
How To Calculate Bond Order Of \[C{{O}_{3}}^{2-}\]
Answer
497.1k+ views
Hint: The difference between the number of bonds and antibonds, as described by Linus Pauling, is known as bond order. The bond number is the total number of electron pairs (bonds) that exist between two atoms. The difference between the number of bonding and antibonding electrons is half the bond order. The bond order of stable bonds is positive. Bond order is a bond strength measure that is widely used in valence bond theory.
Complete answer:
Bond order is defined as half the difference between the number of bonding electrons and the number of antibonding electrons in molecular orbital theory, as seen in the equation below. For bonds around their equilibrium lengths, this generally but not always produces comparable results, but it does not work for stretched bonds. Bond order is also utilized extensively in valence bond theory as a measure of bond strength.
\[\text{B}\text{.O}\text{.}=\dfrac{\text{number of bonding electrons}-\text{number of antibonding electrons}}{2}\ \]
To Calculate Bond Order of \[C{{O}_{3}}^{2-}\]
Now Draw the Lewis Structure.
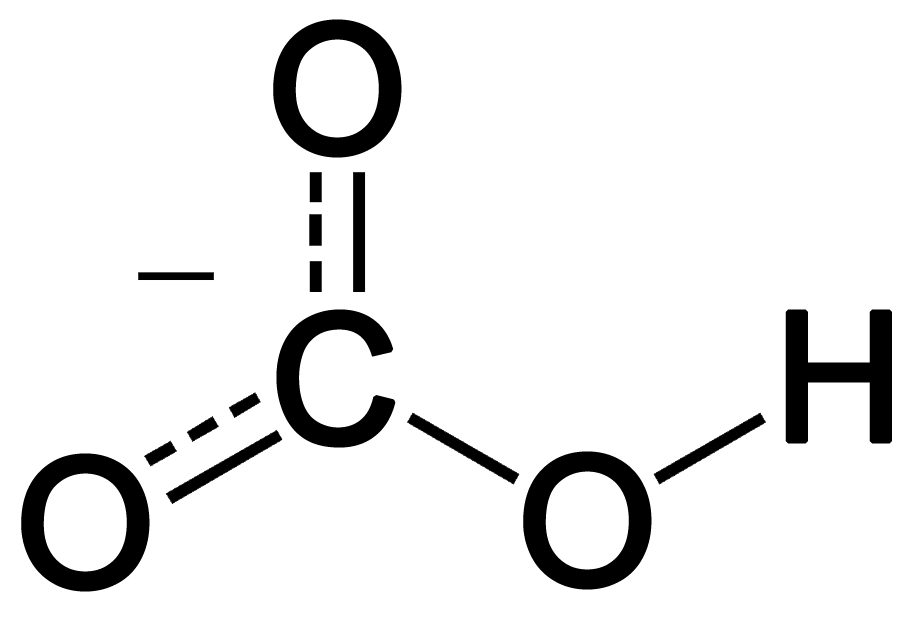
Structure of Carbonate ion
Now We Count the total number of bonds present in the system
The total number of bonds in Carbonate ion \[C{{O}_{3}}^{2-}\] is 4.
The amount of bond groups between particular atoms is then counted.
Individual atoms have a total of three bond groups.
Finally, divide the total number of bonds by the bond groups between individual atoms.
= $\dfrac{4}{3}$=1.33
Therefore, the bond order of Carbonate ions \[C{{O}_{3}}^{2-}\] is 1.33.
Note:
A single bond has a bond order of one, a double bond has a bond order of two, a triple bond has a bond order of three, and so on for n covalent links between two atoms. The molecule cannot form if the bond order is zero. Higher bond ordering implies that the new molecule will be more stable. The bond order in molecules with resonance bonding does not have to be an integer. Bond order for polyatomic compounds may be determined using resonance structures. The ratio of the total number of bonds in the molecule to the total number of resonant structures is used to calculate via resonance structure.
Complete answer:
Bond order is defined as half the difference between the number of bonding electrons and the number of antibonding electrons in molecular orbital theory, as seen in the equation below. For bonds around their equilibrium lengths, this generally but not always produces comparable results, but it does not work for stretched bonds. Bond order is also utilized extensively in valence bond theory as a measure of bond strength.
\[\text{B}\text{.O}\text{.}=\dfrac{\text{number of bonding electrons}-\text{number of antibonding electrons}}{2}\ \]
To Calculate Bond Order of \[C{{O}_{3}}^{2-}\]
Now Draw the Lewis Structure.

Structure of Carbonate ion
Now We Count the total number of bonds present in the system
The total number of bonds in Carbonate ion \[C{{O}_{3}}^{2-}\] is 4.
The amount of bond groups between particular atoms is then counted.
Individual atoms have a total of three bond groups.
Finally, divide the total number of bonds by the bond groups between individual atoms.
= $\dfrac{4}{3}$=1.33
Therefore, the bond order of Carbonate ions \[C{{O}_{3}}^{2-}\] is 1.33.
Note:
A single bond has a bond order of one, a double bond has a bond order of two, a triple bond has a bond order of three, and so on for n covalent links between two atoms. The molecule cannot form if the bond order is zero. Higher bond ordering implies that the new molecule will be more stable. The bond order in molecules with resonance bonding does not have to be an integer. Bond order for polyatomic compounds may be determined using resonance structures. The ratio of the total number of bonds in the molecule to the total number of resonant structures is used to calculate via resonance structure.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




