
When the canal of Schlemm is blocked, what condition is developed?
(a)Intraocular pressure is increased
(b)Retina start to damage
(c)A person may become blind
(d)All of the above
Answer
592.2k+ views
Hint: The canal of Schlemm collects the aqueous humour from the anterior chamber of the eyeball and delivers it to the veins of the eyeball. It maintains fluid homeostasis in the eyes. Damage to it can result in various adverse effects on the vision of the person.
Complete answer:
If the canal of Schlemm is blocked, and the blockage is continuous the person will suffer from chronic glaucoma. This is a painless condition that causes damage to the optic nerve at the back of your eye, also the retina starts to get damaged. Aqueous humour has two main functions i.e. It provides oxygen and nutrients to parts of the lens and cornea and it assists the corneal reflection of light rays. The aqueous humour is continuously produced and circulated by our eye cells, providing nourishment to the cornea, iris and lens, and eliminating debris and the other parts of the human eye. Intraocular pressure (the pressure in the eye), helps the eye keep its shape and function properly. During chronic glaucoma intraocular pressure is increased which can damage your eyesight. The process is so slow and painless, but it gradually reduces the eyesight and can eventually lead to loss of vision. Also, this blockage in the canal of Schlemm can cause hypertension.
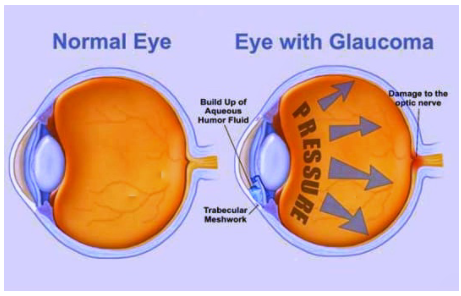
So, when the canal of Schlemm is blocked the intraocular pressure is increased, retina starts damaging, and also the person may become blind.
So, the correct option (d) is correct i.e. ‘all of the above’.
Note: The nerve connection between the eyes and the brain for the transmission of signals is done by the optic nerve. The optic nerve is the only nerve in the human body that does not regenerate once it’s damaged. The optic nerve is regenerated only in some lower vertebrates such as some fishes and frogs.
Complete answer:
If the canal of Schlemm is blocked, and the blockage is continuous the person will suffer from chronic glaucoma. This is a painless condition that causes damage to the optic nerve at the back of your eye, also the retina starts to get damaged. Aqueous humour has two main functions i.e. It provides oxygen and nutrients to parts of the lens and cornea and it assists the corneal reflection of light rays. The aqueous humour is continuously produced and circulated by our eye cells, providing nourishment to the cornea, iris and lens, and eliminating debris and the other parts of the human eye. Intraocular pressure (the pressure in the eye), helps the eye keep its shape and function properly. During chronic glaucoma intraocular pressure is increased which can damage your eyesight. The process is so slow and painless, but it gradually reduces the eyesight and can eventually lead to loss of vision. Also, this blockage in the canal of Schlemm can cause hypertension.

So, when the canal of Schlemm is blocked the intraocular pressure is increased, retina starts damaging, and also the person may become blind.
So, the correct option (d) is correct i.e. ‘all of the above’.
Note: The nerve connection between the eyes and the brain for the transmission of signals is done by the optic nerve. The optic nerve is the only nerve in the human body that does not regenerate once it’s damaged. The optic nerve is regenerated only in some lower vertebrates such as some fishes and frogs.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




