
Why –(-) butan- 2 -ol is optically inactive ?
Answer
578.1k+ views
Hint: For a compound to be optically active, the presence of a chiral center is necessary. A compound having a chiral center can be optically inactive due to the presence of symmetry or some factor that can cancel the optical activity.
Complete answer:
A compound having a chiral center will be optically active. A center having four different substituents is known as a chiral center.
The chiral molecule rotates the light in a clockwise direction are known as dextrorotatory and represented by \[\left( + \right)\] sign and the chiral molecule rotate the light in an anticlockwise direction are known as laevorotatory and represented by \[\left( - \right)\] sign.
A chiral molecule can be optical inactive in two conditions:
- If the molecule has symmetry such as tartaric acid having a plane of symmetry.
- If the molecule exists in two enantiomers and both are present in equal amounts and both rotate the light in opposite directions.
This type of mixture when two enantiomers of a chiral molecule present in the same amount and both rotate the light in opposite directions, is known as a racemic mixture.
Write the structure of –(–) butan- 2 -ol as follows:
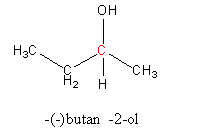
The carbon in red colour is the chiral center because it has four different substituents.
So, butan-2-ol should be optically active.
But the (-) and (+) enantiomers of butan-2-ol, both exist in equal amounts, so both rotate the light in opposite directions in equal amounts. So, rotation of both enantiomers cancel out by each other thus the –(–) butan-2-ol is optically inactive.
Therefore, –(–) butan-2-ol is optically inactive due to racemic mixture.
Note: The racemic mixture is optical active but the optical activity of the racemic mixture is not observed due to the cancelation of optical activity of both enantiomers by each other.
Complete answer:
A compound having a chiral center will be optically active. A center having four different substituents is known as a chiral center.
The chiral molecule rotates the light in a clockwise direction are known as dextrorotatory and represented by \[\left( + \right)\] sign and the chiral molecule rotate the light in an anticlockwise direction are known as laevorotatory and represented by \[\left( - \right)\] sign.
A chiral molecule can be optical inactive in two conditions:
- If the molecule has symmetry such as tartaric acid having a plane of symmetry.
- If the molecule exists in two enantiomers and both are present in equal amounts and both rotate the light in opposite directions.
This type of mixture when two enantiomers of a chiral molecule present in the same amount and both rotate the light in opposite directions, is known as a racemic mixture.
Write the structure of –(–) butan- 2 -ol as follows:

The carbon in red colour is the chiral center because it has four different substituents.
So, butan-2-ol should be optically active.
But the (-) and (+) enantiomers of butan-2-ol, both exist in equal amounts, so both rotate the light in opposite directions in equal amounts. So, rotation of both enantiomers cancel out by each other thus the –(–) butan-2-ol is optically inactive.
Therefore, –(–) butan-2-ol is optically inactive due to racemic mixture.
Note: The racemic mixture is optical active but the optical activity of the racemic mixture is not observed due to the cancelation of optical activity of both enantiomers by each other.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a labelled diagram of the human heart and label class 11 biology CBSE

What is 1s 2s 2p 3s 3p class 11 chemistry CBSE




