear, contain the hearing receptor which helps a person to hear the thing, it changes the vibrations that occur in the environment and reach to the brain.
Complete answer:
Structure of human ear: Anatomically, the ear can be divided into three major sections called
1.The outer ear: The outer ear consists of the pinna and external auditory meatus that leads to a canal. Pinna is a flap of elastic cartilage, visible from outside. Pinna is simply a sound-gathering trumpet. The sound waves or the sound vibrations need a medium to travel and this medium is provided by the air. The pinna collects these sound waves travelling in the air. Next comes the external auditory meatus and canal. (Auditory term comes in the relation of the sound). The canal carries the sound waves, that is why it is called the external auditory canal. The sound waves, present in the air, are collected by the pinna and carried inwards by the external auditory canal. There are very fine' (small) hairs and wax-secretory sebaceous (oil) glands in the skin of the pinna and the meatus. The wax-secreting sebaceous glands produce an oily secretion called the ear wax.
2.The middle ear: The middle ear contains three delicate bones, called the ear ossicles. The three ear ossicles are the malleus, incus and stapes. These are their Latin names, which have simple descriptive English equivalents. The malleus bone is hammer-shaped. Out of the three ear ossicles, malleus is the outer one. The handle of malleus is attached to the inner side of the tympanic membrane. Incus bone lies in the middle of three ear ossicles and is attached to malleus on the outer side and to stapes on the inner side. The incus bone is anvil-shaped (anvil is an instrument, commonly used by cobblers). The third in line of this chain of bones is the stapes which is stirrup-shaped.
3.The inner ear: The inner ear is termed as the labyrinth. The fluid that occurs inside the inner ear is called lymph which is of two types, the perilymph and the endolymph. The labyrinth itself consists of two parts, the bony labyrinth and the membranous labyrinth. The bony labyrinth, as the name depicts, is a series of channels made up of bony parts. Inside the bony labyrinth lies the membranous labyrinth.
Hence, there is compartmentalization inside the inner ear.

Diagram showing ear.
Note: Ear is Act as the sensory organ of the Body, along with eye ear, contain the hearing receptor which helps a person to hear the thing, it changes the vibrations that occur in the environment and reach to the brain.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




