
Calvin cycle consists of three phases. What are they? Explain the significance of each of them.
Answer
547.8k+ views
Hint: The Calvin cycle is an important process of photosynthesis. Through Calvin cycle, three-carbon sugar is generated which helps in making glucose, starch or cellulose which is used in the structure and functioning of the plants. The carbon molecule is absorbed by the air and is converted into the utilisable by-product.
Complete answer:
The plants and algae turn carbon dioxide from the air into sugar through the process of Calvin cycle. The Calvin cycle is the main source of energy and food for the plants.
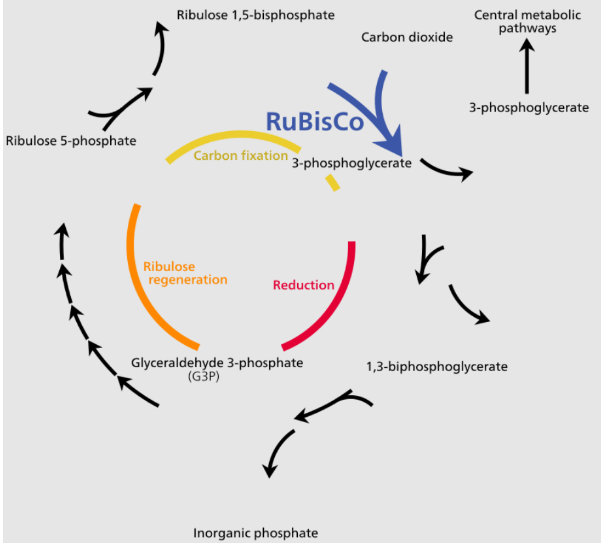
The Calvin cycle is a light- independent reaction which is a photosynthetic carbon reduction cycle of photosynthesis. It takes place in the stroma outside the thylakoid membrane. It is divided into three main stages:
1) Carbon fixation or carboxylation: In this process, the \[CO_2\] is fixed into a stable organic intermediate. The carboxylation of RuBP takes place by the help of \[CO_2\]. This reaction is catalysed by the enzyme RuBisCO to form two molecules of 3-PGA.
2) Reduction: In the reductive phase, glucose is formed. In this step, 2 molecules of ATP are required for phosphorylation, two NADPH is required for reduction for fixing one \[CO_2\]. For generating one molecule of glucose, six \[CO_2\] is required.
3) Regeneration: In this step, regeneration of the \[CO_2\] acceptor takes place. It requires one ATP for phosphorylating RuBP.
So, for the synthesis of one molecule of glucose, 18 ATP and 12 NADPH are required.
Note: The reactions utilise ATP and NADPH which is produced from the light reaction. Calvin cycle is also called the “dark reaction” but it does not take place in the night. It needs reduced NADP which is short lived.
Complete answer:
The plants and algae turn carbon dioxide from the air into sugar through the process of Calvin cycle. The Calvin cycle is the main source of energy and food for the plants.
The Calvin cycle is a light- independent reaction which is a photosynthetic carbon reduction cycle of photosynthesis. It takes place in the stroma outside the thylakoid membrane. It is divided into three main stages:
1) Carbon fixation or carboxylation: In this process, the \[CO_2\] is fixed into a stable organic intermediate. The carboxylation of RuBP takes place by the help of \[CO_2\]. This reaction is catalysed by the enzyme RuBisCO to form two molecules of 3-PGA.
2) Reduction: In the reductive phase, glucose is formed. In this step, 2 molecules of ATP are required for phosphorylation, two NADPH is required for reduction for fixing one \[CO_2\]. For generating one molecule of glucose, six \[CO_2\] is required.
3) Regeneration: In this step, regeneration of the \[CO_2\] acceptor takes place. It requires one ATP for phosphorylating RuBP.
So, for the synthesis of one molecule of glucose, 18 ATP and 12 NADPH are required.

Note: The reactions utilise ATP and NADPH which is produced from the light reaction. Calvin cycle is also called the “dark reaction” but it does not take place in the night. It needs reduced NADP which is short lived.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




