
Calculate the number of optical isomers in the following compound:
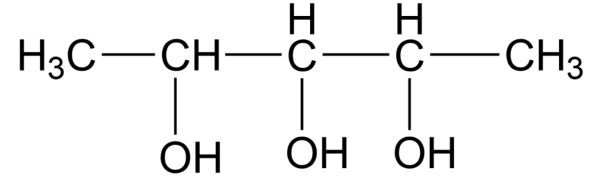
(A) 2
(B) 4
(C) 3
(D) 8

Answer
523.9k+ views
Hint: The chemical molecules which have the same chemical formula but varies in their orientation of atoms are called Optical isomers. The two isomers can bend a plane polarised light in different directions (left or right) that is how we identify a pair of optical isomers. The number of chiral carbons in the structure will help us in calculating the number of optical isomers.
Complete Step by step answer:
- The word isomer originated from the Greek words ‘isos’ meaning ‘equal’ and ‘mers’ meaning ‘parts’, so the word isomers mean equal parts.
- The phenomenon in which two or more compounds have the same chemical formula but differ in their chemical structures is known as Isomerism.
- Isomerism is of two types, that is Structural isomerism and Stereoisomerism.
- In stereoisomerism, the compounds have the same chemical formula but have different orientation of atoms in a 3D space.
- The two types of stereoisomerism are- Geometrical and Optical
- Optical isomers are two compounds which have the same molecular formula but are non- superimposable mirror images of each other.
- The number of optical isomers of a compound is determined by calculating the number of chiral centres in it.
- The maximum number of optical isomers is given by the formula ${{2}^{n- 1}}$, where n is the number of chiral centres.
The molecule above 3 chiral centres,
Using the formula, ${{2}^{n- 1}}={{2}^{3- 1}}={{2}^{2}}=4$
So, the correct answer is option B.
Note: A chiral centre is a carbon atom that is bonded to four different molecules or atoms, and each chiral centre will result in two different optical isomers. A chiral carbon is usually not a branched group, or on the end of a chain, so you can eliminate these carbon atoms to be chiral carbons quickly.
Complete Step by step answer:
- The word isomer originated from the Greek words ‘isos’ meaning ‘equal’ and ‘mers’ meaning ‘parts’, so the word isomers mean equal parts.
- The phenomenon in which two or more compounds have the same chemical formula but differ in their chemical structures is known as Isomerism.
- Isomerism is of two types, that is Structural isomerism and Stereoisomerism.
- In stereoisomerism, the compounds have the same chemical formula but have different orientation of atoms in a 3D space.
- The two types of stereoisomerism are- Geometrical and Optical
- Optical isomers are two compounds which have the same molecular formula but are non- superimposable mirror images of each other.
- The number of optical isomers of a compound is determined by calculating the number of chiral centres in it.
- The maximum number of optical isomers is given by the formula ${{2}^{n- 1}}$, where n is the number of chiral centres.

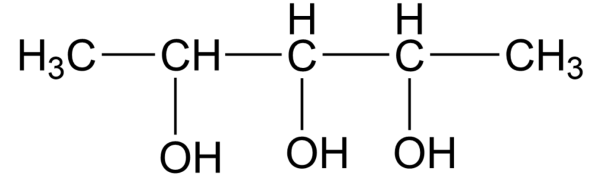
The molecule above 3 chiral centres,
Using the formula, ${{2}^{n- 1}}={{2}^{3- 1}}={{2}^{2}}=4$
So, the correct answer is option B.
Note: A chiral centre is a carbon atom that is bonded to four different molecules or atoms, and each chiral centre will result in two different optical isomers. A chiral carbon is usually not a branched group, or on the end of a chain, so you can eliminate these carbon atoms to be chiral carbons quickly.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




