
Callose blocks
(a)Older tracheids
(b)Heartwood
(c)Sieve tubes in summer
(d)Sieve tubes in winter
Answer
567k+ views
Hint: Callose is a type of cell wall material that blocks the conducting vessels of the vascular bundle of plants in response to mechanical damage. Just like a clot is formed when there is an injury of blood vessels in humans to prevent loss of blood, callose deposits at the site of injury to prevent water loss.
Complete answer:
Callose blocks sieve tubes in winter which is the end of the growing season. Sieve tubes are long, tube-like structures that are one of the types of cells that make up the phloem (food conducting vessel). These tubes are arranged longitudinally with their end walls perforated in a sieve-like manner and hence they are known as sieve plates. Callose is a specialized polysaccharide found in the cell wall of plants made up of 1,3-beta-glucan with 1,6-linkages. Callose is made by the enzyme callose synthase which is located on the plasma membrane. During winter, callose deposits in the pores of the sieve plate resulting in the decrease of the lumen of these pores.
Additional Information:
Let us look at the structure of phloem in detail. It is made up of 4 elements known as:
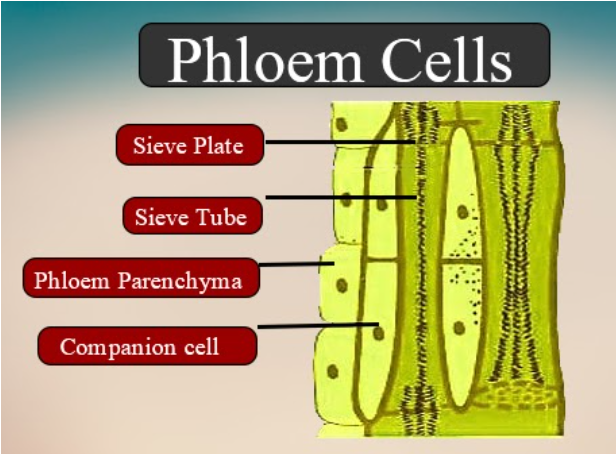
Sieve tube elements: It is made up of long cells that possess a peripheral cytoplasm and a large vacuole but does not contain a nucleus, thus its functions are regulated by companion cells.
Companion cells: Companion cells are specialized parenchymatous cells that help sieve tubes in food conduction by maintaining the pressure gradient in the sieve tubes.
Phloem parenchyma: Phloem parenchyma is made up of long tapering cells that have dense cytoplasm and nucleus. The cells are interconnected with the help of plasmodesmata connections.
Phloem fibres: The cells of phloem fibres lose their protoplasm and become dead with a thick cell wall at maturity. The phloem fibres of jute, flax and hemp are used as commercial fibres.
So, the correct option is ‘Sieve tubes in winter’.
Note:
-Callose forms a plug in the pollen tube to separate the male gametes from the vegetative cell.
-A balloon-shaped structure called tyloses forms in xylem vessels due to the inward growth of xylem parenchyma cells.
-The innermost part of the wood which does not conduct water but only provides mechanical support is known as heartwood. It is also hard, durable and resistant to the attack of microorganisms.
Complete answer:
Callose blocks sieve tubes in winter which is the end of the growing season. Sieve tubes are long, tube-like structures that are one of the types of cells that make up the phloem (food conducting vessel). These tubes are arranged longitudinally with their end walls perforated in a sieve-like manner and hence they are known as sieve plates. Callose is a specialized polysaccharide found in the cell wall of plants made up of 1,3-beta-glucan with 1,6-linkages. Callose is made by the enzyme callose synthase which is located on the plasma membrane. During winter, callose deposits in the pores of the sieve plate resulting in the decrease of the lumen of these pores.
Additional Information:
Let us look at the structure of phloem in detail. It is made up of 4 elements known as:
Sieve tube elements: It is made up of long cells that possess a peripheral cytoplasm and a large vacuole but does not contain a nucleus, thus its functions are regulated by companion cells.
Companion cells: Companion cells are specialized parenchymatous cells that help sieve tubes in food conduction by maintaining the pressure gradient in the sieve tubes.
Phloem parenchyma: Phloem parenchyma is made up of long tapering cells that have dense cytoplasm and nucleus. The cells are interconnected with the help of plasmodesmata connections.
Phloem fibres: The cells of phloem fibres lose their protoplasm and become dead with a thick cell wall at maturity. The phloem fibres of jute, flax and hemp are used as commercial fibres.
So, the correct option is ‘Sieve tubes in winter’.
Note:
-Callose forms a plug in the pollen tube to separate the male gametes from the vegetative cell.
-A balloon-shaped structure called tyloses forms in xylem vessels due to the inward growth of xylem parenchyma cells.
-The innermost part of the wood which does not conduct water but only provides mechanical support is known as heartwood. It is also hard, durable and resistant to the attack of microorganisms.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




