
Brush Border Epithelium occurs in -
a. Trachea
b. Stomach
c. Small Intestine
d. Fallopian Tube
Answer
588.6k+ views
Hint: A remarkable characteristic of the mucosa villi is the irregular, specialized surface of the epithelial cells. This plasma membrane, called the brush border, is wider and richer in proteins and lipids than is the plasma membrane on the epithelial cells at the side and bottom of the villus. The microvilli exhibit an imperative role in the digestion and assimilation of intestinal contents by enlarging the absorbing surface about 25 times.
Complete answer:
Water and solutes surpass through pores in the surface epithelium of the mucosa by active transport and solvent drag; i.e., solutes are carried in a moving stream of water that is responsible for an increased amount of solute on the side of the membrane from which the water had originally come. The size of the pores is different in the ileum from in the jejunum; this difference accounts for the various rates of absorption of water at the two sites.
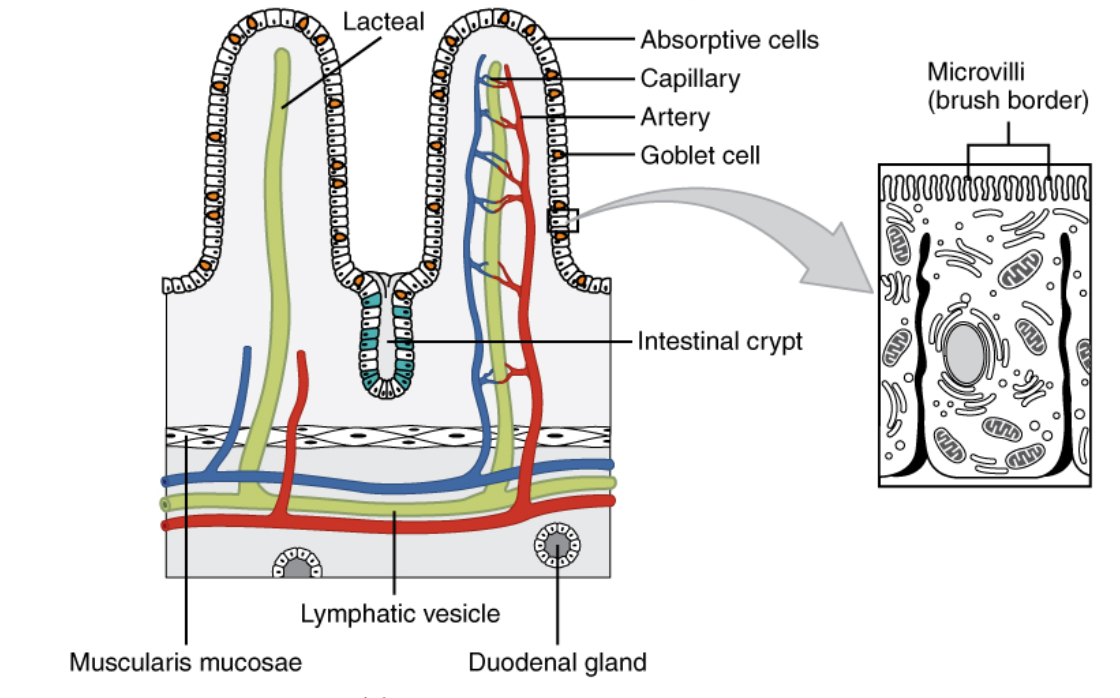
The ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium is the sort of respiratory epithelium found within the linings of the trachea also in the upper tract. The ciliated simple columnar epithelium is found within the Fallopian tube of females. The columnar epithelium possesses cells that are column-like and seem to be pillars. We will find them within the lining of the stomach. These all are quite different from the epithelium found in the intestine.
Hence, the correct answer is option (C).
Note: Thousands of microvilli form a structure called the brush border that is found on the apical surface of some epithelial cells or the lumenal plasma membrane of the absorptive epithelial cell is called brush border. Brush border cells are found in two chief locations: small intestine tract and the kidney. The microvilli display a necessary part in the digestion of intestinal contents by expanding the absorbing area.
Complete answer:
Water and solutes surpass through pores in the surface epithelium of the mucosa by active transport and solvent drag; i.e., solutes are carried in a moving stream of water that is responsible for an increased amount of solute on the side of the membrane from which the water had originally come. The size of the pores is different in the ileum from in the jejunum; this difference accounts for the various rates of absorption of water at the two sites.

The ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium is the sort of respiratory epithelium found within the linings of the trachea also in the upper tract. The ciliated simple columnar epithelium is found within the Fallopian tube of females. The columnar epithelium possesses cells that are column-like and seem to be pillars. We will find them within the lining of the stomach. These all are quite different from the epithelium found in the intestine.
Hence, the correct answer is option (C).
Note: Thousands of microvilli form a structure called the brush border that is found on the apical surface of some epithelial cells or the lumenal plasma membrane of the absorptive epithelial cell is called brush border. Brush border cells are found in two chief locations: small intestine tract and the kidney. The microvilli display a necessary part in the digestion of intestinal contents by expanding the absorbing area.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




