
How can I calculate the focal point of concave mirror?
Answer
561k+ views
Hint: The space between the concave mirror pole $\mathrm{P}$ and the concave mirror pole $\mathrm{F}$ is the concave mirror's focal length. The focal length of the concave mirror can be estimated by obtaining the real image of a distant object at its focus. Depending on the position, it can be real or virtual, inverted or erect and magnified, decreased, or similar in object size.
Complete solution:
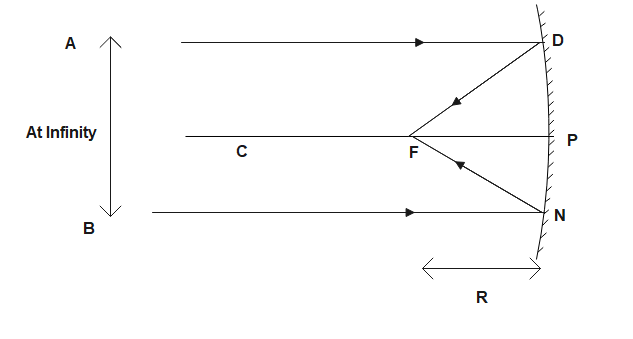
There is a reflecting surface of a concave mirror that caves inwards. At one prime focus point, the mirror also converges the light; hence they are also called converging mirrors. They are applied to the light of focus. The size of the image formed by the concave mirror varies depending on the object's location with respect to the mirror. The convex mirror's focal length is positive, while that of the concave mirror is negative.
By using the mirror formula, the same can also be proven:
f: focal point R: the center of curvature
i: distance between image and vertex (mirror's center)
o: distance between object and vertex $f=\dfrac{R}{2}$
or $\dfrac{1}{f}=\dfrac{1}{o}+\dfrac{1}{i}$
$\dfrac{1}{f}=\dfrac{i+o}{i \cdot o}$
$\therefore f=\dfrac{i\cdot o}{i+o}$
The focal length of the concave Mirror is $f=\dfrac{i\cdot o}{i+o}$.
Note:
For a concave mirror, f, the focal length, is positive and for a convex mirror, negative. The image is on the same side of the mirror as the object when the distance from the image is positive, and it is real and inverted. The image is behind the mirror when the distance from the image is negative, so the image is virtual and upright.
Complete solution:

There is a reflecting surface of a concave mirror that caves inwards. At one prime focus point, the mirror also converges the light; hence they are also called converging mirrors. They are applied to the light of focus. The size of the image formed by the concave mirror varies depending on the object's location with respect to the mirror. The convex mirror's focal length is positive, while that of the concave mirror is negative.
By using the mirror formula, the same can also be proven:
f: focal point R: the center of curvature
i: distance between image and vertex (mirror's center)
o: distance between object and vertex $f=\dfrac{R}{2}$
or $\dfrac{1}{f}=\dfrac{1}{o}+\dfrac{1}{i}$
$\dfrac{1}{f}=\dfrac{i+o}{i \cdot o}$
$\therefore f=\dfrac{i\cdot o}{i+o}$
The focal length of the concave Mirror is $f=\dfrac{i\cdot o}{i+o}$.
Note:
For a concave mirror, f, the focal length, is positive and for a convex mirror, negative. The image is on the same side of the mirror as the object when the distance from the image is positive, and it is real and inverted. The image is behind the mirror when the distance from the image is negative, so the image is virtual and upright.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE

Calculate the equivalent resistance between a and b class 12 physics CBSE

How many states of matter are there in total class 12 chemistry CBSE

Which of the following is the best conductor of electricity class 12 physics CBSE




