
Brine solution on electrolysis will give:
(A) $NaOH$
(B) ${{O}_{2}}$
(C) $C{{l}_{2}}$
(D) ${{H}_{2}}$
Answer
232.8k+ views
HINT: Brine solution refers to the high concentration of salt (NaCl) in water (H2O). Electrolysis is the process in which ionic substances are broken into simpler substances when an electric current is passed through it.
Complete step by step solution:
Brine solutions have the composition of sodium chloride (NaCl) and water (H2O). Other useful chemicals which we will get in this process, sodium hydroxide (NaOH) and hydrogen (H2). The chlorine and sodium hydroxide produced in the process have to be separated in the reaction when they come in contact with each other.
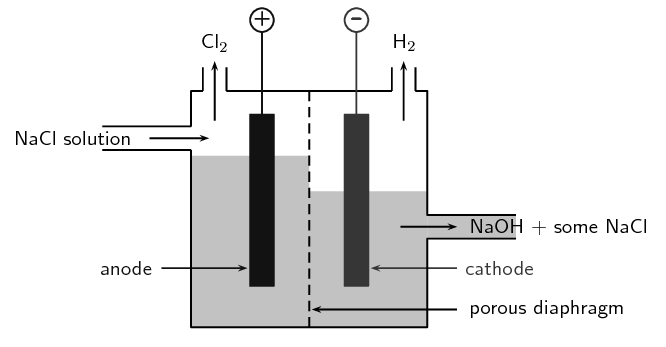
As we know electrolysis is done on the two electrodes which are cathode electrode and the anode electrode.
-Electrolysis on the negative cathode electrode
The negative cathode attracts the Na+ (from sodium chloride) and H+ ions (from water). The only ions discharged at the cathode are Hydrogen ions. More is the reactivity of the metal is, the less readily there is the presence of reduced ions on the electrode surface. Hydrogen ions get reduced by gaining electrons and give hydrogen molecules at the negative electrode which attracts positive ions towards itself.
$2H+\left( aq \right)+2{{\text{e}}^{-}}\to {{H}_{2}}\left( g \right)$
Other equations:
$2{{H}_{2}}O+2{{\text{e}}^{-}}\to {{H}_{2}}\left( g \right)+20{{H}^{-}}\left( aq \right)$
-Electrolysis on the positive anode electrode
The positively charged anode attracts the negative hydroxide OH ions (from water) and chloride Cl ions (from sodium chloride) towards itself. The chloride ion only is discharged in significant quantities during the process which means that it is preferentially oxidized to chlorine.
The chloride ions are oxidized by electron loss to offer chlorine molecules at the positive electrode which attracts negative ions.
\[C{{l}_{2}}\to 2C{{l}^{}}+2{{e}^{-}}\]
The hydroxide ion, with the uncharged sodium ion, from
\[N{{a}^{+}}+OH\to NaOH\]
Thereby, the answer to the above multiple questions is:
\[NaOH,\ C{{l}_{2}},\ {{H}_{2}}\]
As all three options (A), (C) and (D) are answers to this question and given out in the process of brine electrolysis.
Note:-Electrolysis is where ionic compounds are separated to form simple compounds.
-Electrolysis works only if the compound contains ions. Covalent compounds cannot behave as electrolytes because they contain natural atoms in it, these atoms are joined together by covalent bonds rather than ionic bonds.
Complete step by step solution:
Brine solutions have the composition of sodium chloride (NaCl) and water (H2O). Other useful chemicals which we will get in this process, sodium hydroxide (NaOH) and hydrogen (H2). The chlorine and sodium hydroxide produced in the process have to be separated in the reaction when they come in contact with each other.

As we know electrolysis is done on the two electrodes which are cathode electrode and the anode electrode.
-Electrolysis on the negative cathode electrode
The negative cathode attracts the Na+ (from sodium chloride) and H+ ions (from water). The only ions discharged at the cathode are Hydrogen ions. More is the reactivity of the metal is, the less readily there is the presence of reduced ions on the electrode surface. Hydrogen ions get reduced by gaining electrons and give hydrogen molecules at the negative electrode which attracts positive ions towards itself.
$2H+\left( aq \right)+2{{\text{e}}^{-}}\to {{H}_{2}}\left( g \right)$
Other equations:
$2{{H}_{2}}O+2{{\text{e}}^{-}}\to {{H}_{2}}\left( g \right)+20{{H}^{-}}\left( aq \right)$
-Electrolysis on the positive anode electrode
The positively charged anode attracts the negative hydroxide OH ions (from water) and chloride Cl ions (from sodium chloride) towards itself. The chloride ion only is discharged in significant quantities during the process which means that it is preferentially oxidized to chlorine.
The chloride ions are oxidized by electron loss to offer chlorine molecules at the positive electrode which attracts negative ions.
\[C{{l}_{2}}\to 2C{{l}^{}}+2{{e}^{-}}\]
The hydroxide ion, with the uncharged sodium ion, from
\[N{{a}^{+}}+OH\to NaOH\]
Thereby, the answer to the above multiple questions is:
\[NaOH,\ C{{l}_{2}},\ {{H}_{2}}\]
As all three options (A), (C) and (D) are answers to this question and given out in the process of brine electrolysis.
Note:-Electrolysis is where ionic compounds are separated to form simple compounds.
-Electrolysis works only if the compound contains ions. Covalent compounds cannot behave as electrolytes because they contain natural atoms in it, these atoms are joined together by covalent bonds rather than ionic bonds.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




